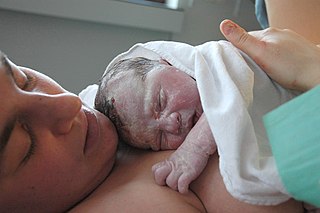
Childbirth, also known as labour, parturition and delivery, is the completion of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million human births globally. In the developed countries, most deliveries occur in hospitals, while in the developing countries most are home births.

Postpartum depression (PPD), also called postnatal depression, is a type of mood disorder experienced after childbirth, which can affect both sexes. Symptoms may include extreme sadness, low energy, anxiety, crying episodes, irritability, and changes in sleeping or eating patterns. PPD can also negatively affect the newborn child.

The postpartum period begins after childbirth and is typically considered to last for six weeks. However, there are three distinct but continuous phases of the postnatal period; the acute phase, lasting for six to twelve hours after birth; the subacute phase, lasting six weeks; and the delayed phase, lasting up to six months. During the delayed phase, some changes to the genitourinary system take much longer to resolve and may result in conditions such as urinary incontinence. The World Health Organization (WHO) describes the postnatal period as the most critical and yet the most neglected phase in the lives of mothers and babies; most maternal and newborn deaths occur during this period.

Placenta praevia is when the placenta attaches inside the uterus but in a position near or over the cervical opening. Symptoms include vaginal bleeding in the second half of pregnancy. The bleeding is bright red and tends not to be associated with pain. Complications may include placenta accreta, dangerously low blood pressure, or bleeding after delivery. Complications for the baby may include fetal growth restriction.

Low birth weight (LBW) is defined by the World Health Organization as a birth weight of an infant of 2,499 g or less, regardless of gestational age. Infants born with LBW have added health risks which require close management, often in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). They are also at increased risk for long-term health conditions which require follow-up over time.

Complications of pregnancy are health problems that are related to, or arise during pregnancy. Complications that occur primarily during childbirth are termed obstetric labor complications, and problems that occur primarily after childbirth are termed puerperal disorders. While some complications improve or are fully resolved after pregnancy, some may lead to lasting effects, morbidity, or in the most severe cases, maternal or fetal mortality.
Postpartum blues, also known as baby blues and maternity blues, is a very common but self-limited condition that begins shortly after childbirth and can present with a variety of symptoms such as mood swings, irritability, and tearfulness. Mothers may experience negative mood symptoms mixed with intense periods of joy. Up to 85% of new mothers are affected by postpartum blues, with symptoms starting within a few days after childbirth and lasting up to two weeks in duration. Treatment is supportive, including ensuring adequate sleep and emotional support. If symptoms are severe enough to affect daily functioning or last longer than two weeks, the individual should be evaluated for related postpartum psychiatric conditions, such as postpartum depression and postpartum anxiety. It is unclear whether the condition can be prevented, however education and reassurance are important to help alleviate patient distress.
Maternal health is the health of women during pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period. In most cases, maternal health encompasses the health care dimensions of family planning, preconception, prenatal, and postnatal care in order to ensure a positive and fulfilling experience. In other cases, maternal health can reduce maternal morbidity and mortality. Maternal health revolves around the health and wellness of pregnant women, particularly when they are pregnant, at the time they give birth, and during child-raising. WHO has indicated that even though motherhood has been considered as a fulfilling natural experience that is emotional to the mother, a high percentage of women develop health problems and sometimes even die. Because of this, there is a need to invest in the health of women. The investment can be achieved in different ways, among the main ones being subsidizing the healthcare cost, education on maternal health, encouraging effective family planning, and ensuring progressive check up on the health of women with children. Maternal morbidity and mortality particularly affects women of color and women living in low and lower-middle income countries.
Postpartum thyroiditis refers to thyroid dysfunction occurring in the first 12 months after pregnancy and may involve hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism or the two sequentially. According to the National Institute of Health, postpartum thyroiditis affects about 8% of pregnancies. There are, however, different rates reported globally. This is likely due to the differing amounts of average postpartum follow times around the world, and due to humans' own innate differences. For example, in Bangkok, Thailand the rate is 1.1%, but in Brazil it is 13.3%. The first phase is typically hyperthyroidism. Then, the thyroid either returns to normal or a woman develops hypothyroidism. Of those women who experience hypothyroidism associated with postpartum thyroiditis, one in five will develop permanent hypothyroidism requiring lifelong treatment.

Postpartum psychosis(PPP), also known as puerperal psychosis or peripartum psychosis, involves the abrupt onset of psychotic symptoms shortly following childbirth, typically within two weeks of delivery but less than 4 weeks postpartum. PPP is a condition currently represented under "Brief Psychotic Disorder" in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Volume V (DSM-V). Symptoms may include delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech (e.g, incoherent speech), and/or abnormal motor behavior (e.g., catatonia). Other symptoms frequently associated with PPP include confusion, disorganized thought, severe difficulty sleeping, variations of mood disorders (including depression, agitation, mania, or a combination of the above), as well as cognitive features such as consciousness that comes and goes (waxing and waning) or disorientation.
A postpartum disorder or puerperal disorder is a disease or condition which presents primarily during the days and weeks after childbirth called the postpartum period. The postpartum period can be divided into three distinct stages: the initial or acute phase, 6–12 hours after childbirth; subacute postpartum period, which lasts two to six weeks, and the delayed postpartum period, which can last up to six months. In the subacute postpartum period, 87% to 94% of women report at least one health problem. Long term health problems are reported by 31% of women.
Early postnatal hospital discharge generally refers to the postpartum hospital discharge of the mother and newborn within 48 hours. The duration of what is considered "early discharge" varies between countries from 12 to 72 hours due to the differences in average duration of hospital stay. The World Health Organisation (WHO) recommends healthy mothers and newborns following an uncomplicated vaginal delivery at a health facility to stay and receive care at the facility for at least 24 hours after delivery. This recommendation is based on findings which suggest that the first 24 hours after giving birth poses the greatest risks for both the mother and newborn.
Sex after pregnancy is often delayed for several weeks or months, and may be difficult and painful for women. Painful intercourse is the most common sexual activity-related complication after childbirth. Since there are no guidelines on resuming sexual intercourse after childbirth, the postpartum patients are generally advised to resume sex when they feel comfortable to do so. Injury to the perineum or surgical cuts (episiotomy) to the vagina during childbirth can cause sexual dysfunction. Sexual activity in the postpartum period other than sexual intercourse is possible sooner, but some women experience a prolonged loss of sexual desire after giving birth, which may be associated with postnatal depression. Common issues that may last more than a year after birth are greater desire by the man than the woman, and a worsening of the woman's body image.
Thyroid disease in pregnancy can affect the health of the mother as well as the child before and after delivery. Thyroid disorders are prevalent in women of child-bearing age and for this reason commonly present as a pre-existing disease in pregnancy, or after childbirth. Uncorrected thyroid dysfunction in pregnancy has adverse effects on fetal and maternal well-being. The deleterious effects of thyroid dysfunction can also extend beyond pregnancy and delivery to affect neurointellectual development in the early life of the child. Due to an increase in thyroxine binding globulin, an increase in placental type 3 deioidinase and the placental transfer of maternal thyroxine to the fetus, the demand for thyroid hormones is increased during pregnancy. The necessary increase in thyroid hormone production is facilitated by high human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) concentrations, which bind the TSH receptor and stimulate the maternal thyroid to increase maternal thyroid hormone concentrations by roughly 50%. If the necessary increase in thyroid function cannot be met, this may cause a previously unnoticed (mild) thyroid disorder to worsen and become evident as gestational thyroid disease. Currently, there is not enough evidence to suggest that screening for thyroid dysfunction is beneficial, especially since treatment thyroid hormone supplementation may come with a risk of overtreatment. After women give birth, about 5% develop postpartum thyroiditis which can occur up to nine months afterwards. This is characterized by a short period of hyperthyroidism followed by a period of hypothyroidism; 20–40% remain permanently hypothyroid.
Childbirth-related post-traumatic stress disorder is a psychological disorder that can develop in women who have recently given birth. This disorder can also affect men or partners who have observed a difficult birth. Its symptoms are not distinct from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It may also be called post-traumatic stress disorder following childbirth (PTSD-FC)
Antenatal depression, also known as prenatal or perinatal depression, is a form of clinical depression that can affect a woman during pregnancy, and can be a precursor to postpartum depression if not properly treated. It is estimated that 7% to 20% of pregnant women are affected by this condition. Any form of prenatal stress felt by the mother can have negative effects on various aspects of fetal development, which can cause harm to the mother and child. Even after birth, a child born from a depressed or stressed mother feels the affects. The child is less active and can also experience emotional distress. Antenatal depression can be caused by the stress and worry that pregnancy can bring, but at a more severe level. Other triggers include unplanned pregnancy, difficulty becoming pregnant, history of abuse, and economic or family situations.
A pre-existing disease in pregnancy is a disease that is not directly caused by the pregnancy, in contrast to various complications of pregnancy, but which may become worse or be a potential risk to the pregnancy. A major component of this risk can result from necessary use of drugs in pregnancy to manage the disease.
Women's reproductive health in the United States refers to the set of physical, mental, and social issues related to the health of women in the United States. It includes the rights of women in the United States to adequate sexual health, available contraception methods, and treatment for sexually transmitted diseases. The prevalence of women's health issues in American culture is inspired by second-wave feminism in the United States. As a result of this movement, women of the United States began to question the largely male-dominated health care system and demanded a right to information on issues regarding their physiology and anatomy. The U.S. government has made significant strides to propose solutions, like creating the Women's Health Initiative through the Office of Research on Women's Health in 1991. However, many issues still exist related to the accessibility of reproductive healthcare as well as the stigma and controversy attached to sexual health, contraception, and sexually transmitted diseases.
Mental disorders can be a consequence of miscarriage or early pregnancy loss. Even though women can develop long-term psychiatric symptoms after a miscarriage, acknowledging the potential of mental illness is not usually considered. A mental illness can develop in women who have experienced one or more miscarriages after the event or even years later. Some data suggest that men and women can be affected up to 15 years after the loss. Though recognized as a public health problem, studies investigating the mental health status of women following miscarriage are still lacking. Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can develop in women who have experienced a miscarriage. Risks for developing PTSD after miscarriage include emotional pain, expressions of emotion, and low levels of social support. Even if relatively low levels of stress occur after the miscarriage, symptoms of PTSD including flashbacks, intrusive thoughts, dissociation and hyperarousal can later develop. Clinical depression also is associated with miscarriage. Past responses by clinicians have been to prescribe sedatives.
Maternal health outcomes differ significantly between racial groups within the United States. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists describes these disparities in obstetric outcomes as "prevalent and persistent." Black, indigenous, and people of color are disproportionately affected by many of the maternal health outcomes listed as national objectives in the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services's national health objectives program, Healthy People 2030. The American Public Health Association considers maternal mortality to be a human rights issue, also noting the disparate rates of Black maternal death. Race affects maternal health throughout the pregnancy continuum, beginning prior to conception and continuing through pregnancy (antepartum), during labor and childbirth (intrapartum), and after birth (postpartum).






