Related Research Articles
In legal terminology, a complaint is any formal legal document that sets out the facts and legal reasons that the filing party or parties believes are sufficient to support a claim against the party or parties against whom the claim is brought that entitles the plaintiff(s) to a remedy. For example, the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure (FRCP) that govern civil litigation in United States courts provide that a civil action is commenced with the filing or service of a pleading called a complaint. Civil court rules in states that have incorporated the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure use the same term for the same pleading.

A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states and international organizations, but can sometimes include individuals, business entities, and other legal persons. A treaty may also be known as an international agreement, protocol, covenant, convention, pact, or exchange of letters, among other terms. However, only documents that are legally binding on the parties are considered treaties under international law.

A will or testament is a legal document that expresses a person's (testator) wishes as to how their property (estate) is to be distributed after their death and as to which person (executor) is to manage the property until its final distribution. For the distribution (devolution) of property not determined by a will, see inheritance and intestacy.

A power of attorney (POA) or letter of attorney is a written authorization to represent or act on another's behalf in private affairs, business, or some other legal matter. The person authorizing the other to act is the principal, grantor, or donor. The one authorized to act is the agent, attorney, or in some common law jurisdictions, the attorney-in-fact.
Legal instrument is a legal term of art that is used for any formally executed written document that can be formally attributed to its author, records and formally expresses a legally enforceable act, process, or contractual duty, obligation, or right, and therefore evidences that act, process, or agreement. Examples include a certificate, deed, bond, contract, will, legislative act, notarial act, court writ or process, or any law passed by a competent legislative body in municipal (domestic) or international law. Many legal instruments were written under seal by affixing a wax or paper seal to the document in evidence of its legal execution and authenticity. However, today many jurisdictions have done away with the requirement of documents being under seal in order to give them legal effect.
In law, a summary judgment is a judgment entered by a court for one party and against another party summarily, i.e., without a full trial. Summary judgments may be issued on the merits of an entire case, or on discrete issues in that case. The formulation of the summary judgment standard is stated in somewhat different ways by courts in different jurisdictions. In the United States, the presiding judge generally must find there is "no genuine dispute as to any material fact and the movant is entitled to judgment as a matter of law." In England and Wales, the court rules for a party without a full trial when "the claim, defence or issue has no real prospect of success and there is no other compelling reason why the case or issue should be disposed of at a trial."
In common law, a deed is any legal instrument in writing which passes, affirms or confirms an interest, right, or property and that is signed, attested, delivered, and in some jurisdictions, sealed. It is commonly associated with transferring (conveyancing) title to property. The deed has a greater presumption of validity and is less rebuttable than an instrument signed by the party to the deed. A deed can be unilateral or bilateral. Deeds include conveyances, commissions, licenses, patents, diplomas, and conditionally powers of attorney if executed as deeds. The deed is the modern descendant of the medieval charter, and delivery is thought to symbolically replace the ancient ceremony of livery of seisin.
The law of agency is an area of commercial law dealing with a set of contractual, quasi-contractual and non-contractual fiduciary relationships that involve a person, called the agent, that is authorized to act on behalf of another to create legal relations with a third party. Succinctly, it may be referred to as the equal relationship between a principal and an agent whereby the principal, expressly or implicitly, authorizes the agent to work under their control and on their behalf. The agent is, thus, required to negotiate on behalf of the principal or bring them and third parties into contractual relationship. This branch of law separates and regulates the relationships between:
Service of process is the procedure by which a party to a lawsuit gives an appropriate notice of initial legal action to another party, court, or administrative body in an effort to exercise jurisdiction over that person so as to force that person to respond to the proceeding before the court, body, or other tribunal.
A memorandum of understanding (MoU) is a type of agreement between two (bilateral) or more (multilateral) parties. It expresses a convergence of will between the parties, indicating an intended common line of action. It is often used either in cases where parties do not imply a legal commitment or in situations where the parties cannot create a legally enforceable agreement. It is a more formal alternative to a gentlemen's agreement.

Novation, in contract law and business law, is the act of –
- replacing an obligation to perform with another obligation; or
- adding an obligation to perform; or
- replacing a party to an agreement with a new party.

Offer and acceptance are generally recognised as essential requirements for the formation of a contract, and analysis of their operation is a traditional approach in contract law. The offer and acceptance formula, developed in the 19th century, identifies a moment of formation when the parties are of one mind. This classical approach to contract formation has been modified by developments in the law of estoppel, misleading conduct, misrepresentation, unjust enrichment, and power of acceptance.
A voidable contract, unlike a void contract, is a valid contract which may be either affirmed or rejected at the option of one of the parties. At most, one party to the contract is bound. The unbound party may repudiate (reject) the contract, at which time the contract becomes void.

In the law, a seal affixed to a contract or other legal instrument has had special legal significance at various times in the jurisdictions that recognise it. In the courts of common law jurisdictions, a contract which was sealed was treated differently from other written contracts, although this practice gradually fell out of favour in most of these jurisdictions in the 19th and early 20th century. The legal term seal arises from the wax seal used throughout history for authentication.

A contractual term is "any provision forming part of a contract". Each term gives rise to a contractual obligation, the breach of which may give rise to litigation. Not all terms are stated expressly and some terms carry less legal gravity as they are peripheral to the objectives of the contract.

A contract is a legally enforceable agreement that creates, defines, and governs mutual rights and obligations among its parties. A contract typically involves the transfer of goods, services, money, or a promise to transfer any of those at a future date. In the event of a breach of contract, the injured party may seek judicial remedies such as damages or rescission. Contract law, the field of the law of obligations concerned with contracts, is based on the principle that agreements must be honoured.
Contractual terms in English law is a topic which deals with four main issues.
Formalities in English law are required in some kinds of transaction by English contract law and trusts law. In a limited number of cases, agreements and trusts will be unenforceable unless they meet a certain form prescribed by statute. The main kinds of formality that a statute can require are to put the transaction in writing, to make a deed, or to register it at a government registrar.
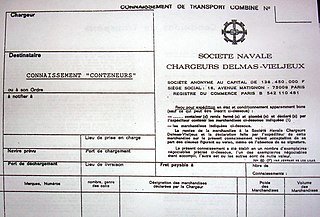
A bill of lading is a document issued by a carrier to acknowledge receipt of cargo for shipment. Although the term historically related only to carriage by sea, a bill of lading may today be used for any type of carriage of goods. Bills of lading are one of three crucial documents used in international trade to ensure that exporters receive payment and importers receive the merchandise. The other two documents are a policy of insurance and an invoice. Whereas a bill of lading is negotiable, both a policy and an invoice are assignable. In international trade outside the United States, bills of lading are distinct from waybills in that the latter are not transferable and do not confer title. Nevertheless, the UK Carriage of Goods by Sea Act 1992 grants "all rights of suit under the contract of carriage" to the lawful holder of a bill of lading, or to the consignee under a sea waybill or a ship's delivery order.

Rock Advertising Ltd v MWB Business Exchange Centres Ltd[2018] UKSC 24 is a judicial decision of the Supreme Court of the United Kingdom relating to contract law, concerning consideration and estoppel. Specifically it concerned the effectiveness of "no oral variation" clauses, which provide that any amendments or waiver in relation to the contract must be in writing.
References
- ↑ "What is informal contract? definition and meaning". Archived from the original on 2020-09-18. Retrieved 2020-08-29.
- ↑ "Informal vs. Formal Contracts: Examples, Differences & Definitions" . Retrieved 2020-08-28.
- ↑ Miller, and Cross. "Chapter 11: Contract Law." Business Law: Text and Cases. By Clarkson. 12th ed. Mason: Cengage Learning, 2012. 210. Print.