Anal sex or anal intercourse is generally the insertion and thrusting of the erect penis into a person's anus, or anus and rectum, for sexual pleasure. Other forms of anal sex include anal fingering, the use of sex toys, anilingus, pegging, as well as electrostimulation and erotic torture such as figging. Although anal sex most commonly means penile–anal penetration, sources sometimes use anal intercourse to exclusively denote penile–anal penetration, and anal sex to denote any form of anal sexual activity, especially between pairings as opposed to anal masturbation.

Orgasm, or sexual climax, is the sudden discharge of accumulated sexual excitement during the sexual response cycle, resulting in rhythmic, involuntary muscular contractions in the pelvic region characterized by sexual pleasure. Experienced by males and females, orgasms are controlled by the involuntary or autonomic nervous system. They are usually associated with involuntary actions, including muscular spasms in multiple areas of the body, a general euphoric sensation, and, frequently, body movements and vocalizations. The period after orgasm is typically a relaxing experience, attributed to the release of the neurohormones oxytocin and prolactin as well as endorphins.
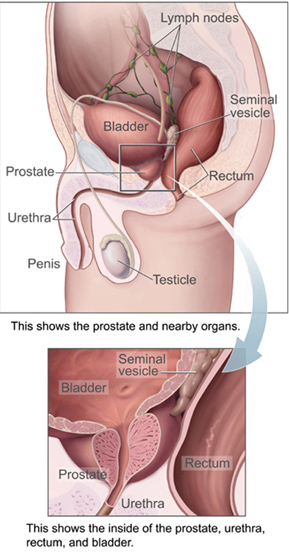
The prostate is both an accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found in all male mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemically, and physiologically. Anatomically, the prostate is found below the bladder, with the urethra passing through it. It is described in gross anatomy as consisting of lobes and in microanatomy by zone. It is surrounded by an elastic, fibromuscular capsule and contains glandular tissue, as well as connective tissue.

The nipple is a raised region of tissue on the surface of the breast from which, in females, milk leaves the breast through the lactiferous ducts to feed an infant. The milk can flow through the nipple passively or it can be ejected by smooth muscle contractions that occur along with the ductal system. Male mammals also have nipples but without the same level of function, and often surrounded by body hair.
A nocturnal emission, also known as a wet dream, sex dream, nightfall, or sleep orgasm, is a spontaneous orgasm during sleep that includes ejaculation for a male, or vaginal lubrication or an orgasm for a female.
Anorgasmia is a type of sexual dysfunction in which a person cannot achieve orgasm despite adequate stimulation. Anorgasmia is far more common in females than in males and is especially rare in younger men. The problem is greater in women who are post-menopausal. In males, it is most closely associated with delayed ejaculation. Anorgasmia can often cause sexual frustration.
Dyspareunia is painful sexual intercourse due to medical or psychological causes. The term dyspareunia covers both female dyspareunia and male dyspareunia, but many discussions that use the term without further specification concern the female type, which is more common than the male type. In females, the pain can primarily be on the external surface of the genitalia, or deeper in the pelvis upon deep pressure against the cervix. Medically, dyspareunia is a pelvic floor dysfunction and is frequently underdiagnosed. It can affect a small portion of the vulva or vagina or be felt all over the surface. Understanding the duration, location, and nature of the pain is important in identifying the causes of the pain.

Sexual stimulation is any stimulus that leads to, enhances and maintains sexual arousal, and may lead to orgasm. Although sexual arousal may arise without physical stimulation, achieving orgasm usually requires it.
Sexual dysfunction is difficulty experienced by an individual or partners during any stage of normal sexual activity, including physical pleasure, desire, preference, arousal, or orgasm. The World Health Organization defines sexual dysfunction as a "person's inability to participate in a sexual relationship as they would wish". This definition is broad and is subject to many interpretations. A diagnosis of sexual dysfunction under the DSM-5 requires a person to feel extreme distress and interpersonal strain for a minimum of six months. Sexual dysfunction can have a profound impact on an individual's perceived quality of sexual life. The term sexual disorder may not only refer to physical sexual dysfunction, but to paraphilias as well; this is sometimes termed disorder of sexual preference.
Blue balls is slang for an uncomfortable testicular sensation that can occur during a state of male sexual arousal. The term is thought to have originated in the United States, first appearing in 1916. Another slang term used for the condition is lover's nuts. Some urologists call this condition epididymal hypertension or sexual arousal orchialgia. Most often it describes a temporary fluid congestion (vasocongestion) in the testicles, caused by prolonged sexual arousal in the human male without ejaculation.
The human sexual response cycle is a four-stage model of physiological responses to sexual stimulation, which, in order of their occurrence, are the excitement, plateau, orgasmic, and resolution phases. This physiological response model was first formulated by William H. Masters and Virginia E. Johnson, in their 1966 book Human Sexual Response. Since that time, other models regarding human sexual response have been formulated by several scholars who have criticized certain inaccuracies in the human sexual response cycle model.
Sexual medicine or Psychosexual medicine as defined by Masters and Johnsons in their classic Textbook of Sexual Medicine, is "that branch of medicine that focuses on the evaluation and treatment of sexual disorders, which have a high prevalence rate." Examples of disorders treated with sexual medicine are erectile dysfunction, hypogonadism, and prostate cancer. Sexual medicine often uses a multidisciplinary approach involving physicians, mental health professionals, social workers, and sex therapists. Sexual medicine physicians often approach treatment with medicine and surgery, while sex therapists often focus on behavioral treatments.

Prostatectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the prostate gland. This operation is done for benign conditions that cause urinary retention, as well as for prostate cancer and for other cancers of the pelvis.
Sexual headache is a type of headache that occurs in the skull and neck during sexual activity, including masturbation or orgasm. These headaches are usually benign, but occasionally are caused by intracranial hemorrhage and cerebral infarction, especially if the pain is sudden and severe. They may be caused by general exertion, sexual excitement, or contraction of the neck and facial muscles. Most cases can be successfully treated with medication.
In human sexuality, the refractory period is usually the recovery phase after orgasm, during which it is physiologically impossible for a man to have additional orgasms. This phase begins immediately after ejaculation and lasts until the excitement phase of the human sexual response cycle begins anew with low-level response. Although it is generally reported that women do not experience a refractory period and can thus experience an additional orgasm soon after the first one, some sources state that both men and women experience a refractory period because women may also experience a moment after orgasm in which further sexual stimulation does not produce excitement.

Ejaculation is the discharge of semen from the male reproductive tract as a result of an orgasm. It is the final stage and natural objective of male sexual stimulation, and an essential component of natural conception. Ejaculation can occur spontaneously during sleep, and is a normal part of human sexual development. In rare cases, ejaculation occurs because of prostatic disease. Anejaculation is the condition of being unable to ejaculate. Ejaculation is usually very pleasurable for men; dysejaculation is an ejaculation that is painful or uncomfortable. Retrograde ejaculation is the condition where semen travels backwards into the bladder rather than out of the urethra.
Postorgasmic illness syndrome (POIS) is a syndrome in which people have chronic physical and cognitive symptoms following ejaculation. The symptoms usually onset within seconds, minutes, or hours, and last for up to a week. The cause and prevalence are unknown; it is considered a rare disease.
Sexual anhedonia, also known as pleasure dissociative orgasmic disorder, is a condition in which an individual cannot feel pleasure from an orgasm. It is thought to be a variant of hypoactive sexual desire disorder.

Sexual arousal describes the physiological and psychological responses in preparation for sexual intercourse or when exposed to sexual stimuli. A number of physiological responses occur in the body and mind as preparation for sexual intercourse, and continue during intercourse. Male arousal will lead to an erection, and in female arousal the body's response is engorged sexual tissues such as nipples, vulva, clitoris, vaginal walls, and vaginal lubrication. Mental stimuli and physical stimuli such as touch, and the internal fluctuation of hormones, can influence sexual arousal.

Although spinal cord injury (SCI) often causes sexual dysfunction, many people with SCI are able to have satisfying sex lives. Physical limitations acquired from SCI affect sexual function and sexuality in broader areas, which in turn has important effects on quality of life. Damage to the spinal cord impairs its ability to transmit messages between the brain and parts of the body below the level of the lesion. This results in lost or reduced sensation and muscle motion, and affects orgasm, erection, ejaculation, and vaginal lubrication. More indirect causes of sexual dysfunction include pain, weakness, and side effects of medications. Psycho-social causes include depression and altered self-image. Many people with SCI have satisfying sex lives, and many experience sexual arousal and orgasm. People with SCI may employ a variety of adaptations to help carry on their sex lives healthily, by focusing on different areas of the body and types of sexual acts. Neural plasticity may account for increases in sensitivity in parts of the body that have not lost sensation, so people often find newly sensitive erotic areas of the skin in erogenous zones or near borders between areas of preserved and lost sensation.







