
A Linux distribution is an operating system made from a software collection that includes the Linux kernel, and often a package management system. Linux users usually obtain their operating system by downloading one of the Linux distributions, which are available for a wide variety of systems ranging from embedded devices and personal computers to powerful supercomputers.

GNU GRUB is a boot loader package from the GNU Project. GRUB is the reference implementation of the Free Software Foundation's Multiboot Specification, which provides a user the choice to boot one of multiple operating systems installed on a computer or select a specific kernel configuration available on a particular operating system's partitions.

Privilege escalation is the act of exploiting a bug, a design flaw, or a configuration oversight in an operating system or software application to gain elevated access to resources that are normally protected from an application or user. The result is that an application with more privileges than intended by the application developer or system administrator can perform unauthorized actions.

UEFI is a set of specifications written by the UEFI Forum. They define the architecture of the platform firmware used for booting and its interface for interaction with the operating system. Examples of firmware that implement these specifications are AMI Aptio, Phoenix SecureCore Tiano, TianoCore EDK II and InsydeH2O.
A softmod is a method of using software to modify the intended behavior of hardware, such as video cards, sound cards, or game consoles in a way that can overcome restrictions of the firmware, or install custom firmware.
Homebrew, when applied to video games, refers to games produced by hobbyists for proprietary video game consoles which are not intended to be user-programmable. The official documentation is often only available to licensed developers, and these systems may use storage formats that make distribution difficult, such as ROM cartridges or encrypted CD-ROMs. Many consoles have hardware restrictions to prevent unauthorized development. A non-professional developer for a system intended to be user-programmable, like the Commodore 64, is simply called a hobbyist.

Xbox Linux was a project that ported the Linux operating system to the Xbox video game console. Because the Xbox uses a digital signature system to prevent the public from running unsigned code, one must either use a modchip, or a softmod. Originally, modchips were the only option; however, it was later demonstrated that the TSOP chip on which the Xbox's BIOS is held may be reflashed. This way, one may flash on the "Cromwell" BIOS, which was developed legally by the Xbox Linux project. Catalyzed by a large cash prize for the first team to provide the possibility of booting Linux on an Xbox without the need of a hardware hack, numerous software-only hacks were also found. For example, a buffer overflow was found in the game 007: Agent Under Fire that allowed the booting of a Linux loader ("xbeboot") straight from a save game.

PlayStation Portable homebrew refers to the process of using exploits and hacks to execute unsigned code on the PlayStation Portable (PSP).
In the context of free and open-source software, proprietary software only available as a binary executable is referred to as a blob or binary blob. The term usually refers to a device driver module loaded into the kernel of an open-source operating system, and is sometimes also applied to code running outside the kernel, such as system firmware images, microcode updates, or userland programs. The term blob was first used in database management systems to describe a collection of binary data stored as a single entity.
HAL is a software subsystem for UNIX-like operating systems providing hardware abstraction.
OtherOS is a feature of early versions of the PlayStation 3 video game console, allowing user installed software, such as Linux or FreeBSD. The feature was removed since system firmware update 3.21, released on April 1, 2010.
authbind is an open-source system utility written by Ian Jackson and is distributed under the GNU General Public License. The authbind software allows a program that would normally require superuser privileges to access privileged network services to run as a non-privileged user. authbind allows the system administrator to permit specific users and groups access to bind to TCP and UDP ports below 1024. Ports 0 - 1023 are normally privileged and reserved for programs that are run as the root user. Allowing regular users limited access to privileged ports helps prevent possible privilege escalation and system compromise if the software happens to contain software bugs or is found to be vulnerable to unknown exploits.
The PlayStation Portable system software is the official firmware for the PlayStation Portable (PSP). It uses the XrossMediaBar (XMB) as its user interface, similar to the PlayStation 3 console. Updates add new functionality as well as security patches to prevent unsigned code from being executed on the system. Updates can be obtained in four ways:
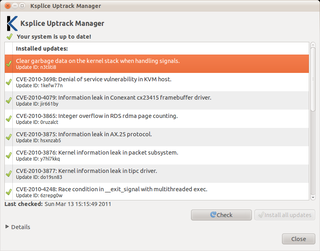
Ksplice is an open-source extension of the Linux kernel that allows security patches to be applied to a running kernel without the need for reboots, avoiding downtimes and improving availability. Ksplice supports only the patches that do not make significant semantic changes to kernel's data structures.

Linux-libre is a modified version of the Linux kernel that contains no binary blobs, obfuscated code, or code released under proprietary licenses. In the Linux kernel, they are mostly used for proprietary firmware images. While generally redistributable, binary blobs do not give the user the freedom to audit, modify, or, consequently, redistribute their modified versions. The GNU Project keeps Linux-libre in synchronization with the mainline Linux kernel.
The hacking of consumer electronics is an increasingly common practice which users perform in order to customize and modify their devices beyond what is typically possible. This activity has a long history, dating from the days of early computer, programming, and electronics hobbyists.
Xbox modding is the practice of circumventing the built-in hardware and software security mechanisms of the Xbox video game console.
Homebrew software was first run on the PlayStation 3 by a group of hackers under the name "Team Ice" by exploiting a vulnerability in the game Resistance: Fall of Man. Following various other hacks executed from Linux, Sony removed the ability to install another operating system in the 3.21 firmware update. This event caused backlash among the hacker communities, and eventually the group Fail0verflow found a flaw in the generation of encryption keys which they leveraged to restore the ability to install Linux. George Hotz (Geohot), often misattributed as the genesis of homebrew on the PS3, later created the first homebrew signed using the private "metldr" encryption key which he leaked onto the internet. Leaking the key led to Hotz being sued by Sony. The court case was settled out of court, with the result of George Hotz not being able to further reverse engineer the PS3.
Custom firmware, also known as aftermarket firmware, is an unofficial new or modified version of firmware created by third parties on devices such as video game consoles and various embedded device types to provide new features or to unlock hidden functionality. In the video game console community, the term is often written as custom firmware or simply CFW, referring to an altered version of the original system software inside a video game console such as the PlayStation Portable, PlayStation 3, PlayStation Vita/PlayStation TV, PlayStation 4, Nintendo 3DS and Nintendo Switch. Installing custom firmware typically requires bootloader unlocking.








