
Cryptozoology is a pseudoscience and subculture that searches for and studies unknown, legendary, or extinct animals whose present existence is disputed or unsubstantiated, particularly those popular in folklore, such as Bigfoot, the Loch Ness Monster, Yeti, the chupacabra, the Jersey Devil, or the Mokele-mbembe. Cryptozoologists refer to these entities as cryptids, a term coined by the subculture. Because it does not follow the scientific method, cryptozoology is considered a pseudoscience by mainstream science: it is neither a branch of zoology nor of folklore studies. It was originally founded in the 1950s by zoologists Bernard Heuvelmans and Ivan T. Sanderson.

The mokele-mbembe, Lingala for "one who stops the flow of rivers", is a mythical water-dwelling entity that supposedly lives in the Congo River Basin, sometimes described as a living creature, sometimes as a spirit. Descriptions vary widely among those who claim to have seen the creature, but it is often described as a large quadrupedal herbivore with smooth skin, a long neck and a single tooth or horn.

A squid is a mollusc with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fitting these criteria. Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, bilateral symmetry, and a mantle. They are mainly soft-bodied, like octopuses, but have a small internal skeleton in the form of a rod-like gladius or pen, made of chitin.
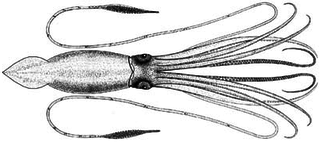
The giant squid is a species of deep-ocean dwelling squid in the family Architeuthidae. It can grow to a tremendous size, offering an example of abyssal gigantism: recent estimates put the maximum size at around 12–13 m (39–43 ft) for females and 10 m (33 ft) for males, from the posterior fins to the tip of the two long tentacles. The mantle of the giant squid is about 2 m long, and the length of the squid excluding its tentacles rarely exceeds 5 m (16 ft). Claims of specimens measuring 20 m (66 ft) or more have not been scientifically documented.

Willy Otto Oskar Ley was a German and American science writer and proponent of cryptozoology. The crater Ley on the far side of the Moon is named in his honor.

Bernard Heuvelmans was a Belgian-French scientist, explorer, researcher, and writer probably best known, along with Scottish-American biologist Ivan T. Sanderson, as a founding figure in the pseudoscience and subculture of cryptozoology. His 1958 book On the Track of Unknown Animals is often regarded as one of the most influential cryptozoology texts.
Karl Shuker is a British zoologist, cryptozoologist and author. He lives in the Midlands, England, where he works as a zoological consultant and writer. A columnist in Fortean Times and contributor to various magazines, Shuker is also the editor-in-chief of the Journal of Cryptozoology, which began in November 2012.
"Man in Space" is an episode of the American television series Disneyland which originally aired on March 9, 1955. It was directed by Disney animator Ward Kimball. This Disneyland episode, was narrated partly by Kimball and also by such scientists Willy Ley, Heinz Haber, and Wernher von Braun, as well as Dick Tufeld of Lost in Space fame.

The giant squid's elusive nature and fearsome appearance have long made it a popular subject of legends and folk tales. Its popularity as an image continues today with references and depictions in literature, film, television, and video games.

A zoophyte (animal-plant) is an obsolete term for an organism thought to be intermediate between animals and plants, or an animal with plant-like attributes or appearance. In the 19th century they were reclassified as Radiata which included various taxa, a term superseded by Coelenterata referring more narrowly to the animal phyla Cnidaria, sponges, and Ctenophora.

On the Track of Unknown Animals is a cryptozoological book by the Belgian-French zoologist Bernard Heuvelmans that was first published in 1955 under the title Sur la Piste des Bêtes Ignorées. The English translation by Richard Garnett was published in 1958 with some updating by the author and with a foreword by Gerald Durrell. A revised and abridged edition was published in 1965, and a further edition in 1995. It is credited with introducing the term cryptozoology and established its author as the "Father of Cryptozoology."

Cephalopods, which include squids and octopuses, vary enormously in size. The smallest are only about 1 centimetre (0.39 in) long and weigh less than 1 gram (0.035 oz) at maturity, while the giant squid can exceed 10 metres (33 ft) in length and the colossal squid weighs close to half a tonne (1,100 lb), making them the largest living invertebrates. Living species range in mass more than three-billion-fold, or across nine orders of magnitude, from the lightest hatchlings to the heaviest adults. Certain cephalopod species are also noted for having individual body parts of exceptional size.
Heather Hazel Angel MSc is a British nature photographer, author and television presenter.

All cephalopods possess flexible limbs extending from their heads and surrounding their beaks. These appendages, which function as muscular hydrostats, have been variously termed arms, legs or tentacles.

The kraken is a legendary sea monster of enormous size, etymologically akin to a squid or octopus, said to appear in the sea between Norway and Iceland. It is believed the legend of the Kraken may have originated from sightings of giant squid, which may grow to 12–15 m in length.

The Search for the Giant Squid is a non-fiction book by Richard Ellis on the biology, history and mythology of the giant squid of the genus Architeuthis. It was well received upon its release in 1998. Though soon rendered outdated by important developments in giant squid research, it is still considered an important reference on the subject.













