
The Etruscan civilization was an ancient civilization created by the Etruscans, a people who inhabited Etruria in ancient Italy, with a common language and culture who formed a federation of city-states. After conquering adjacent lands, its territory covered, at its greatest extent, roughly what is now Tuscany, western Umbria, and northern Lazio, as well as what are now the Po Valley, Emilia-Romagna, south-eastern Lombardy, southern Veneto, and western Campania.

Adria is a town and comune in the province of Rovigo in the Veneto region of northern Italy, situated between the mouths of the rivers Adige and Po. The remains of the Etruscan city of Atria or Hatria are to be found below the modern city, three to four metres below the current level. Adria and Spina were the Etruscan ports and depots for Felsina. Adria may have given its name during an early period to the Adriatic Sea, to which it was connected by channels.

The Veneti were an Indo-European people who inhabited northeastern Italy, in an area corresponding to the modern-day region of Veneto, from the middle of the 2nd millennium BC and developing their own original civilization along the 1st millennium BC.
The Camunic language is an extinct language that was spoken in the 1st millennium BC in Val Camonica, a valley in the Central Alps. The language is sparsely attested to an extent that makes any classification attempt uncertain – even the discussion of whether it should be considered a pre–Indo-European or an Indo-European language has remained indecisive. Among several suggestions, it has been hypothesized that Camunic is related to the Raetic language from the Tyrsenian language family, or to the Celtic languages.

The Lepontii were an ancient Celtic people occupying portions of Rhaetia in the Alps during the late Bronze Age/Iron Age. Recent archeological excavations and their association with the Golasecca culture and Canegrate culture point to a Celtic affiliation. From the analysis of their language and the place names of the old Lepontic areas, it was hypothesized that these people represent a layer similar to that Celtic but previous to the Gallic penetration in the Po valley. The suggestion has been made that the Lepontii may have been celticized Ligurians.

Cisalpine Gaul was the name given, especially during the 4th and 3rd centuries BC, to a region of land inhabited by Celts (Gauls), corresponding to what is now most of northern Italy.

Venetic is an extinct Indo-European language, usually classified into the Italic subgroup, that was spoken by the Veneti people in ancient times in northeast Italy and part of modern Slovenia, between the Po Delta and the southern fringe of the Alps, associated with the Este culture.
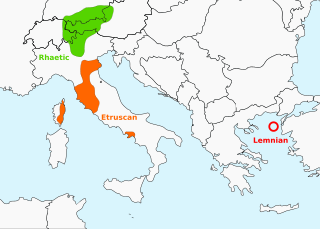
Rhaetic or Raetic, also known as Rhaetian, was a Tyrsenian language spoken in the ancient region of Rhaetia in the eastern Alps in pre-Roman and Roman times. It is documented by around 280 texts dated from the 5th up until the 1st century BC, which were found through northern Italy, southern Germany, eastern Switzerland, Slovenia and western Austria, in two variants of the Old Italic scripts. Rhaetic is largely accepted as being closely related to Etruscan.
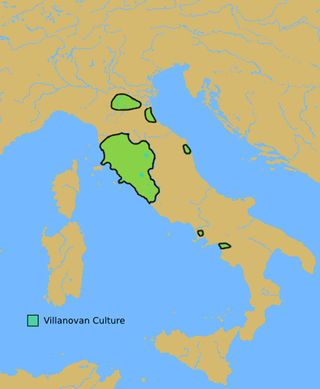
The Villanovan culture, regarded as the earliest phase of the Etruscan civilization, was the earliest Iron Age culture of Italy. It directly followed the Bronze Age Proto-Villanovan culture which branched off from the Urnfield culture of Central Europe. The name derives from the locality of Villanova, a fraction of the municipality of Castenaso in the Metropolitan City of Bologna where, between 1853 and 1855, Giovanni Gozzadini found the remains of a necropolis, bringing to light 193 tombs, of which there were 179 cremations and 14 inhumations.

The Italic peoples were an ethnolinguistic group identified by their use of Italic languages, a branch of the Indo-European language family.

Tyrsenian, named after the Tyrrhenians is a proposed extinct family of closely related ancient languages put forward by linguist Helmut Rix (1998), which consists of the Etruscan language of northern, central and south-western Italy, and eastern Corsica (France); the Raetic language of the Alps, named after the Rhaetian people; and the Lemnian language of the Aegean Sea. Camunic in northern Lombardy, between Etruscan and Raetic, may belong to the family as well, but evidence of such is limited. The Tyrsenian languages are generally considered Pre-Indo-European and Paleo-European.

Situla, from the Latin word for bucket or pail, is the term in archaeology and art history for a variety of elaborate bucket-shaped vessels from the Bronze Age to the Middle Ages, usually with a handle at the top. All types may be highly decorated, most characteristically with reliefs in bands or friezes running round the vessel.

The Golasecca culture was a Late Bronze Age/Early Iron Age culture in northern Italy, whose type-site was excavated at Golasecca in the province of Varese, Lombardy, where, in the area of Monsorino at the beginning of the 19th century, Abbot Giovanni Battista Giani made the first findings of about fifty graves with pottery and metal objects.

Etruscan history is the written record of Etruscan civilization compiled mainly by Greek and Roman authors. Apart from their inscriptions, from which information mainly of a sociological character can be extracted, we do not have any historical works written by the Etruscans themselves, nor is there any mention in the Roman authors that any was ever written. Remnants of Etruscan writings are almost exclusively concerned with religion.

The prehistory of Italy began in the Paleolithic period, when species of Homo inhabited the Italian territory for the first time, and ended in the Iron Age, when the first written records appeared in Italy.

In classical antiquity, several theses were elaborated on the origin of the Etruscans from the 5th century BC, when the Etruscan civilization had been already established for several centuries in its territories, that can be summarized into three main hypotheses. The first is the autochthonous development in situ out of the Villanovan culture, as claimed by the Greek historian Dionysius of Halicarnassus who described the Etruscans as indigenous people who had always lived in Etruria. The second is a migration from the Aegean sea, as claimed by two Greek historians: Herodotus, who described them as a group of immigrants from Lydia in Anatolia, and Hellanicus of Lesbos who claimed that the Tyrrhenians were the Pelasgians originally from Thessaly, Greece, who entered Italy at the head of the Adriatic sea in Northern Italy. The third hypothesis was reported by Livy and Pliny the Elder, and puts the Etruscans in the context of the Rhaetian people to the north and other populations living in the Alps.
The Proto-Villanovan culture was a late Bronze Age culture that appeared in Italy in the first half of the 12th century BC and lasted until the 10th century BC, part of the central European Urnfield culture system.

The Benvenuti Situla is a bronze situla that dates to c. 600 BC. It is a product of the situla art that spread north from the Etruscans in this period, in this case to the Este culture that flourished in Este, Veneto during the 7th century BC. The vessel is now conserved in the local National Museum Atestino. The relief work on the vessel depicts scenes of aristocratic life. These include banqueting as well as scenes of military victory. The iconography of the relief scenes of the situla may indicate Etruscan influence.
Carlo De Simone was an Italian linguist, specialising in Ancient Greek and Latin texts and Etruscan epigraphs. He is best known for his research into Etruscan, Lemnian and Rhaetian languages.

























