The discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis, in financial analysis, is a method used to value a security, project, company, or asset, that incorporates the time value of money. Discounted cash flow analysis is widely used in investment finance, real estate development, corporate financial management, and patent valuation. Used in industry as early as the 1700s or 1800s, it was widely discussed in financial economics in the 1960s, and U.S. courts began employing the concept in the 1980s and 1990s.

Natural capital is the world's stock of natural resources, which includes geology, soils, air, water and all living organisms. Some natural capital assets provide people with free goods and services, often called ecosystem services. All of these underpin our economy and society, and thus make human life possible.

Environmental economics is a sub-field of economics concerned with environmental issues. It has become a widely studied subject due to growing environmental concerns in the twenty-first century. Environmental economics "undertakes theoretical or empirical studies of the economic effects of national or local environmental policies around the world. ... Particular issues include the costs and benefits of alternative environmental policies to deal with air pollution, water quality, toxic substances, solid waste, and global warming."

Ecological economics, bioeconomics, ecolonomy, eco-economics, or ecol-econ is both a transdisciplinary and an interdisciplinary field of academic research addressing the interdependence and coevolution of human economies and natural ecosystems, both intertemporally and spatially. By treating the economy as a subsystem of Earth's larger ecosystem, and by emphasizing the preservation of natural capital, the field of ecological economics is differentiated from environmental economics, which is the mainstream economic analysis of the environment. One survey of German economists found that ecological and environmental economics are different schools of economic thought, with ecological economists emphasizing strong sustainability and rejecting the proposition that physical (human-made) capital can substitute for natural capital.
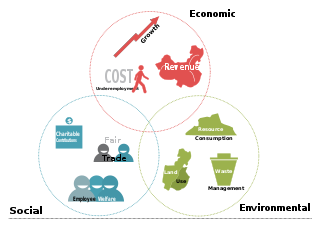
The triple bottom line is an accounting framework with three parts: social, environmental and economic. Some organizations have adopted the TBL framework to evaluate their performance in a broader perspective to create greater business value. Business writer John Elkington claims to have coined the phrase in 1994.
Cost–benefit analysis (CBA), sometimes also called benefit–cost analysis, is a systematic approach to estimating the strengths and weaknesses of alternatives. It is used to determine options which provide the best approach to achieving benefits while preserving savings in, for example, transactions, activities, and functional business requirements. A CBA may be used to compare completed or potential courses of action, and to estimate or evaluate the value against the cost of a decision, project, or policy. It is commonly used to evaluate business or policy decisions, commercial transactions, and project investments. For example, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission must conduct cost-benefit analyses before instituting regulations or deregulations.
A financial analyst is a professional, undertaking financial analysis for external or internal clients as a core feature of the job. The role may specifically be titled securities analyst, research analyst, equity analyst, investment analyst, or ratings analyst. The job title is a broad one: in banking, and industry more generally, various other analyst-roles cover financial management and (credit) risk management, as opposed to focusing on investments and valuation; these are also discussed in this article.
In corporate finance, capital structure refers to the mix of various forms of external funds, known as capital, used to finance a business. It consists of shareholders' equity, debt, and preferred stock, and is detailed in the company's balance sheet. The larger the debt component is in relation to the other sources of capital, the greater financial leverage the firm is said to have. Too much debt can increase the risk of the company and reduce its financial flexibility, which at some point creates concern among investors and results in a greater cost of capital. Company management is responsible for establishing a capital structure for the corporation that makes optimal use of financial leverage and holds the cost of capital as low as possible.
A green economy is an economy that aims at reducing environmental risks and ecological scarcities, and that aims for sustainable development without degrading the environment. It is closely related with ecological economics, but has a more politically applied focus. The 2011 UNEP Green Economy Report argues "that to be green, an economy must not only be efficient, but also fair. Fairness implies recognizing global and country level equity dimensions, particularly in assuring a Just Transition to an economy that is low-carbon, resource efficient, and socially inclusive."
Ecosystem valuation is an economic process which assigns a value to an ecosystem and/or its ecosystem services. By quantifying, for example, the human welfare benefits of a forest to reduce flooding and erosion while sequestering carbon, providing habitat for endangered species, and absorbing harmful chemicals, such monetization ideally provides a tool for policy-makers and conservationists to evaluate management impacts and compare a cost-benefit analysis of potential policies. However, such valuations are estimates, and involve the inherent quantitative uncertainty and philosophical debate of evaluating a range non-market costs and benefits.

Ecosystem services are the many and varied benefits to humans provided by the natural environment and healthy ecosystems. Such ecosystems include, for example, agroecosystems, forest ecosystem, grassland ecosystems, and aquatic ecosystems. These ecosystems, functioning in healthy relationships, offer such things as natural pollination of crops, clean air, extreme weather mitigation, and human mental and physical well-being. Collectively, these benefits are becoming known as ecosystem services, and are often integral to the provision of food, the provisioning of clean drinking water, the decomposition of wastes, and the resilience and productivity of food ecosystems.
Valuation using discounted cash flows is a method of estimating the current value of a company based on projected future cash flows adjusted for the time value of money. The cash flows are made up of those within the “explicit” forecast period, together with a continuing or terminal value that represents the cash flow stream after the forecast period. In several contexts, DCF valuation is referred to as the "income approach".
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to finance:

The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity (TEEB) was a study led by Pavan Sukhdev from 2007 to 2011. It is an international initiative to draw attention to the global economic benefits of biodiversity. Its objective is to highlight the growing cost of biodiversity loss and ecosystem degradation and to draw together expertise from the fields of science, economics and policy to enable practical actions. TEEB aims to assess, communicate and mainstream the urgency of actions through its five deliverables—D0: science and economic foundations, policy costs and costs of inaction, D1: policy opportunities for national and international policy-makers, D2: decision support for local administrators, D3: business risks, opportunities and metrics and D4: citizen and consumer ownership.
In cost–benefit analysis and social welfare economics, the term option value refers to the value that is placed on private willingness to pay for maintaining or preserving a public asset or service even if there is little or no likelihood of the individual actually ever using it. The concept is most commonly used in public policy assessment to justify continuing investment in parks, wildlife refuges and land conservation, as well as rail transportation facilities and services. It is also recognized as an element of the total economic value of environmental resources.

Corporate finance is the area of finance that deals with the sources of funding, and the capital structure of corporations, the actions that managers take to increase the value of the firm to the shareholders, and the tools and analysis used to allocate financial resources. The primary goal of corporate finance is to maximize or increase shareholder value.
Natural capital accounting is the process of calculating the total stocks and flows of natural resources and services in a given ecosystem or region. Accounting for such goods may occur in physical or monetary terms. This process can subsequently inform government, corporate and consumer decision making as each relates to the use or consumption of natural resources and land, and sustainable behaviour.
Susana Mourato is a professor of environmental economics at the London School of Economics and Political Science. She holds a leader position at the Grantham Research Institute on Climate Change and the Environment.

Natural resource valuation is a process of providing of benefits, costs, damage of or to natural and environmental resources. It has a fundamental role in the practice of cost-benefit analysis of health, safety, and environmental issues.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to corporate finance:








