
The American Civil War was a civil war in the United States between the Union and the Confederacy, formed by states that had seceded from it. The cause of the war was the dispute over whether slavery would be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prevented from doing so, which many believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction.

Joseph "Fighting Joe" Wheeler was a Confederate military commander and politician. He was a cavalry general in the Confederate States Army in the 1860s during the American Civil War, and then a general in the United States Army during both the Spanish-American and Philippine–American Wars near the turn of the twentieth century. For much of the Civil War, he was the senior cavalry general in the Army of Tennessee and fought in most of its battles in the Western Theater.

The Battle of Atlanta was a battle of the Atlanta Campaign fought during the American Civil War on July 22, 1864, just southeast of Atlanta, Georgia. Continuing their summer campaign to seize the important rail and supply hub of Atlanta, Union forces commanded by William Tecumseh Sherman overwhelmed and defeated Confederate forces defending the city under John Bell Hood. Union Maj. Gen. James B. McPherson was killed during the battle, the second-highest-ranking Union officer killed in action during the war. Despite the implication of finality in its name, the battle occurred midway through the Atlanta campaign, and the city did not fall until September 2, 1864, after a Union siege and various attempts to seize railroads and supply lines leading to Atlanta. After taking the city, Sherman's troops headed south-southeastward toward Milledgeville, the state capital, and on to Savannah with the March to the Sea.

Sherman's March to the Sea was a military campaign of the American Civil War conducted through Georgia from November 15 until December 21, 1864, by William Tecumseh Sherman, major general of the Union Army. The campaign began on November 15 with Sherman's troops leaving Atlanta, recently taken by Union forces, and ended with the capture of the port of Savannah on December 21. His forces followed a "scorched earth" policy, destroying military targets as well as industry, infrastructure, and civilian property, disrupting the Confederacy's economy and transportation networks. The operation debilitated the Confederacy and helped lead to its eventual surrender. Sherman's decision to operate deep within enemy territory without supply lines was unusual for its time, and the campaign is regarded by some historians as an early example of modern warfare or total war.

Forty acres and a mule was part of Special Field Orders No. 15, a wartime order proclaimed by Union General William Tecumseh Sherman on January 16, 1865, during the American Civil War, to allot land to some freed families, in plots of land no larger than 40 acres (16 ha). Sherman later ordered the army to lend mules for the agrarian reform effort. The field orders followed a series of conversations between Secretary of War Edwin M. Stanton and Radical Republican abolitionists Charles Sumner and Thaddeus Stevens following disruptions to the institution of slavery provoked by the American Civil War. Many freed people believed, after being told by various political figures, that they had a right to own the land they had been forced to work as slaves and were eager to control their own property. Freed people widely expected to legally claim 40 acres of land. However, Abraham Lincoln's successor as president, Andrew Johnson, tried to reverse the intent of Sherman's wartime Order No. 15 and similar provisions included in the second Freedmen's Bureau bills.

Henry Warner Slocum Sr., was a Union general during the American Civil War and later served in the United States House of Representatives from New York. During the war, he was one of the youngest major generals in the Army and fought numerous major battles in the Eastern Theater and in Georgia and the Carolinas. While commanding a regiment, a brigade, a division, and a corps in the Army of the Potomac, he saw action at First Bull Run, the Peninsula Campaign, Harpers Ferry, South Mountain, Antietam, and Chancellorsville.

The Atlanta campaign was a series of battles fought in the Western Theater of the American Civil War throughout northwest Georgia and the area around Atlanta during the summer of 1864. Union Maj. Gen. William Tecumseh Sherman invaded Georgia from the vicinity of Chattanooga, Tennessee, beginning in May 1864, opposed by the Confederate general Joseph E. Johnston.

The Battle of Jonesborough was fought between Union Army forces led by William Tecumseh Sherman and Confederate forces under William J. Hardee during the Atlanta Campaign in the American Civil War. On the first day, on orders from Army of Tennessee commander John Bell Hood, Hardee's troops attacked the Federals and were repulsed with heavy losses. That evening, Hood ordered Hardee to send half his troops back to Atlanta. On the second day, five Union corps converged on Jonesborough. For the only time during the Atlanta Campaign, a major Federal frontal assault succeeded in breaching the Confederate defenses. The attack took 900 prisoners, but the defenders were able to halt the breakthrough and improvise new defenses. Despite facing overwhelming odds, Hardee's corps escaped undetected to the south that evening.

The Carolinas campaign, also known as the campaign of the Carolinas, was the final campaign conducted by the Union Army against the Confederate Army in the Western Theater of the American Civil War. On January 1, Union Maj. Gen. William T. Sherman advanced north from Savannah, Georgia, through the Carolinas, with the intention of linking up with Union forces in Virginia. The campaign culminated in the defeat of Confederate Gen. Joseph E. Johnston's army at the Battle of Bentonville, and its unconditional surrender to Union forces on April 26, 1865. Coming just two weeks after the defeat of Robert E. Lee's army at the Battle of Appomattox Court House, it signaled that the war was effectively over.

The western theater of the American Civil War encompassed major military operations in the states of Alabama, Georgia, Florida, Mississippi, North Carolina, Kentucky, South Carolina and Tennessee, as well as Louisiana east of the Mississippi River. Operations on the coasts of these states, except for Mobile Bay, are considered part of the Lower Seaboard Theater. Most other operations east of the Appalachian Mountains are part of the eastern theater. Operations west of the Mississippi River took place in the trans-Mississippi theater.

Contraband was a term commonly used in the US military during the American Civil War to describe a new status for certain people who escaped slavery or those who affiliated with Union forces. In August 1861, the Union Army and the US Congress determined that the US would no longer return people who escaped slavery who went to Union lines, but they would be classified as "contraband of war," or captured enemy property. They used many as laborers to support Union efforts and soon began to pay wages.
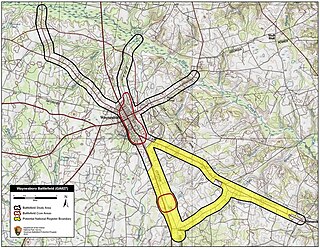
The Battle of Waynesboro was an American Civil War battle fought on December 4, 1864 in eastern Georgia, towards the end of Sherman's March to the Sea. Union cavalry forces under Brig. Gen. Judson Kilpatrick defeated Confederate cavalry led by Maj. Gen. Joseph Wheeler, opening the way for William T. Sherman's armies to approach their objective, Savannah.

Louisville in the American Civil War was a major stronghold of Union forces, which kept Kentucky firmly in the Union. It was the center of planning, supplies, recruiting and transportation for numerous campaigns, especially in the Western Theater. By the end of the war, Louisville had not been attacked once, although skirmishes and battles, including the battles of Perryville and Corydon, Indiana, took place nearby.

Georgia was one of the original seven slave states that formed the Confederate States of America in February 1861, triggering the U.S. Civil War. The state governor, Democrat Joseph E. Brown, wanted locally raised troops to be used only for the defence of Georgia, in defiance of Confederate president Jefferson Davis, who wanted to deploy them on other battlefronts. When the Union blockade prevented Georgia from exporting its plentiful cotton in exchange for key imports, Brown ordered farmers to grow food instead, but the breakdown of transport systems led to desperate shortages.

African Americans, including former slaves, served in the American Civil War. The 186,097 black men who joined the Union Army included 7,122 officers and 178,975 enlisted soldiers. Approximately 20,000 black sailors served in the Union Navy and formed a large percentage of many ships' crews. Later in the war, many regiments were recruited and organized as the United States Colored Troops, which reinforced the Northern forces substantially during the conflict's last two years. Both Northern Free Negro and Southern runaway slaves joined the fight. Throughout the course of the war, black soldiers served in forty major battles and hundreds of more minor skirmishes; sixteen African Americans received the Medal of Honor.
William Henry Singleton gained freedom in North Carolina and served as a sergeant in the United States Colored Troops during the American Civil War. After its end and emancipation, he moved North to New Haven, Connecticut. There he became literate and a minister in the African Methodist Episcopal Zion Church, serving also in Maine and New York.

Slavery played the central role during the American Civil War. The primary catalyst for secession was slavery, especially Southern political leaders' resistance to attempts by Northern antislavery political forces to block the expansion of slavery into the western territories. Slave life went through great changes, as the South saw Union Armies take control of broad areas of land. During and before the war, enslaved people played an active role in their own emancipation, and thousands of enslaved people escaped from bondage during the war.
The Skirmish at Terre Noire Creek, also known as the Skirmish at Wolf Creek or Skirmish at Antoine, an engagement during the Camden Expedition of the American Civil War, was fought on April 2, 1864. The action occurred about 1 mile (1.6 km) east of Terre Noire Creek along a defile near the towns of Hollywood, Arkansas and Antoine, Arkansas. A Confederate States Army cavalry brigade under Brigadier General Joseph O. Shelby attacked a Union supply train of more than 200 wagons accompanying Union Army Major General Frederick Steele's force which was attempting to reach Shreveport, Louisiana to join with Major General Nathaniel Banks's force in the Red River Campaign with the objective of occupying Shreveport and controlling western Louisiana.
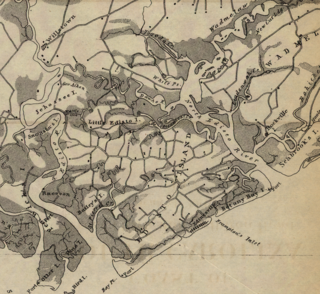
Edisto Island during the American Civil War was the location of a number of minor engagements and for a time of a large colony of escaped African-American slaves during the American Civil War (1861–1865). Edisto Island was largely abandoned by planters in November 1861 and in December 1861, escaped slaves began setting up their own refugee camps there. In January 1862, armed African Americans from the island and Confederate forces clashed and a Confederate raid in reprisal killed a small number of unarmed African Americans. In February, Union forces were stationed on the island to develop it as a staging area for future campaigns against Charleston, twenty-five miles away, as well as to protect the colony, which would eventually number thousands of African Americans. As Union forces took control of the island, a number of skirmishes occurred, but Confederates withdrew. In June, most of the Union troops left the island in a campaign, which culminated in the Battle of Secessionville. In July, the remaining troops withdrew, and the colony was removed to St. Helena Island. For the rest of the war, a small number of escaped slaves and plantation owners remained and farmed the island, but it was largely abandoned. Near the end of the war, the island was again used as a location of colonies of freed slaves.
Garrison Frazier was an African-American Baptist minister and public figure during the U.S. Civil War. He acted as spokesman for twenty African-American Baptist and Methodist ministers who met on January 12, 1865 with Major General William Tecumseh Sherman, of the Union Army's Military Division of the Mississippi, and with U.S. Secretary of War Edwin Stanton, at General Sherman's headquarters in Savannah, Georgia. This meeting is commonly known as the "Savannah Colloquy" or the "Forty acres and a mule" meeting.

















