
Barge nowadays generally refers to a flat-bottomed inland waterway vessel which does not have its own means of mechanical propulsion. The first modern barges were pulled by tugs, but nowadays most are pushed by pusher boats, or other vessels. The term barge has a rich history, and therefore there are many other types of barges.

Sailing employs the wind—acting on sails, wingsails or kites—to propel a craft on the surface of the water, on ice (iceboat) or on land over a chosen course, which is often part of a larger plan of navigation.
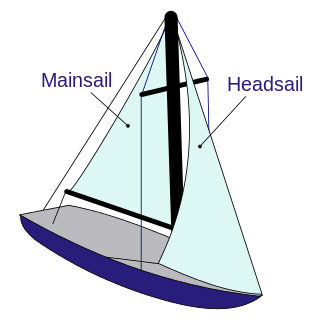
A sailboat or sailing boat is a boat propelled partly or entirely by sails and is smaller than a sailing ship. Distinctions in what constitutes a sailing boat and ship vary by region and maritime culture.

The Norfolk wherry is a type of boat used on The Broads in Norfolk and Suffolk, England. Three main types were developed over its life, all featuring the distinctive gaff rig with a single, high-peaked sail and the mast stepped well forward.

A yawl is a type of boat. The term has several meanings. It can apply to the rig, to the hull type or to the use which the vessel is put.

Dhow is the generic name of a number of traditional sailing vessels with one or more masts with settee or sometimes lateen sails, used in the Red Sea and Indian Ocean region. Typically sporting long thin hulls, dhows are trading vessels primarily used to carry heavy items, such as fruit, fresh water, or other heavy merchandise, along the coasts of Eastern Arabia, East Africa, Yemen and coastal South Asia. Larger dhows have crews of approximately thirty, smaller ones typically around twelve.

Dinghy sailing is the activity of sailing small boats by using five essential controls:

Empire of the Ants is a 1977 science fiction horror film co-scripted and directed by Bert I. Gordon. Based very loosely on the 1905 short story "Empire of the Ants" by H. G. Wells, the film involves a group of prospective land buyers led by a land developer, pitted against large mutated ants.

A smack was a traditional fishing boat used off the coast of Britain and the Atlantic coast of America for most of the 19th century and, in small numbers, up to the Second World War. Many larger smacks were originally cutter-rigged sailing boats until about 1865, when smacks had become so large that cutter main booms were unhandy. The smaller smacks retain the gaff cutter rig. The larger smacks were lengthened and re-rigged and new ketch-rigged smacks were built, but boats varied from port to port. Some boats had a topsail on the mizzen mast, while others had a bowsprit carrying a jib.
Written in the late 19th century by H. G. Wells and first published in The Butterfly, and collected in The Obliterated Man and Other Stories, "A Vision of Judgment" is a short story in 9 sections. It portrays a Last Judgment in which God and the archangel Gabriel laugh at sinners and saints alike, embarrassing them until they flee "up the sleeve of God." After every human soul has taken shelter there, all of humanity, "enlightened" and "in new clean bodies," is given a second chance. God shakes them—or rather us—"out of his sleeve upon the planet he had given us to live upon, the planet that whirled about green Sirius for a sun," saying "now that you understand me and each other a little better. . . . try again."

H. G. Wells was a prolific writer of both fiction and non-fiction. His writing career spanned more than sixty years, and his early science fiction novels earned him the title of "The Father of Science Fiction".
"Triumphs of a Taxidermist" is an 1894 short story by British writer H. G. Wells. The story was originally published anonymously in the March 3 and 15, 1894 issues of the Pall Mall Gazette and later published in the 1895 short story collection The Stolen Bacillus and Other Incidents.

The Way the World Is Going is a 1928 nonfiction book written by British author H. G. Wells.
Gordon Cochrane Home was an English landscape artist, writer, and illustrator.

The Memnon was the first clipper ship to arrive in San Francisco after the Gold Rush, and the only clipper to arrive in San Francisco before 1850. Built in 1848, she made record passages to San Francisco and to China, and sailed in the first clipper race around Cape Horn.

Forces on sails result from movement of air that interacts with sails and gives them motive power for sailing craft, including sailing ships, sailboats, windsurfers, ice boats, and sail-powered land vehicles. Similar principles in a rotating frame of reference apply to wind mill sails and wind turbine blades, which are also wind-driven. They are differentiated from forces on wings, and propeller blades, the actions of which are not adjusted to the wind. Kites also power certain sailing craft, but do not employ a mast to support the airfoil and are beyond the scope of this article.

Charles Ernest Nicholson was a British yacht designer.
"The Beautiful Suit" is a short story by H. G. Wells, originally published under the title "A Moonlight Fable" in the April 10, 1909, number of Collier's Weekly. Written in the manner of Hans Christian Andersen's fairy tales, the story features but two characters: an unnamed "little man", and his mother. The mother has made "a beautiful suit of clothes" for the man, who takes inordinate delight in this possession.

Joan and Peter, a 1918 novel by H. G. Wells, is at once a satirical portrait of late-Victorian and Edwardian England, a critique of the English educational system on the eve of World War I, a study of the impact of that war on English society, and a general reflection on the purposes of education. Wells regarded it as "one of the most ambitious" of his novels.

Insects have appeared in literature from classical times to the present day, an aspect of their role in culture more generally. Insects represent both positive qualities like cooperation and hard work, and negative ones like greed.
















