
Area 51 is the common name of a highly classified United States Air Force (USAF) facility within the Nevada Test and Training Range. A remote detachment administered by Edwards Air Force Base, the facility is officially called Homey Airport (XTA/KXTA) or Groom Lake. Details of its operations are not made public, but the USAF says that it is an open training range, and it is commonly thought to support the development and testing of experimental aircraft and weapons systems. The USAF and CIA acquired the site in 1955, primarily for flight testing the Lockheed U-2 aircraft.

Nellis Air Force Base is a United States Air Force installation in southern Nevada. Nellis hosts air combat exercises such as Exercise Red Flag and close air support exercises such as Green Flag-West flown in "Military Operations Area (MOA) airspace", associated with the nearby Nevada Test and Training Range (NTTR). The base also has the Combined Air and Space Operations Center-Nellis.

The Tonopah Test Range is a highly classified, restricted military installation of the United States Department of Defense, and United States Department of Energy located about 30 miles (48 km) southeast of Tonopah, Nevada. It is part of the northern fringe of the Nellis Range, measuring 625 sq mi (1,620 km2). Tonopah Test Range is located about 70 miles (110 km) northwest of Groom Lake, the home of the Area 51 facility.

Carson Sink is a playa in the northeastern portion of the Carson Desert in present-day Nevada, United States of America, that was formerly the terminus of the Carson River. Today the sink is fed by drainage canals of the Truckee-Carson Irrigation District. The southeastern fringe of the sink, where the canals enter, is a wetland of the Central Basin and Range ecoregion.

Naval Air Station Fallon or NAS Fallon is the United States Navy's premier air-to-air and air-to-ground training facility. It is located southeast of the city of Fallon, east of Reno in western Nevada. Since 1996, it has been home to the U.S. Navy-Fighter Weapons School (TOPGUN) taking over from the former NAS Miramar, California, and the surrounding area contains 240,000 acres (97,000 ha) of bombing and electronic warfare ranges. It is also home to the Naval Aviation Warfighting Development Center (NAWDC), which includes TOPGUN, the Carrier Airborne Early Warning Weapons School (CAEWWS) and the Navy Rotary Wing Weapons School. Navy SEAL Combat Search and Rescue (CSAR) training also takes place there.

The Naval Aviation Warfighting Development Center was formerly known as the Naval Strike and Air Warfare Center at Naval Air Station Fallon located in the city of Fallon in western Nevada. It is the center of excellence for naval aviation training and tactics development. NAWDC provides service to aircrews, squadrons and air wings throughout the United States Navy through flight training, academic instructional classes, and direct operational and intelligence support. The name was changed from NSAWC to NAWDC to align with the naming convention of the Navy's other Warfighting Development Centers (including Naval Surface and Mine Warfighting Development Center, Naval Information Warfighting Development Center, and the Undersea Warfighting Development Center.
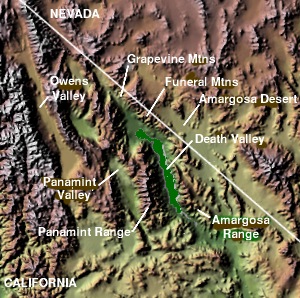
The Panamint Valley is a long basin located east of the Argus and Slate ranges, and west of the Panamint Range in the northeastern reach of the Mojave Desert, in eastern California, United States.

Tonopah Test Range Airport, at the Tonopah Test Range is 27 NM southeast of Tonopah, Nevada and 140 mi (230 km) northwest of Las Vegas, Nevada. It is a major airfield with a 12,000 ft × 150 ft runway, instrument approach facilities, and nighttime illumination. The facility boasts over fifty hangars and an extensive support infrastructure.

Special use airspace (SUA) is an area designated for operations of a nature such that limitations may be imposed on aircraft not participating in those operations. Often these operations are of a military nature. The designation of SUAs identifies for other users the areas where such activity occurs, provides for segregation of that activity from other users, and allows charting to keep airspace users informed of potential hazards. Most SUAs are depicted on aeronautical charts and FAA maintains a page showing the current status of most SUAs.

The Nevada Test and Training Range (NTTR) is one of two military training areas at the Nellis Air Force Base Complex in Nevada and used by the United States Air Force Warfare Center at Nellis Air Force Base. The NTTR land area includes a "simulated Integrated Air Defense System", several individual ranges with 1200 targets, and 4 remote communication sites. The current NTTR area and the range's former areas have been used for aerial gunnery and bombing, for nuclear tests, as a proving ground and flight test area, for aircraft control and warning, and for Blue Flag, Green Flag, and Red Flag exercises.

Tonopah Air Force Base is a Formerly Used Defense Site (FUDS) in the USA that was a Tonopah Basin military installation until shortly after it was designated an Air Force Base in 1948. Two of the runways still in use are maintained by Nye County, Nevada; and World War II building foundations and three hangars of the base remain at the municipal Tonopah Airport.

The History of Nevada as a state began when it became the 36th state on October 31, 1864, after telegraphing the Constitution of Nevada to the Congress days before the November 8 presidential election. Statehood was rushed to help ensure three electoral votes for Abraham Lincoln's reelection and add to the Republican congressional majorities.
The Dixie Valley is an endorheic basin which had plentiful ground water around which ranches were built. Prior to the US Navy TOPGUN school moving from California to Nevada, the valley was purchased in 1995 for $100 million and is used as an electronic warfare range for nearby Fallon Naval Air Station.
During World War II, the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) established numerous airfields in Nevada for training pilots and aircrews of USAAF fighters and bombers.

Strike Fighter Squadron 204 (VFA-204), also known as the "River Rattlers", is a U.S. Navy Reserve strike fighter squadron flying the F/A-18C/D Hornet. The squadron is based out of Naval Air Station Joint Reserve Base New Orleans and is part of the United States Navy Reserve's Tactical Support Wing. Their radio callsign is River and their tail code is AF.

Nevada during World War II was a time of great change that began immediately after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, in December 1941. The population of Nevada grew significantly, largely due to an influx of service men who were stationed at several newly built military bases. The economy also improved as the number of workers steadily increased and new jobs became available.
Tonopah Bombing Range was the original southern Nevada military area designated in 1940 and may refer to:

Hawthorne Bomb Plot is a Formerly Used Defense Site that had a Strategic Air Command (SAC) AUTOTRACK radar station during the Cold War. Operations began at a temporary RBS train site for RBS Express #2 was at the Hawthorne area in December 1961, and the 11th Radar Bomb Scoring Squadron subsequently established the fixed military installation for Radar Bomb Scoring in Babbitt, Nevada, the military housing community near the local Navy/Army depot.

The Nellis Air Force Base Complex is the southern Nevada military region of federal facilities and lands, e.g., currently and formerly used for military and associated testing and training such as Atomic Energy Commission atmospheric nuclear detonations of the Cold War. The largest land area of the complex is the Nevada Test and Training Range, and numerous Formerly Used Defense Sites remain federal lands of the complex. Most of the facilities are controlled by the United States Air Force and/or the Bureau of Land Management, and many of the controlling units are based at Creech and Nellis Air Force Bases. Initiated by a 1939 military reconnaissance for a bombing range, federal acquisition began in 1940, and McCarren Field became the World War II training area's 1st of 3 Nevada World War II Army Airfields and 10 auxiliary fields. The area's first military unit was initially headquartered in the Las Vegas Federal Building while the WWII Las Vegas Army Airfield buildings were constructed.

Lovelock Aerial Gunnery Range was a World War II facility in two Nevada areas used for "aerial gunnery, strafing, dive bombing [and] rocket fire". By 21 November 1944, the Lovelock Range had been approved by the Secretary of the Navy to be developed for Naval Air Station Fallon, and on 13 January 1945, "Lovelock Air to Air" began when "leased under the Second War Powers Act". By February 1945, land was being acquired for the North Range in the Black Rock Desert which was 1,122 sq mi (2,910 km2) that included 64.4 sq mi (167 km2) of "Patented" land. The South Range in the Granite Springs Valley was 2,436 sq mi (6,310 km2), and in March 1945 "1920 Acres more" were added.


















