Related Research Articles

The Intel 80186, also known as the iAPX 186, or just 186, is a microprocessor and microcontroller introduced in 1982. It was based on the Intel 8086 and, like it, had a 16-bit external data bus multiplexed with a 20-bit address bus.

A motherboard is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expandable systems. It holds and allows communication between many of the crucial electronic components of a system, such as the central processing unit (CPU) and memory, and provides connectors for other peripherals. Unlike a backplane, a motherboard usually contains significant sub-systems, such as the central processor, the chipset's input/output and memory controllers, interface connectors, and other components integrated for general use.

PowerPC is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) created by the 1991 Apple–IBM–Motorola alliance, known as AIM. PowerPC, as an evolving instruction set, has been named Power ISA since 2006, while the old name lives on as a trademark for some implementations of Power Architecture–based processors.

An embedded system is a computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including electrical or electronic hardware and mechanical parts. Because an embedded system typically controls physical operations of the machine that it is embedded within, it often has real-time computing constraints. Embedded systems control many devices in common use. In 2009, it was estimated that ninety-eight percent of all microprocessors manufactured were used in embedded systems.

A single-board computer (SBC) is a complete computer built on a single circuit board, with microprocessor(s), memory, input/output (I/O) and other features required of a functional computer. Single-board computers are commonly made as demonstration or development systems, for educational systems, or for use as embedded computer controllers. Many types of home computers or portable computers integrate all their functions onto a single printed circuit board.
Windows Embedded Compact, formerly Windows Embedded CE, Windows Powered and Windows CE, is a discontinued operating system developed by Microsoft for mobile and embedded devices. It was part of the Windows Embedded family and served as the foundation of several classes of devices including the Handheld PC, Pocket PC, Auto PC, Windows Mobile, Windows Phone 7 and others.
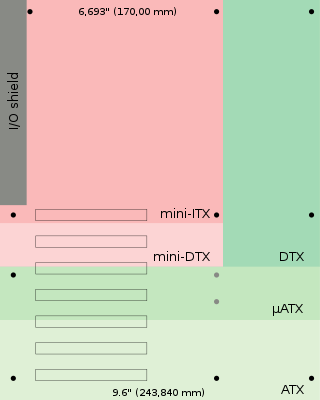
Mini-ITX is a 170 mm × 170 mm motherboard form factor developed by VIA Technologies in 2001. Mini-ITX motherboards have been traditionally used in small-configured computer systems. Originally, Mini-ITX was a niche standard designed for fanless cooling with a low power consumption architecture, which made them useful for home theater PC systems, where fan noise can detract from the cinema experience.
PowerPC G4 is a designation formerly used by Apple to describe a fourth generation of 32-bit PowerPC microprocessors. Apple has applied this name to various processor models from Freescale, a former part of Motorola. Motorola and Freescale's proper name of this family of processors is PowerPC 74xx.
PowerPC Reference Platform (PReP) was a standard system architecture for PowerPC-based computer systems developed at the same time as the PowerPC processor architecture. Published by IBM in 1994, it allowed hardware vendors to build a machine that could run various operating systems, including Windows NT, OS/2, Solaris, Taligent and AIX.

PC/104 is a family of embedded computer standards which define both form factors and computer buses by the PC/104 Consortium. Its name derives from the 104 pins on the interboard connector (ISA) in the original PC/104 specification and has been retained in subsequent revisions, despite changes to connectors. PC/104 is intended for specialized environments where a small, rugged computer system is required. The standard is modular, and allows consumers to stack together boards from a variety of COTS manufacturers to produce a customized embedded system.
Power.org was a global computer industry organization from 2004 to 2013, then succeeded by OpenPOWER Foundation, to develop and promote POWER Architecture technology by establishing its open standards, guidelines, best practices, and certifications.
In computing, the motherboard form factor is the specification of a motherboard – the dimensions, power supply type, location of mounting holes, number of ports on the back panel, etc. Specifically, in the IBM PC compatible industry, standard form factors ensure that parts are interchangeable across competing vendors and generations of technology, while in enterprise computing, form factors ensure that server modules fit into existing rackmount systems. Traditionally, the most significant specification is for that of the motherboard, which generally dictates the overall size of the case. Small form factors have been developed and implemented.

Motorola Single Board Computers is Motorola's production line of computer boards for embedded systems. There are three different lines : mvme68k, mvmeppc and mvme88k. The first version of the board appeared in 1988. Motorola still makes those boards and the last one is MVME3100.
Embedded Platform for Industrial Computing (EPIC) is a computer form factor, a standard for an industrial-quality single-board computer, in use from about 2004 through 2016.

Asus EeeBox PC is a nettop computer line from ASUSTeK Computer Incorporated, and a part of the Asus Eee product family. First released on August 11, 2008, the Asus EeeBox PC series is marketed as a small, light, inexpensive and energy-efficient counterpart to the Asus Eee PC netbook / subnotebook laptop series. Its motherboard employs Splashtop technology called Express Gate by Asus.
A decompiler is a computer program that translates an executable file to high-level source code. It does therefore the opposite of a typical compiler, which translates a high-level language to a low-level language. While disassemblers translate an executable into assembly language, decompilers go a step further and translate the code into a higher level language such as C or Java, requiring more sophisticated techniques. Decompilers are usually unable to perfectly reconstruct the original source code, thus will frequently produce obfuscated code. Nonetheless, they remain an important tool in the reverse engineering of computer software.

A mini PC is a small-sized, inexpensive, low-power, legacy-free desktop computer designed for basic tasks such as web browsing, accessing web-based applications, document processing, and audio/video playback.
Eurotech is a company dedicated to the research, development, production and marketing of miniature computers (NanoPCs) and high performance computers (HPCs).
WinSystems is an employee owned embedded systems manufacturer specializing in ruggedized, highly reliable industrial computer systems. The company was founded by Jerry Winfield in 1982 and is headquartered in Grand Prairie, Texas.
The PC/104 Consortium is a technology consortium that was established in February 1992 by 12 companies, all sharing a vision of adapting desktop computer technology for embedded applications. Based on the technologies of a IBM PC-based single-board computer developed by American company Ampro in 1987, the PC/104 Consortium has since had a positive effect on the embedded computer marketplace and now includes over 50 member companies. The PC/104 Consortium's technological philosophy is to support legacy technology while developing new solutions for the future. Longevity is a requirement for embedded systems and one of the hallmarks of PC/104 technology.