Related Research Articles

Common Lisp (CL) is a dialect of the Lisp programming language, published in American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standard document ANSI INCITS 226-1994 (S20018). The Common Lisp HyperSpec, a hyperlinked HTML version, has been derived from the ANSI Common Lisp standard.

Lisp is a family of programming languages with a long history and a distinctive, fully parenthesized prefix notation. Originally specified in 1960, Lisp is the second-oldest high-level programming language still in common use, after Fortran. Lisp has changed since its early days, and many dialects have existed over its history. Today, the best-known general-purpose Lisp dialects are Common Lisp, Scheme, Racket, and Clojure.

A quine is a computer program which takes no input and produces a copy of its own source code as its only output. The standard terms for these programs in the computability theory and computer science literature are "self-replicating programs", "self-reproducing programs", and "self-copying programs".
Rebol is a cross-platform data exchange language and a multi-paradigm dynamic programming language designed by Carl Sassenrath for network communications and distributed computing. It introduces the concept of dialecting: small, optimized, domain-specific languages for code and data, which is also the most notable property of the language according to its designer Carl Sassenrath:
Although it can be used for programming, writing functions, and performing processes, its greatest strength is the ability to easily create domain-specific languages or dialects

Scheme is a dialect of the Lisp family of programming languages. Scheme was created during the 1970s at the MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory and released by its developers, Guy L. Steele and Gerald Jay Sussman, via a series of memos now known as the Lambda Papers. It was the first dialect of Lisp to choose lexical scope and the first to require implementations to perform tail-call optimization, giving stronger support for functional programming and associated techniques such as recursive algorithms. It was also one of the first programming languages to support first-class continuations. It had a significant influence on the effort that led to the development of Common Lisp.

Lua is a lightweight, high-level, multi-paradigm programming language designed primarily for embedded use in applications. Lua is cross-platform, since the interpreter of compiled bytecode is written in ANSI C, and Lua has a relatively simple C API to embed it into applications.
In computer programming, the scope of a name binding is the part of a program where the name binding is valid; that is, where the name can be used to refer to the entity. In other parts of the program, the name may refer to a different entity, or to nothing at all. Scope helps prevent name collisions by allowing the same name to refer to different objects – as long as the names have separate scopes. The scope of a name binding is also known as the visibility of an entity, particularly in older or more technical literature—this is from the perspective of the referenced entity, not the referencing name.
In programming languages, a closure, also lexical closure or function closure, is a technique for implementing lexically scoped name binding in a language with first-class functions. Operationally, a closure is a record storing a function together with an environment. The environment is a mapping associating each free variable of the function with the value or reference to which the name was bound when the closure was created. Unlike a plain function, a closure allows the function to access those captured variables through the closure's copies of their values or references, even when the function is invoked outside their scope.
In computer science, a dynamic programming language is a class of high-level programming languages, which at runtime execute many common programming behaviours that static programming languages perform during compilation. These behaviors could include an extension of the program, by adding new code, by extending objects and definitions, or by modifying the type system. Although similar behaviors can be emulated in nearly any language, with varying degrees of difficulty, complexity and performance costs, dynamic languages provide direct tools to make use of them. Many of these features were first implemented as native features in the Lisp programming language.
In computer science, reflective programming or reflection is the ability of a process to examine, introspect, and modify its own structure and behavior.
Metaprogramming is a programming technique in which computer programs have the ability to treat other programs as their data. It means that a program can be designed to read, generate, analyze or transform other programs, and even modify itself while running. In some cases, this allows programmers to minimize the number of lines of code to express a solution, in turn reducing development time. It also allows programs a greater flexibility to efficiently handle new situations without recompilation.
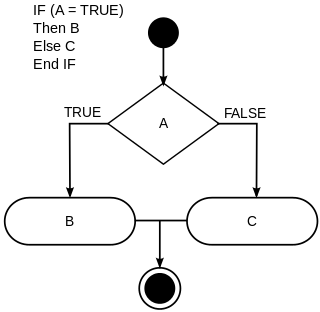
In computer science, conditionals are programming language commands for handling decisions. Specifically, conditionals perform different computations or actions depending on whether a programmer-defined Boolean condition evaluates to true or false. In terms of control flow, the decision is always achieved by selectively altering the control flow based on some condition . Although dynamic dispatch is not usually classified as a conditional construct, it is another way to select between alternatives at runtime. Conditional statements are the checkpoints in the programe that determines behaviour according to situation.
In computer programming, an entry point is the place in a program where the execution of a program begins, and where the program has access to command line arguments.
A read–eval–print loop (REPL), also termed an interactive toplevel or language shell, is a simple interactive computer programming environment that takes single user inputs, executes them, and returns the result to the user; a program written in a REPL environment is executed piecewise. The term usually refers to programming interfaces similar to the classic Lisp machine interactive environment. Common examples include command-line shells and similar environments for programming languages, and the technique is very characteristic of scripting languages.
In computer programming, homoiconicity is a property of some programming languages. A language is homoiconic if a program written in it can be manipulated as data using the language, and thus the program's internal representation can be inferred just by reading the program itself. This property is often summarized by saying that the language treats code as data.

The syntax of the Python programming language is the set of rules that defines how a Python program will be written and interpreted. The Python language has many similarities to Perl, C, and Java. However, there are some definite differences between the languages. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including structured, object-oriented programming, and functional programming, and boasts a dynamic type system and automatic memory management.
In computer programming, an anonymous function is a function definition that is not bound to an identifier. Anonymous functions are often arguments being passed to higher-order functions or used for constructing the result of a higher-order function that needs to return a function. If the function is only used once, or a limited number of times, an anonymous function may be syntactically lighter than using a named function. Anonymous functions are ubiquitous in functional programming languages and other languages with first-class functions, where they fulfil the same role for the function type as literals do for other data types.
This comparison of programming languages compares the features of language syntax (format) for over 50 computer programming languages.
A scripting language or script language is a programming language that is used to manipulate, customize, and automate the facilities of an existing system. Scripting languages are usually interpreted at runtime rather than compiled.
Nemerle is a general-purpose, high-level, statically typed programming language designed for platforms using the Common Language Infrastructure (.NET/Mono). It offers functional, object-oriented, aspect-oriented, reflective and imperative features. It has a simple C#-like syntax and a powerful metaprogramming system.
References
- ↑ "Flash 8 LiveDocs". 2006-10-10. Archived from the original on 2006-10-10.
- ↑ ActionScript 3 Eval Library
- ↑ "The D.eval API". Archived from the original on 2013-03-14.
- ↑ John McCarthy, "History of Lisp - The Implementation of Lisp"
- ↑ "PHP: eval - Manual". PHP.net. Retrieved 2015-09-10.
- ↑ "Volume 1 Commands and Utilities". UNIX Programmer's Manual (PDF). AT&T. 1986. p. 41.
- ↑ Allen-Babcock. "Draft EVAL Microprogram" (PDF). Bitsavers.org. Retrieved Jan 17, 2016.
- ↑ Rochester, Nathaniel. "Conversational Programming System Progress Report" (PDF). Bitsavers.org. Retrieved Jan 17, 2016.
- ↑ The Metacircular Evaluator (SICP Section 4.1)