Related Research Articles

A bulletin board system (BBS), also called a computer bulletin board service (CBBS), was a computer server running software that allowed users to connect to the system using a terminal program. Once logged in, the user can perform functions such as uploading and downloading software and data, reading news and bulletins, and exchanging messages with other users through public message boards and sometimes via direct chatting. In the early 1980s, message networks such as FidoNet were developed to provide services such as NetMail, which is similar to internet-based email.
In journalism, yellow journalism and the yellow press are American newspapers that use eye-catching headlines and sensationalized exaggerations for increased sales. The English term is chiefly used in the US. In the United Kingdom, a similar term is tabloid journalism. Other languages, e.g. Russian, sometimes have terms derived from the American term. Yellow journalism emerged in the intense battle for readers by two newspapers in New York City in 1890s. It was not common in other cities.
An online service provider (OSP) can, for example, be an Internet service provider, an email provider, a news provider (press), an entertainment provider, a search engine, an e-commerce site, an online banking site, a health site, an official government site, social media, a wiki, or a Usenet newsgroup.

Newsday is a daily newspaper in the United States primarily serving Nassau and Suffolk counties on Long Island, although it is also sold throughout the New York metropolitan area. The slogan of the newspaper is "Newsday, Your Eye on LI", and formerly it was "Newsday, the Long Island Newspaper". The newspaper's headquarters are located in Melville, New York.
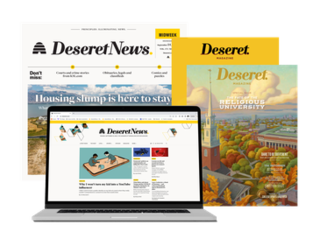
The Deseret News is a multi-platform newspaper based in Salt Lake City, published by Deseret News Publishing Company, a subsidiary of Deseret Management Corporation, which is owned by the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. Founded in 1850, it was the first newspaper to be published in Utah. The publication's name is from the geographic area of Deseret identified by Utah's pioneer settlers, and much of the publication's reporting is rooted in that region.

In typography, text or font in all caps contains capital letters without any lowercase letters. For example:
THIS TEXT IS IN ALL CAPS.
StarText was an online ASCII-based computer service run by the Fort Worth Star-Telegram and the Tandy Corporation and marketed in the Dallas-Fort Worth Metroplex newspaper circulation area from May 3, 1982 until March 3, 1997. Its name was derived from Star and Text.
The Mail & Guardian, formerly the Weekly Mail, is a South African weekly newspaper and website, published by M&G Media in Johannesburg, South Africa. It focuses on political analysis, investigative reporting, Southern African news, local arts, music and popular culture.
The MetroWest Daily News is an American daily newspaper published in Framingham, Massachusetts, serving the MetroWest region of suburban Boston. The newspaper is owned by Gannett.

The Winnipeg Tribune was a metropolitan daily newspaper serving Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada from January 28, 1890, to August 27, 1980. The paper was founded by R.L. Richardson and D.L. McIntyre who acquired the press and premises of the old Winnipeg Sun newspaper. It was often viewed as a liberal newspaper focused on local news and events. The paper was owned by Southam Inc at the time of its demise. It was frequently referred to as The Trib.
Nando was an American internet news service and Internet service provider (ISP), founded in 1993 by the publishers of The News & Observer newspaper in Raleigh, North Carolina. Initially it relied on access via bulletin board technology. One of the first 24-hour news websites, the Nando Times, was launched in 1994, providing edited information from major news agencies that had not then developed their own websites.

The Press-Telegram is a paid daily newspaper published in Long Beach, California. Coverage area for the Press-Telegram includes Long Beach, Lakewood, Signal Hill, Artesia, Bellflower, Cerritos, Compton, Downey, Hawaiian Gardens, Lynwood, Norwalk and Paramount.

The Tech, first published on November 16, 1881, is the student newspaper at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Editions are published on Thursdays throughout the academic year and about once a month over the summer. The Tech established an early presence on the World Wide Web, and continues to publish online in tandem with the print edition.

In computing, a news aggregator, also termed a feed aggregator, content aggregator, feed reader, news reader, or simply an aggregator, is client software or a web application that aggregates digital content such as online newspapers, blogs, podcasts, and video blogs (vlogs) in one location for easy viewing. The updates distributed may include journal tables of contents, podcasts, videos, and news items.
An offline reader is computer software that downloads e-mail, newsgroup posts or web pages, making them available when the computer is offline: not connected to a server. Offline readers are useful for portable computers and dial-up access.
The Enterprise-Sun, and its predecessors, the Hudson Daily Sun and Marlboro Enterprise, were daily newspapers covering the city of Marlborough and adjoining town of Hudson, both in Middlesex County, Massachusetts.

Chums was a boys' weekly newspaper started in 1892 by Cassell & Company and later, from 1927, published by Amalgamated Press. The publisher gathered the weekly paper into monthly and annual editions. The monthly versions were published on the 25th of the month, and up to November 1920 included all the content of the weekly editions. From then on, the monthly editions had all the story content of the weeklies, but left out the covers. This left a gap which was then filled by short stories, articles and even serials that were not included in the weekly edition. The serial ceased publication in 1941.

Telex is a telecommunication service that provides text-based message exchange over the circuits of the public switched telephone network or by private lines. The technology operates on switched station-to-station basis with teleprinter devices at the receiving and sending locations. Telex was a major method of sending written messages electronically between businesses in the post–World War II period. Its usage went into decline as the fax machine grew in popularity in the 1980s.

The Fort Worth Star-Telegram is an American daily newspaper serving Fort Worth and Tarrant County, the western half of the North Texas area known as the Metroplex. It is owned by The McClatchy Company.
Started in 1983, Boston CitiNet was a local online service developed by Applied Videotex Systems, Inc. of Belmont, Massachusetts. The service allowed modem-equipped personal computer users to dial-in and access a range of information and messaging services including chat, forums, email and a variety of content. There were several other companies offering paid/subscription services as the time like The Source, CompuServe and Boston-based Delphi. Boston Citinet was unique since it was free to access and was supported by advertising. Messaging services such as email and chat required registration and a monthly fee of $9.95 - an early example of the now popular freemium business model.
References
- ↑ "Eleven Newspapers Chosen for Electronic Delivery Test". The Boston Globe, p. 1, June 27, 1980.
- ↑ "McKelvey, Karen. CERFnet: No-fee dial-ups, 1991". Archived from the original on 2006-09-28. Retrieved 2006-08-19.