
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire or the Dual Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. Austria-Hungary was a military and diplomatic alliance of two sovereign states, with a single monarch who was titled both Emperor of Austria and King of Hungary. Austria-Hungary constituted the last phase in the constitutional evolution of the Habsburg monarchy: it was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 in the aftermath of the Austro-Prussian War and was dissolved shortly after Hungary terminated the union with Austria on 31 October 1918.

Pan-Slavism, a movement which crystallized in the mid-19th century, is the political ideology concerned with the advancement of integrity and unity for the Slavic people. Its main impact occurred in the Balkans, where non-Slavic empires had ruled the South Slavs for centuries. These were mainly the Byzantine Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Venice.
The history of Austria covers the history of Austria and its predecessor states. In the late Iron Age Austria was occupied by people of the Hallstatt Celtic culture, they first organized as a Celtic kingdom referred to by the Romans as Noricum, dating from c. 800 to 400 BC. At the end of the 1st century BC, the lands south of the Danube became part of the Roman Empire. In the Migration Period, the 6th century, the Bavarii, a Germanic people, occupied these lands until it fell to the Frankish Empire establish by the Germanic Franks in the 9th century. The name Ostarrîchi (Austria) has been in use since 996 AD when it was a margravate of the Duchy of Bavaria and from 1156 an independent duchy of the Holy Roman Empire.

Franz Joseph I or Francis Joseph I was Emperor of Austria, King of Hungary, and the ruler of the other states of the Habsburg monarchy from 2 December 1848 until his death on 21 November 1916. In the early part of his reign, his realms and territories were referred to as the Austrian Empire, but were reconstituted as the dual monarchy of the Austro-Hungarian Empire in 1867. From 1 May 1850 to 24 August 1866, he was also president of the German Confederation.

Klemens Wenzel Nepomuk Lothar, Prince of Metternich-Winneburg zu Beilstein, known as Klemens von Metternich or Prince Metternich, was a conservative Austrian statesman and diplomat who was at the center of the European balance of power known as the Concert of Europe for three decades as the Austrian Empire's foreign minister from 1809 and Chancellor from 1821 until the liberal Revolutions of 1848 forced his resignation.
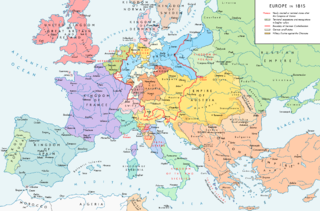
The Concert of Europe was a general consensus among the great powers of 19th-century Europe to maintain the European balance of power, political boundaries, and spheres of influence. Never a perfect unity and subject to disputes and jockeying for position and influence, the Concert was an extended period of relative peace and stability in Europe following the Wars of the French Revolution and Napoleonic Wars which had consumed the continent since the 1790s. There is considerable scholarly dispute over the exact nature and duration of the Concert. Some scholars argue that it fell apart nearly as soon as it began in the 1820s when the great powers disagreed over the handling of liberal revolts in Italy, while others argue that it lasted until the outbreak of World War I and others for points in between. For those arguing for a longer duration, there is generally agreement that the period after the Revolutions of 1848 and the Crimean War (1853–1856) represented a different phase with different dynamics than the earlier period.

The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a multinational European great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, it was the third most populous monarchy in Europe after the Russian Empire and the United Kingdom. Along with Prussia, it was one of the two major powers of the German Confederation. Geographically, it was the third-largest empire in Europe after the Russian Empire and the First French Empire.

The Revolutions of 1848 in the Austrian Empire were a set of revolutions that took place in the Austrian Empire from March 1848 to November 1849. Much of the revolutionary activity had a nationalist character: the Empire, ruled from Vienna, included ethnic Germans, Hungarians, Slovenes, Poles, Czechs, Slovaks, Ruthenians (Ukrainians), Romanians, Croats, Venetians and Serbs; all of whom attempted in the course of the revolution to either achieve autonomy, independence, or even hegemony over other nationalities. The nationalist picture was further complicated by the simultaneous events in the German states, which moved toward greater German national unity.

The Czech lands, then also known as Lands of the Bohemian Crown, were largely subject to the Habsburgs from the end of the Thirty Years' War in 1648 until the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867. There were invasions by the Turks early in the period, and by the Prussians in the next century. The Habsburgs consolidated their rule and under Maria Theresa (1740–1780) adopted enlightened absolutism, with distinct institutions of the Bohemian Kingdom absorbed into centralized structures. After the Napoleonic Wars and the establishment of the Austrian Empire, a Czech National Revival began as a scholarly trend among educated Czechs, led by figures such as František Palacký. Czech nationalism took a more politically active form during the 1848 revolution, and began to come into conflict not only with the Habsburgs but with emerging German nationalism.

The Zollverein, or German Customs Union, was a coalition of German states formed to manage tariffs and economic policies within their territories. Organized by the 1833 Zollverein treaties, it formally started on 1 January 1834. However, its foundations had been in development from 1818 with the creation of a variety of custom unions among the German states. By 1866, the Zollverein included most of the German states. The Zollverein was not part of the German Confederation (1815-1866).
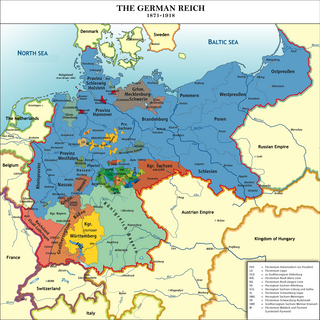
The unification of Germany was a process of building the first nation-state for Germans with federal features based on the concept of Lesser Germany. It commenced on 18 August 1866 with adoption of the North German Confederation Treaty establishing the North German Confederation, initially a military alliance de facto dominated by Prussia which was subsequently deepened through adoption of the North German Constitution. The process symbolically concluded when most of south German states joined the North German Confederation with the ceremonial proclamation of the German Empire i.e. the German Reich having 25 member states and led by the Kingdom of Prussia of Hohenzollerns on 18 January 1871; the event was later celebrated as the customary date of the German Empire's foundation, although the legally meaningful events relevant to the accomplishment of unification occurred on 1 January 1871 and 4 May 1871.

Felix Ludwig Johann Friedrich, Prince of Schwarzenberg was a Bohemian nobleman and an Austrian statesman who restored the Austrian Empire as a European great power following the Revolutions of 1848. He served as Minister-President of the Austrian Empire and Foreign Minister of the Austrian Empire from 1848 to 1852.

The word Kleinstaaterei is a pejorative term coined in the early nineteenth century to denote the territorial fragmentation of Germany. While the term referred primarily to the territorial fragmentation of the German Confederation, it is also applied by extension to the even more extreme territorial fragmentation of the Holy Roman Empire. In this period, Germany was split into a great number of nearly sovereign small and medium-sized secular and ecclesiastical principalities and free imperial cities, some of which were little larger than a single town or the surrounding grounds of the monastery of an Imperial abbey. Estimates of the total number of German states at any time during the 18th century vary, ranging from 294 to 348 or more; however, the number of states rapidly decreased with the onset of German mediatisation in the early 19th century.

Vormärz was a period in the history of Germany preceding the 1848 March Revolution in the states of the German Confederation. The beginning of the period is less well-defined. Some place the starting point directly after the fall of Napoleon and the establishment of the German Confederation in 1815. Others, typically those who emphasise the Vormärz as a period of political uprising, place the beginning at the French July Revolution of 1830.

The First Silesian War was a war between Prussia and Austria that lasted from 1740 to 1742 and resulted in Prussia's seizing most of the region of Silesia from Austria. The war was fought mainly in Silesia, Moravia and Bohemia and formed one theatre of the wider War of the Austrian Succession. It was the first of three Silesian Wars fought between Frederick the Great's Prussia and Maria Theresa's Austria in the mid-18th century, all three of which ended in Prussian control of Silesia.

Neighborly relations exist between Austria and the Czech Republic, two member states of the European Union. Austria has given full support to Czech Republic's membership of the European Union. The Czech Republic is a member state of NATO, while Austria is not.
The European balance of power is a tenet in international relations that no single power should be allowed to achieve hegemony over a substantial part of Europe. During much of the Modern Age, the balance was achieved by having a small number of ever-changing alliances contending for power, which culminated in the World Wars of the early 20th century. By 1945, European-led global dominance and rivalry had ended and the doctrine of European balance of power was replaced by a worldwide balance of power involving the United States and the Soviet Union as the modern superpowers.
The "German question" was a debate in the 19th century, especially during the Revolutions of 1848, over the best way to achieve a unification of all or most lands inhabited by Germans. From 1815 to 1866, about 37 independent German-speaking states existed within the German Confederation. The Großdeutsche Lösung favored unifying all German-speaking peoples under one state, and was promoted by the Austrian Empire and its supporters. The Kleindeutsche Lösung sought only to unify the northern German states and did not include any part of Austria ; this proposal was favored by the Kingdom of Prussia.

Wenzel Anton, Prince of Kaunitz-Rietberg was an Austrian and Czech diplomat and statesman in the Habsburg monarchy. A proponent of enlightened absolutism, he held the office of State Chancellor for about four decades and was responsible for the foreign policies during the reigns of Maria Theresa, Joseph II, and Leopold II. In 1764, he was elevated to the noble rank of a Prince of the Holy Roman Empire (Reichfürst).

The economy of Austria-Hungary changed slowly during the existence of the Dual Monarchy, 1867-1918. The capitalist way of production spread throughout the Empire during its 50-year existence replacing medieval institutions. In 1873, the old capital Buda and Óbuda merged with the third city, Pest, thus creating the new metropolis of Budapest. The dynamic Pest grew into Hungary's administrative, political, economic, trade and cultural hub. Many of the state institutions and the modern administrative system of Hungary were established during this period. It was a large, heavily rural country with wealth and income levels a bit below the European average. Growth rates were similar to Europe as a whole. After 1895. migration became a major factor, with most headed to the United States.

















