
The 6800 is an 8-bit microprocessor designed and first manufactured by Motorola in 1974. The MC6800 microprocessor was part of the M6800 Microcomputer System that also included serial and parallel interface ICs, RAM, ROM and other support chips. A significant design feature was that the M6800 family of ICs required only a single five-volt power supply at a time when most other microprocessors required three voltages. The M6800 Microcomputer System was announced in March 1974 and was in full production by the end of that year.

The Motorola 6809 ("sixty-eight-oh-nine") is an 8-bit microprocessor with some 16-bit features. It was designed by Motorola's Terry Ritter and Joel Boney and introduced in 1978. Although source compatible with the earlier Motorola 6800, the 6809 offered significant improvements over it and 8-bit contemporaries like the MOS Technology 6502, including a hardware multiplication instruction, 16-bit arithmetic, system and user stack registers allowing re-entrant code, improved interrupts, position-independent code and an orthogonal instruction set architecture with a comprehensive set of addressing modes.

The RadioShack TRS-80 Color Computer, later marketed as the Tandy Color Computer and sometimes nicknamed the CoCo, is a line of home computers developed and sold by Tandy Corporation. Despite sharing a name with the earlier TRS-80, the Color Computer is a completely different, incompatible system and a radical departure in design and compatibility with its Motorola 6809E processor rather than the Zilog Z80 earlier models were built around.
OS-9 is a family of real-time, process-based, multitasking, multi-user operating systems, developed in the 1980s, originally by Microware Systems Corporation for the Motorola 6809 microprocessor. It was purchased by Radisys Corp in 2001, and was purchased again in 2013 by its current owner Microware LP.
Microware Systems Corporation was an American software company based in Clive, Iowa, that produced the OS-9 real-time operating system.
File Allocation Table (FAT) is a file system developed for personal computers and was the default filesystem for MS-DOS and Windows 9x operating systems. Originally developed in 1977 for use on floppy disks, it was adapted for use on hard disks and other devices. The increase in disk drives capacity required three major variants: FAT12, FAT16 and FAT32. FAT was replaced with NTFS as the default file system on Microsoft operating systems starting with Windows XP. Nevertheless, FAT continues to be used on flash and other solid-state memory cards and modules, many portable and embedded devices because of its compatibility and ease of implementation.
Microsoft BASIC is the foundation software product of the Microsoft company and evolved into a line of BASIC interpreters and compiler(s) adapted for many different microcomputers. It first appeared in 1975 as Altair BASIC, which was the first version of BASIC published by Microsoft as well as the first high-level programming language available for the Altair 8800 microcomputer.
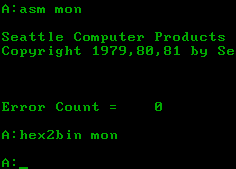
86-DOS is a discontinued operating system developed and marketed by Seattle Computer Products (SCP) for its Intel 8086-based computer kit.

Southwest Technical Products Corporation, or SWTPC, was an American producer of electronic kits, and later complete computer systems. It was incorporated in 1967 in San Antonio, Texas, succeeding the Daniel E. Meyer Company. In 1990, SWTPC became Point Systems, before ceasing a few years later.
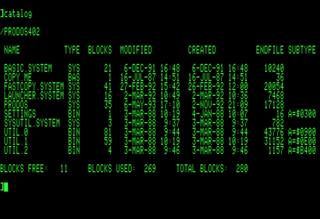
ProDOS is the name of two similar operating systems for the Apple II series of personal computers. The original ProDOS, renamed ProDOS 8 in version 1.2, is the last official operating system usable by all 8-bit Apple II series computers, and was distributed from 1983 to 1993. The other, ProDOS 16, was a stop-gap solution for the 16-bit Apple IIGS that was replaced by GS/OS within two years.

TRSDOS is the operating system for the Tandy TRS-80 line of eight-bit Zilog Z80 microcomputers that were sold through Radio Shack from 1977 through 1991. Tandy's manuals recommended that it be pronounced triss-doss. TRSDOS should not be confused with Tandy DOS, a version of MS-DOS licensed from Microsoft for Tandy's x86 line of personal computers (PCs).

The Rainbow 100 is a microcomputer introduced by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) in 1982. This desktop unit had a monitor similar to the VT220 and a dual-CPU box with both 4 MHz Zilog Z80 and 4.81 MHz Intel 8088 CPUs. The Rainbow 100 was a triple-use machine: VT100 mode, 8-bit CP/M mode, and CP/M-86 or MS-DOS mode using the 8088. It ultimately failed to in the marketplace which became dominated by the simpler IBM PC and its clones which established the industry standard as compatibility with CP/M became less important than IBM PC compatibility. Writer David Ahl called it a disastrous foray into the personal computer market. The Rainbow was launched along with the similarly packaged DEC Professional and DECmate II which were also not successful. The failure of DEC to gain a significant foothold in the high-volume PC market would be the beginning of the end of the computer hardware industry in New England, as nearly all computer companies located there were focused on minicomputers for large organizations, from DEC to Data General, Wang, Prime, Computervision, Honeywell, and Symbolics Inc.
UniFLEX is a Unix-like operating system developed by Technical Systems Consultants (TSC) for the Motorola 6809 family which allowed multitasking and multiprocessing.
AmigaOS is the proprietary native operating system of the Amiga personal computer. Since its introduction with the launch of the Amiga 1000 in 1985, there have been four major versions and several minor revisions of the operating system.
MSX-DOS is a discontinued disk operating system developed by Microsoft for the 8-bit home computer standard MSX, and is a cross between MS-DOS v1.25 and CP/M-80 v2.2.

DOS is a family of disk-based operating systems for IBM PC compatible computers. The DOS family primarily consists of IBM PC DOS and a rebranded version, Microsoft's MS-DOS, both of which were introduced in 1981. Later compatible systems from other manufacturers include DR-DOS (1988), ROM-DOS (1989), PTS-DOS (1993), and FreeDOS (1998). MS-DOS dominated the IBM PC compatible market between 1981 and 1995.

The floppy disk is a data storage and transfer medium that was ubiquitous from the mid-1970s well into the 2000s. Besides the 3½-inch and 5¼-inch formats used in IBM PC compatible systems, or the 8-inch format that preceded them, many proprietary floppy disk formats were developed, either using a different disk design or special layout and encoding methods for the data held on the disk.
The IBM Personal Computer Basic, commonly shortened to IBM BASIC, is a programming language first released by IBM with the IBM Personal Computer, Model 5150 in 1981. IBM released four different versions of the Microsoft BASIC interpreter, licensed from Microsoft for the PC and PCjr. They are known as Cassette BASIC, Disk BASIC, Advanced BASIC (BASICA), and Cartridge BASIC. Versions of Disk BASIC and Advanced BASIC were included with IBM PC DOS up to PC DOS 4. In addition to the features of an ANSI standard BASIC, the IBM versions offered support for the graphics and sound hardware of the IBM PC line. Source code could be typed in with a full-screen editor, and very limited facilities were provided for rudimentary program debugging. IBM also released a version of the Microsoft BASIC compiler for the PC, concurrently with the release of PC DOS 1.10 in 1982.
Smoke Signal Broadcasting, Inc. (SSB), later known as Smoke Signal, was an American computer company founded in 1976 by Frederic Jerome "Ric" Hammond of Hollywood, California. The company earned its reputation by offering expansions for the Southwest Technical Products (SWTPC) 6800 microcomputer. It later manufactured its own line of computers, called the Chieftain. Though it remains little-known, Smoke Signal was an early and important manufacturer of multi-user computer systems.










