
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.

A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be transformed, by a connecting rod and crank, into rotational force for work. The term "steam engine" is most commonly applied to reciprocating engines as just described, although some authorities have also referred to the steam turbine and devices such as Hero's aeolipile as "steam engines". The essential feature of steam engines is that they are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separated from the combustion products. The ideal thermodynamic cycle used to analyze this process is called the Rankine cycle. In general usage, the term steam engine can refer to either complete steam plants, such as railway steam locomotives and portable engines, or may refer to the piston or turbine machinery alone, as in the beam engine and stationary steam engine.

An electric boat is a powered watercraft driven by electric motors, which are powered by either on-board battery packs, solar panels or generators.
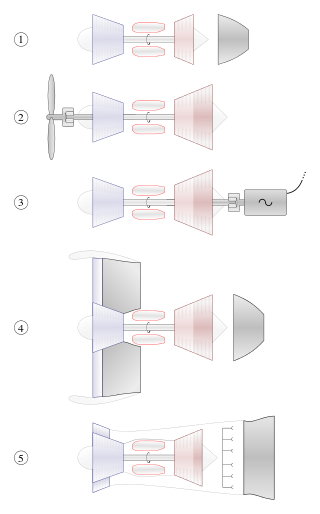
A gas turbine, gas turbine engine, or also known by its old name internal combustion turbine, is a type of continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part and are, in the direction of flow:

An icebreaker is a special-purpose ship or boat designed to move and navigate through ice-covered waters, and provide safe waterways for other boats and ships. Although the term usually refers to ice-breaking ships, it may also refer to smaller vessels, such as the icebreaking boats that were once used on the canals of the United Kingdom.

A diesel–electric transmission, or diesel–electric powertrain, is a transmission system for vehicles powered by diesel engines in road, rail, and marine transport. Diesel–electric transmission is based on petrol–electric transmission, a transmission system used for petrol engines.

An azimuth thruster is a configuration of marine propellers placed in pods that can be rotated to any horizontal angle (azimuth), making a rudder redundant. These give ships better maneuverability than a fixed propeller and rudder system.

Volvo Penta is a Swedish marine and industrial engine manufacturer, a joint stock company within the Volvo Group. Volvo Penta was founded as Penta in 1907 with the production of its first marine engine, the B1. The Penta company soon became an established internal combustion engine manufacturer, which in 1927 delivered the engine for Volvo's first passenger car.

Nuclear marine propulsion is propulsion of a ship or submarine with heat provided by a nuclear reactor. The power plant heats water to produce steam for a turbine used to turn the ship's propeller through a gearbox or through an electric generator and motor. Nuclear propulsion is used primarily within naval warships such as nuclear submarines and supercarriers. A small number of experimental civil nuclear ships have been built.

USS Makin Island (LHD-8), a Wasp-class amphibious assault ship, is the second ship of the United States Navy to be named for Makin Island, target of the Marine Raiders' Makin Island raid early on in the United States' involvement in World War II.

GTS Radiance of the Seas is a cruise ship owned and operated by Royal Caribbean International. She is the lead ship of the Radiance class, which includes Jewel of the Seas, Brilliance of the Seas and Serenade of the Seas. All of the Radiance-class ships have a gas turbine powertrain, which produces higher efficient speeds than other cruise ships, and emissions to the air are much lower than cruise ships powered by diesel engines.

A thermal power station is a type of power station in which heat energy is converted to electrical energy. In a steam-generating cycle heat is used to boil water in a large pressure vessel to produce high-pressure steam, which drives a steam turbine connected to an electrical generator. The low-pressure exhaust from the turbine enters a steam condenser where it is cooled to produce hot condensate which is recycled to the heating process to generate more high pressure steam. This is known as a Rankine cycle.

An engine officer or simply engineer, is a licensed mariner qualified and responsible for operating and maintaining the propulsion plants and support systems for a watercraft and its crew, passengers and cargo. Engineering officers are usually educated and qualified as engineering technicians.

Marine propulsion is the mechanism or system used to generate thrust to move a watercraft through water. While paddles and sails are still used on some smaller boats, most modern ships are propelled by mechanical systems consisting of an electric motor or internal combustion engine driving a propeller, or less frequently, in pump-jets, an impeller. Marine engineering is the discipline concerned with the engineering design process of marine propulsion systems.

Taymyr is a shallow-draft nuclear-powered icebreaker, and the first of two similar vessels. She was built in 1989 for the Soviet Union in Finland, at the Helsinki Shipyard by Wärtsilä Marine, by order of the Murmansk Shipping Company. Her sister ship is Vaygach.

TSS (RMS) Mona's Queen (III) No. 145308, was a ship built for the Isle of Man Steam Packet Company in 1934. The steamer, which was the third vessel in the company's history to bear the name, was one of five ships to be specially commissioned by the company between 1927 and 1937. They were replacements for the various second-hand steamers that had been purchased to replace the company's losses during the First World War. However, the life of the Mona's Queen proved to be short: six years after being launched she was sunk by a sea mine during the Dunkirk evacuation on 29 May 1940.

On a ship, the fire room, or FR or boiler room or stokehold, referred to the space, or spaces, of a vessel where water was brought to a boil. The steam was then transmitted to a separate engine room, often located immediately aft, where it was utilized to power the vessel. To increase the safety and damage survivability of a vessel, the machinery necessary for operations may be segregated into various spaces, the fire room was one of these spaces, and was among the largest physical compartment of the machinery space. On some ships, the space comprised more than one fire room, such as forward and aft, or port or starboard fire rooms, or may be simply numbered. Each room was connected to a flue, exhausting into a stack ventilating smoke.

An internal combustion engine is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high-pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some component of the engine. The force is typically applied to pistons, turbine blades, a rotor, or a nozzle. This force moves the component over a distance, transforming chemical energy into kinetic energy which is used to propel, move or power whatever the engine is attached to.

Steam-powered vessels include steamboats and steamships. Smaller steamboats were developed first. They were replaced by larger steamships which were often ocean-going. Steamships required a change in propulsion technology from sail to paddlewheel to screw to steam turbines. The latter innovation changed the design of vessels to one that could move faster through the water. Engine propulsion changed to steam turbine in the early 20th century. In the latter part of the 20th century, these, in turn, were replaced by gas turbines.

A turbine–electric transmission system includes a turboshaft gas turbine connected to an electrical generator, creating electricity that powers electric traction motors. No clutch is required.

























