Related Research Articles

The Université catholique de Louvain is Belgium's largest French-speaking university. It is located in Louvain-la-Neuve, which was expressly built to house the university, and Brussels, Charleroi, Mons, Tournai and Namur. Since September 2018, the university has used the branding UCLouvain, replacing the acronym UCL, following a merger with Saint-Louis University, Brussels.

The Louvain School of Management is the international business school of the University of Louvain (UCLouvain), Belgium, founded in 1897. The faculty offers courses on the campuses of Louvain-la-Neuve, UCLouvain FUCaM Mons and UCLouvain Charleroi.
Claroline is a collaborative eLearning and eWorking platform released under the GPL open-source license. It allows hundreds of organizations worldwide ranging from universities to schools and from companies to associations to create and administer courses and collaboration spaces over the web. The platform is used in more than 100 countries and is available in 35 languages.
HCL Connections is a Web 2.0 enterprise social software application developed originally by IBM and acquired by HCL Technologies in July 2019. Connections is an enterprise-collaboration platform which helps teams work more efficiently. Connections is part of HCL collaboration suite which also includes Notes / Domino, Sametime, Portal and Connections.
The Method for an Integrated Knowledge Environment (MIKE2.0) is an open source delivery methodology for enterprise information management consultants. MIKE2.0 was released in December 2006 by BearingPoint's Information Management team under the leadership of Robert Hillard. The project used Creative Commons Attribution License and was implemented by Sean McClowry. The project is now run by the MIKE2.0 Governance Association, a non-profit organisation based in Switzerland, with BearingPoint and Deloitte as the founding members. In March 2013 a book Information Development Using MIKE2.0 was published promoting it.
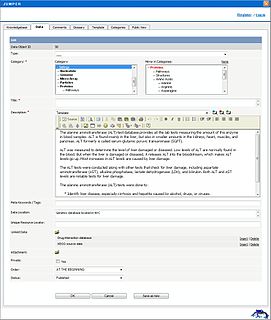
ApexKB, is a discontinued free and open-source script for collaborative search and knowledge management powered by a shared enterprise bookmarking engine that is a fork of KnowledgebasePublisher. It was publicly announced on 29 September 2008. A stable version of Jumper was publicly released under the GNU General Public License and made available on SourceForge on 26 March 2009.
Enterprise bookmarking is a method for Web 2.0 users to tag, organize, store, and search bookmarks of both web pages on the Internet and data resources stored in a distributed database or fileserver. This is done collectively and collaboratively in a process by which users add tag (metadata) and knowledge tags.
Folksonomy is a classification system in which end users apply public tags to online items, typically to make those items easier for themselves or others to find later. Over time, this can give rise to a classification system based on those tags and how often they are applied or searched for, in contrast to a taxonomic classification designed by the owners of the content and specified when it is published. This practice is also known as collaborative tagging, social classification, social indexing, and social tagging. Folksonomy was originally "the result of personal free tagging of information [...] for one's own retrieval", but online sharing and interaction expanded it into collaborative forms. Social tagging is the application of tags in an open online environment where the tags of other users are available to others. Collaborative tagging is tagging performed by a group of users. This type of folksonomy is commonly used in cooperative and collaborative projects such as research, content repositories, and social bookmarking.

The Pirate Party of Belgium is a political party in Belgium. Based on the model of the Swedish Pirate Party, it supports reform of copyright law, the abolition of patents, and respect for privacy. It was a founding member of Pirate Parties International.
Q-Sensei is a privately owned software company developing search technology and search-based applications for searching through unstructured and structured data. They make searching through diverse types and sources of data faster, easier, and more powerful. They developed enterprise search applications and are developing analytic features.

The Musée L or Musée universitaire de Louvain, French for: Louvain University Museum, is a Belgian university museum of the University of Louvain (UCLouvain) located in Louvain-la-Neuve, Walloon Brabant, Belgium.

UCLouvain Charleroi is a campus of the University of Louvain in Charleroi, Belgium. Consisting of 3 faculties and a series of research centers and institutes, UCLouvain Charleroi consists of the Maison Georges Lemaître, in the center of the city, and a branch in Montignies-sur-Sambre.

The Faculty of Economic, Social and Political Sciences and Communication (ESPO) is a faculty of the University of Louvain, located on the campuses of Louvain-la-Neuve, FUCaM Mons and UCLouvain Charleroi. It originates in the School of Political and Social Sciences founded by Jules Van den Heuvel in Louvain in 1892. With over 6000 students, it is UCLouvain's largest faculty.

The Aula Magna is a postmodern building of the University of Louvain located in Louvain-la-Neuve, a section of the Belgian city of Ottignies-Louvain-la-Neuve, in Walloon Brabant. It holds one of the country's largest auditoria, with a maximum capacity of 1050 seats, and Wallonia's largest stage. Inaugurated in 2001, the complex was designed by Philippe Samyn.

The Louvain-la-Neuve Cyclotron is a brutalist architectural complex of the University of Louvain built from 1970 to 1972 in Louvain-la-Neuve, Walloon Brabant, Belgium, notably holding UCLouvain's CYCLONE particle accelerators. It is the first building completed by the university when it moved following the Leuven crisis and was the largest cyclotron in Europe at the time of its construction. The Louvain Cyclotron can also refer to Belgium's first cyclotron built in Louvain (Leuven) in 1947, which was replaced by the Louvain-la-Neuve center.

The Louvain School of Engineering or École polytechnique de Louvain (EPL) is a faculty of the University of Louvain, Belgium, founded in 1864. Known as the Faculty of Applied Sciences prior to 2008, it currently operates on the campuses of Louvain-la-Neuve and UCLouvain Charleroi.

The Faculty of Architecture, Architectural Engineering and Urban Planning, often called LOCI, is the 14th faculty of the University of Louvain, Belgium. It became an independent faculty in 2009, with the merger of three institutes founded between 1867 and 1882, and is active in Brussels (Saint-Gilles), Tournai and Louvain-la-Neuve.
References
- ↑ "Hyperweek Joins Knowledge Plaza". 4 September 2013.
- ↑ "Useo Etude Rse Tome2 V1". Useo. Retrieved 2010-01-26.
- ↑ "Press release: Knowledge Plaza becomes Elium | elium". elium. 2017-03-09. Retrieved 2017-05-15.
- ↑ "Elium announces funding round of 4 million euros with Serena Capital | elium". elium. 2017-03-09. Retrieved 2017-08-31.
- ↑ "Data News Awards for Excellence 2011". Data News Magazine. Retrieved 2011-06-01.
- ↑ "Knowledge Plaza selected as a KMWorld Award 2010 finalist". Whatever Company. Retrieved 2010-12-01.
- ↑ Nouvelle, L'Usine (15 June 2010). "I-Expo et KM/Forum : la veille et la connaissance à l'heure des choix". Usinenouvelle.com/. UsineNouvelle. Retrieved 2010-06-15.
- ↑ "Le Prix Lionel Van den Bossche 2008 pour l'entrepreneuriat attribué à la start-up Whatever (Louvain-la-Neuve)". Fondation Roi Baudhuin. Archived from the original on 2012-09-04. Retrieved 2010-06-15.
- ↑ "Optimize tagging UI for people search". Thomas Vander Wal. Retrieved 2009-01-24.