E-Science or eScience is computationally intensive science that is carried out in highly distributed network environments, or science that uses immense data sets that require grid computing; the term sometimes includes technologies that enable distributed collaboration, such as the Access Grid. The term was created by John Taylor, the Director General of the United Kingdom's Office of Science and Technology in 1999 and was used to describe a large funding initiative starting in November 2000. E-science has been more broadly interpreted since then, as "the application of computer technology to the undertaking of modern scientific investigation, including the preparation, experimentation, data collection, results dissemination, and long-term storage and accessibility of all materials generated through the scientific process. These may include data modeling and analysis, electronic/digitized laboratory notebooks, raw and fitted data sets, manuscript production and draft versions, pre-prints, and print and/or electronic publications." In 2014, IEEE eScience Conference Series condensed the definition to "eScience promotes innovation in collaborative, computationally- or data-intensive research across all disciplines, throughout the research lifecycle" in one of the working definitions used by the organizers. E-science encompasses "what is often referred to as big data [which] has revolutionized science... [such as] the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN... [that] generates around 780 terabytes per year... highly data intensive modern fields of science...that generate large amounts of E-science data include: computational biology, bioinformatics, genomics" and the human digital footprint for the social sciences.
A collaboratory, as defined by William Wulf in 1989, is a “center without walls, in which the nation’s researchers can perform their research without regard to physical location, interacting with colleagues, accessing instrumentation, sharing data and computational resources, [and] accessing information in digital libraries”.
United States federal research funders use the term cyberinfrastructure to describe research environments that support advanced data acquisition, data storage, data management, data integration, data mining, data visualization and other computing and information processing services distributed over the Internet beyond the scope of a single institution. In scientific usage, cyberinfrastructure is a technological and sociological solution to the problem of efficiently connecting laboratories, data, computers, and people with the goal of enabling derivation of novel scientific theories and knowledge.
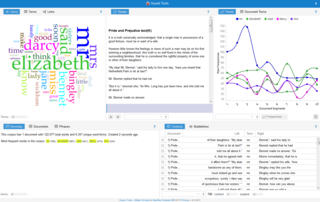
Digital humanities (DH) is an area of scholarly activity at the intersection of computing or digital technologies and the disciplines of the humanities. It includes the systematic use of digital resources in the humanities, as well as the analysis of their application. DH can be defined as new ways of doing scholarship that involve collaborative, transdisciplinary, and computationally engaged research, teaching, and publishing. It brings digital tools and methods to the study of the humanities with the recognition that the printed word is no longer the main medium for knowledge production and distribution.

The Energy Sciences Network (ESnet) is a high-speed computer network serving United States Department of Energy (DOE) scientists and their collaborators worldwide. It is managed by staff at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.

The National Institute of Business Management also known as NIBM, is a public business school based in Colombo, Sri Lanka.

Open science is the movement to make scientific research and its dissemination accessible to all levels of society, amateur or professional. Open science is transparent and accessible knowledge that is shared and developed through collaborative networks. It encompasses practices such as publishing open research, campaigning for open access, encouraging scientists to practice open-notebook science, broader dissemination and engagement in science and generally making it easier to publish, access and communicate scientific knowledge.
Simula Research Laboratory is a Norwegian non-profit research organisation located in Oslo, Norway.

HASTAC (/ˈhāˌstak/'), also known as the Humanities, Arts, Science and Technology Alliance and Collaboratory, is a virtual organization and platform of more than 18,000 individuals and 400+ affiliate-institutions dedicated to innovative new modes of learning and research. HASTAC network members contribute to the community by sharing work and ideas with others via the open-access website, by hosting HASTAC conferences and workshops online or in their region by initiating conversations, or by working collaboratively with others in the HASTAC network.

The Dutch Research Council is the national research council of the Netherlands. NWO funds thousands of top researchers at universities and institutes and steers the course of Dutch science by means of subsidies and research programmes. NWO promotes quality and innovation in science. NWO is an independent administrative body under the auspices of the Dutch Ministry of Education, Culture and Science. NWO directs its approximate budget of 1 billion euros towards Dutch universities and institutes, often on a project basis. Also, NWO has its own research institutes and facilitates international cooperation. Current president of NWO since April 1, 2021 is Marcel Levi. Former NWO presidents include Stan Gielen, Peter Nijkamp and Jos Engelen.

Deb Verhoeven is currently the Canada 150 Research Chair in Gender and Cultural Informatics at the University of Alberta. Previously she was Associate Dean of Engagement and Innovation at the University of Technology Sydney, and before this she was Professor of Media and Communication at Deakin University. Until 2011 she held the role of director of the AFI Research Collection at RMIT. A writer, broadcaster, film critic and commentator, Verhoeven is the author of more than 100 journal articles and book chapters. Her book Jane Campion published by Routledge, is a detailed case study of the commercial and cultural role of the auteur in the contemporary film industry.

Heritage science is the interdisciplinary domain of scientific study of cultural and natural heritage. Heritage science draws on diverse humanities, sciences and engineering disciplines. It focuses on enhancing the understanding, care and sustainable use of heritage so it can enrich people's lives, both today and in the future. Heritage science is an umbrella term encompassing all forms of scientific enquiry into human works and the combined works of nature and humans, of value to people.

The Alliance of Digital Humanities Organizations (ADHO) is a digital humanities umbrella organization formed in 2005 to coordinate the activities of several regional DH organizations, referred to as constituent organizations.

David Charles De Roure is an English computer scientist who is a professor of e-Research at the University of Oxford, where he is responsible for Digital Humanities in The Oxford Research Centre in the Humanities (TORCH), and is a Turing Fellow at The Alan Turing Institute. He is a supernumerary Fellow of Wolfson College, Oxford, and Oxford Martin School Senior Alumni Fellow.
Science & Technology Australia (STA), formerly known as the Federation of Australian Scientific and Technological Societies (FASTS), is an organisation representing the interests of more than 90,000 Australian scientists and technologists, and promoting their views on a wide range of policy issues to the Australian Government, Australian industry, and the Australian community.

The Australian Research Data Commons (ARDC) is a limited company, formed on 1 July 2018 by combining the Australian National Data Service (ANDS), Nectar and Research Data Services (RDS). Its purpose is to enable Australian researchers and industry access to nationally significant eInfrastructure, skills platforms, and data collections.
T-Labs, formerly known as "Telekom Innovation Laboratories", is the R&D unit of Deutsche Telekom. T-Labs current research areas are: Future Networks, Spatial Computing and Decentralized Systems.

The "Alessandro Faedo" Istituto di Scienza e Tecnologie dell'Informazione is an institute of the Italian National Research Council (CNR). The institute is located in the CNR research area in the Ghezzano Province of Pisa about 5 km from San Giuliano Terme.
The National Documentation Centre is a Greek public organisation that promotes knowledge, research, innovation and digital transformation. It was established in 1980 with funding from the United Nations Development Programme with the aim to strengthen the collection and distribution of research-related material, and to ensure full accessibility to it. It has been designated as a National Scientific Infrastructure, a National Authority of the Hellenic Statistical System, and National Contact Point for European Research and Innovation Programmes. Since August 2019, it has been established as a discrete public-interest legal entity under private law, and is supervised by the Ministry of Digital Governance. The management bodies of EKT are the Administrative Board and the Director who, since 2013, has been Dr. Evi Sachini.

The Technology Innovation Institute (TII) is an Abu Dhabi government funded research institution that operates in the areas of artificial intelligence, quantum computing, autonomous robotics, cryptography, advanced materials, digital science, directed energy and secure systems. The institute is a part of the Abu Dhabi Government’s Advanced Technology Research Council (ATRC).













