
The Geological Society of London, known commonly as the Geological Society, is a learned society based in the United Kingdom. It is the oldest national geological society in the world and the largest in Europe, with more than 12,000 Fellows.

Hydrocarbon exploration is the search by petroleum geologists and geophysicists for deposits of hydrocarbons, particularly petroleum and natural gas, in the Earth's crust using petroleum geology.
The American Association of Petroleum Geologists (AAPG) is one of the world's largest professional geological societies with about 17,000 members across 129 countries. The AAPG works to "advance the science of geology, especially as it relates to petroleum, natural gas, other subsurface fluids, and mineral resources; to promote the technology of exploring for, finding, and producing these materials in an economically and environmentally sound manner; and to advance the professional well-being of its members." The AAPG was founded in 1917 and is headquartered in Tulsa, Oklahoma; currently almost one-third of its members live outside the United States.

The Society of Exploration Geophysicists (SEG) is a learned society dedicated to promoting the science and education of exploration geophysics in particular and geophysics in general. The Society fosters the expert and ethical practice of geophysics in the exploration and development of natural resources, in characterizing the near-surface, and in mitigating earth hazards. As of November 2019, SEG has more than 14,000 members working in more than 114 countries. SEG was founded in 1930 in Houston, Texas but its business office has been headquartered in Tulsa, Oklahoma since the mid-1940s. While most SEG members are involved in exploration for petroleum, SEG members also are involved in application of geophysics methods to mineral exploration as well as environmental and engineering problems, archaeology, and other scientific endeavors. SEG publishes The Leading Edge (TLE), a monthly professional magazine, Geophysics, a peer-reviewed archival publication, and Interpretation, a peer-reviewed journal co-published by SEG and the American Association of Petroleum Geologists.
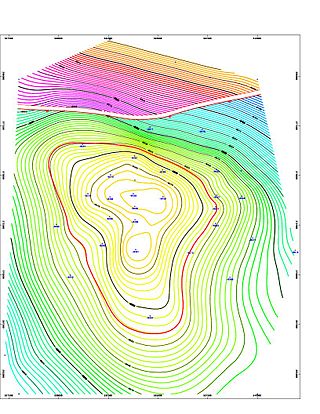
Geologic modelling,geological modelling or geomodelling is the applied science of creating computerized representations of portions of the Earth's crust based on geophysical and geological observations made on and below the Earth surface. A geomodel is the numerical equivalent of a three-dimensional geological map complemented by a description of physical quantities in the domain of interest. Geomodelling is related to the concept of Shared Earth Model; which is a multidisciplinary, interoperable and updatable knowledge base about the subsurface.

Magnetotellurics (MT) is an electromagnetic geophysical method for inferring the earth's subsurface electrical conductivity from measurements of natural geomagnetic and geoelectric field variation at the Earth's surface.
The United Nations General Assembly declared 2008 as the International Year of Planet Earth to increase awareness of the importance of Earth sciences for the advancement of sustainable development. UNESCO was designated as the lead agency. The Year's activities spanned the three years 2006–2009.
The Geological Association of Canada (GAC) is a learned society that promotes and develops the geological sciences in Canada. The organization holds conferences, meetings and exhibitions for the discussion of geological problems and the exchange of views in matters related to geology. It publishes various journals and collections of learned papers dealing with geology.

CGG SA (CGG) is a multinational geoscience technology services company that specializes on solving complex natural resource, environmental and infrastructure challenges.

The Environmental and Engineering Geophysical Society (EEGS) is an international, applied scientific organization that has 700 members. One of the society’s major activities is producing its annual meeting, the Application of Geophysics to Engineering and Environmental Problems (SAGEEP). It develops and distributes a peer-reviewed scientific journal, the Journal of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics (JEEG), as well as an electronic quarterly newsletter, FastTIMES. It publishes, markets, and distributes books and CD-ROMs on the application and use of near-surface geophysical technologies, both in print and electronically.

A geologist is a scientist who studies the solid, liquid, and gaseous matter that constitutes Earth and other terrestrial planets, as well as the processes that shape them. Geologists usually study geology, earth science, or geophysics, although backgrounds in physics, chemistry, biology, and other sciences are also useful. Field research is an important component of geology, although many subdisciplines incorporate laboratory and digitalized work. Geologists can be classified in a larger group of scientists, called geoscientists.
Michael Schoenberg (1939–2008) was an American theoretical geophysicist noted for his fundamental contributions to the understanding of anisotropy in the real earth and its application to the determination of texture, fracture porosity, and flow properties of reservoir rocks.
Infrasonic passive seismic spectroscopy (IPSS) is a passive seismic low frequency technique used for mapping potential oil and gas hydrocarbon accumulations.

Sergo OrdzhonikidzeRussian State University for Geological Prospecting, or the Russian State University for Geological Prospecting is named after Sergo Ordzhonikidze and previously known as the Moscow Geological Prospecting Institute, is a public university based in Moscow, Russia, specialising in geology, geophysics, gemmology, ecology and other earth-science disciplines.

Abel Idowu OlayinkaFAS is a Nigerian professor of applied geophysics. He is a former deputy vice chancellor and former vice chancellor of the University of Ibadan. He is also the president of the West African Research and Innovation Management Association.

The Chamber of Geophysical Engineers of Turkey (CGET) is a nonprofit organization found in 1986 and promotes the expert and ethical practice of geophysics in the exploration and development of natural resources, in characterizing the near-surface, and in mitigating earth hazards. While most CGET members are involved in engineering problems and groundwater explorations, CGET members also are involved in application of geophysics methods to mineral and petroleum explorations, archaeological researches, seismology and other scientific activities.
Sherilyn Williams-Stroud has been active in the field of geology for over three decades, where she has been recognized as one of the most important women in the field. In terms of representation in STEM. Throughout her career she has been paving the way for women, ethnic minorities, members of the LGBT community as well as other communities to nullify that underrepresentation. Williams-Stroud attended Oberlin College where she studied geology and graduated from in 1981, and she earned both her master's degree in geology (1984) and her PhD in structural geology (1988) from Johns Hopkins University. Although her work is dedicated to sedimentology, geophysics and geochemistry, she does have particular areas of expertise in fracture modelling, stress and strain analysis, rock fracture mechanics with applications to oil and gas production and exploration, geothermal energy, evaporite, geochemistry and other resources. Williams-Stroud created her own company Confractus, Inc. Williams-Stroud is an active member of several professional organizations as well as a leading activist of the Black Lives Matter movement.

Geological engineering is a discipline of engineering concerned with the application of geological science and engineering principles to fields, such as civil engineering, mining, environmental engineering, and forestry, among others. The work of geological engineers often directs or supports the work of other engineering disciplines such as assessing the suitability of locations for civil engineering, environmental engineering, mining operations, and oil and gas projects by conducting geological, geoenvironmental, geophysical, and geotechnical studies. They are involved with impact studies for facilities and operations that affect surface and subsurface environments. The engineering design input and other recommendations made by geological engineers on these projects will often have a large impact on construction and operations. Geological engineers plan, design, and implement geotechnical, geological, geophysical, hydrogeological, and environmental data acquisition. This ranges from manual ground-based methods to deep drilling, to geochemical sampling, to advanced geophysical techniques and satellite surveying. Geological engineers are also concerned with the analysis of past and future ground behaviour, mapping at all scales, and ground characterization programs for specific engineering requirements. These analyses lead geological engineers to make recommendations and prepare reports which could have major effects on the foundations of construction, mining, and civil engineering projects. Some examples of projects include rock excavation, building foundation consolidation, pressure grouting, hydraulic channel erosion control, slope and fill stabilization, landslide risk assessment, groundwater monitoring, and assessment and remediation of contamination. In addition, geological engineers are included on design teams that develop solutions to surface hazards, groundwater remediation, underground and surface excavation projects, and resource management. Like mining engineers, geological engineers also conduct resource exploration campaigns, mine evaluation and feasibility assessments, and contribute to the ongoing efficiency, sustainability, and safety of active mining projects
Bernard Ifeanyi Odoh is a Nigerian Politician and Professor of Applied Geophysics. He was the Secretary to the Ebonyi State Government from 2015 to 2018. He also was the gubernatorial nominee of the All Progressives Grand Alliance in Ebonyi State in 2023.












