
Alberta is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is a part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Territories to the north, and the U.S. state of Montana to the south. It is one of the only two landlocked provinces in Canada, with Saskatchewan being the other. The eastern part of the province is occupied by the Great Plains, while the western part borders the Rocky Mountains. The province has a predominantly continental climate but experiences quick temperature changes due to air aridity. Seasonal temperature swings are less pronounced in western Alberta due to occasional Chinook winds.

The University of Calgary is a public research university located in Calgary, Alberta, Canada. The University of Calgary started in 1944 as the Calgary branch of the University of Alberta, founded in 1908, prior to being instituted into a separate, autonomous university in 1966. It is composed of 14 faculties and over 85 research institutes and centres. The main campus is located in the northwest quadrant of the city near the Bow River and a smaller south campus is located in the city centre. The main campus houses most of the research facilities and works with provincial and federal research and regulatory agencies, several of which are housed next to the campus such as the Geological Survey of Canada. The main campus covers approximately 200 hectares.
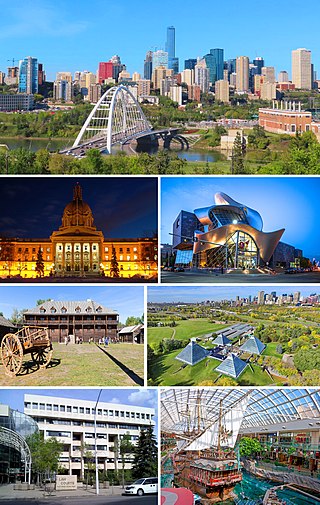
Edmonton is the capital city of the Canadian province of Alberta. Edmonton is situated on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Alberta's central region. The city anchors the northern end of what Statistics Canada defines as the "Calgary–Edmonton Corridor", a region spanning between Edmonton and the city of Calgary, which includes the many smaller municipalities between the two.

The University of Alberta is a public research university located in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. It was founded in 1908 by Alexander Cameron Rutherford, the first premier of Alberta, and Henry Marshall Tory, the university's first president. It was enabled through the Post-secondary Learning Act. The university is considered a "comprehensive academic and research university" (CARU), which means that it offers a range of academic and professional programs that generally lead to undergraduate and graduate level credentials.

The culture of Alberta refers to the art, customs, and traditions of the people of Alberta. Alberta entered into Confederation in 1905, placing her in a tie with Saskatchewan as the country's second youngest province. Despite her short history, the province possesses a rich culture. The vastness of the land and variation of geography – which includes mountains, foothills, grassland, parkland, forest, and rockland – have served as important sources of creative inspiration across all art forms. Alberta's primary industries of farming, ranching, and petroleum also play a major part in the province's culture and identity.

A normal school or normal college is an institution created to train teachers by educating them in the norms of pedagogy and curriculum. In the 19th century in the United States, instruction in normal schools was at the high school level, turning out primary school teachers. Many such schools are now called teacher training colleges or teachers' colleges, but in Mexico, continue to be called normal schools, with student-teachers being known as normalistas. Many schools currently require a high school diploma for entry, and may be part of a comprehensive university. Normal schools in the United States, Canada, and Argentina trained teachers for primary schools, while in Europe, the equivalent colleges typically educated teachers for primary schools and later extended their curricula to also cover secondary schools.

Athabasca University (AU) is a Canadian public research university that primarily operates through online distance education. Founded in 1970, it is one of four comprehensive academic and research universities in Alberta, and was the first Canadian university to specialize in distance education.
The Southern Alberta Institute of Technology (SAIT) is a polytechnic institute in Calgary, Alberta, Canada. SAIT offers more than 110 career programs in technology, trades and business. Established in 1916, it is Calgary's second oldest post-secondary institution and Canada's first publicly funded technical institute.

Mount Royal University (MRU) is a public university in Calgary, Alberta, Canada.

The Toronto Normal School was a teachers college in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Opened in 1847, the Normal School was located at Church and Gould streets in central Toronto, and was a predecessor to the current Ontario Institute for Studies in Education. The Royal Ontario Museum, the Ontario College of Art & Design and the Ontario Agricultural College all originated at the Normal School's campus and the provincial Department of Education was also located there. Officially named St. James Square, the school became known as "the cradle of Ontario's education system". The school's landmark Gothic-Romanesque building was designed by architects Thomas Ridout and Frederick William Cumberland in 1852. The landmark building was demolished in 1963, but architectural elements of the structure remain on the campus of Toronto Metropolitan University.

Guangxi Normal University is a provincial research university located in Guilin, Guangxi, China with historical strengths in teacher education, basic arts and sciences, and international exchange programs. Established in 1932 as one of the earliest normal schools in China, GXNU has evolved into a comprehensive university granting undergraduate, graduate, and doctoral degrees across 21 colleges and departments with 75 undergraduate majors.

The Canada Saskatchewan Production Studios are located in Regina, Saskatchewan at the corner of College Avenue and Broad Street. Built in 1913, the structure has served as a normal school, military training facility, and fine arts building for the University of Regina. It was internally gutted and reconstructed as a movie and television studio facility in 2002.
Education in Alberta is provided mainly through funding from the provincial government. The earliest form of formal education in Alberta is usually preschool which is not mandatory and is then followed by the partially-mandatory kindergarten to Grade 12. This is managed by Alberta Education which has divided the province into 379 school authorities. Higher education in the province is managed by Alberta Advanced Education.

Calgary is a city in the Canadian province of Alberta. It is the largest city in Alberta and the largest metro area within the three Prairie Provinces region. As of 2021, the city proper had a population of 1,306,784 and a metropolitan population of 1,481,806, making it the third-largest city and fifth-largest metropolitan area in Canada.

Higher education in Alberta refers to the post secondary education system for the province of Alberta. The Ministry of Advanced Education in Alberta oversees educational delivery through universities, publicly funded colleges, technical institutions, and private colleges. These institutions offer a variety of academic and vocational pursuits. Students have access to post-secondary options through most regions of Alberta, and a developed articulation system allows for increased student mobility.

Concordia University of Edmonton, is a publicly funded independent academic institution in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada; accredited under the Alberta Post-secondary Learning Act. Concordia offers arts, science, and management undergraduate degree programs, as well as graduate degree programs in education, information technology, information security, and psychology. Concordia is primarily funded by tuition and private donations and as of 2022, receives nearly one third of its funding from the government of Alberta.
MaKami College is a post-secondary college in Edmonton and Calgary, Alberta, Canada. It was incorporated in Edmonton in 2001, and was designated an Independent Academic Institution in Alberta in 2023, the first for-profit post-secondary institution to receive this designation in the province.
The University of Alberta Faculty of Rehabilitation Medicine, located in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada, is home to North America's only free-standing faculty of rehabilitation medicine and is composed of three departments, 11 research groups, six student clinics and programs and five institutes and centres. It provides academic training in rehabilitation science, physical therapy, occupational therapy and speech-language pathology.
Demetrios Nicolaides is a Canadian politician who was elected in the 2019 Alberta general election to represent the electoral district of Calgary-Bow in the 30th Alberta Legislature. He is a member of the United Conservative Party. On April 30, 2019, he was appointed to be the Minister of Advanced Education in the Executive Council of Alberta.
Donalda James Dickie was a Canadian normal school teacher in Alberta from the 1910s to 1940s. During this time period, Dickie wrote textbooks and co-created a new syllabus for Albertan elementary schoolteachers. After ending her education career, Dickie continued to write textbooks in the 1950s. Of her works, Dickie wrote series on geography, history and literature. Her Canadian history book for schoolchildren, The Great Adventure, received the 1950 Governor General's Award for juvenile fiction.














