Libranet was an operating system based on Debian.

Mark Spencer is an American computer engineer and is the original author of the GTK+-based instant messaging client Gaim, the L2TP daemon l2tpd and the Cheops Network User Interface.

Anaconda is a free and open-source system installer for Linux distributions.

Asterisk is a software implementation of a private branch exchange (PBX). In conjunction with suitable telephony hardware interfaces and network applications, Asterisk is used to establish and control telephone calls between telecommunication endpoints such as customary telephone sets, destinations on the public switched telephone network (PSTN) and devices or services on voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) networks. Its name comes from the asterisk (*) symbol for a signal used in dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF) dialing.

Webmin is a web-based server management control panel for Unix-like systems. Webmin allows the user to configure operating system internals, such as users, disk quotas, services and configuration files, as well as modify and control open-source apps, such as BIND, Apache HTTP Server, PHP, and MySQL.

Digium, Inc. is a communications technology company based in Huntsville, Alabama, and since 2018, a subsidiary of Sangoma Technologies Corporation. The company makes VoIP business phone systems, IP phones, and hardware products. It was founded in 1999 by Mark Spencer.
GNU variants are operating systems based upon the GNU operating system. According to the GNU project and others, these also include most operating systems using the Linux kernel and a few others using BSD-based kernels.

Snom Technology GmbH is a German company which manufactures Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) telephones, based on the IETF standard Session Initiation Protocol (SIP). Snom's products are targeted at the small- to medium-sized business sector, home offices, Internet service providers, carriers, and original equipment manufacturers. The company, founded in 1996 and headquartered in Berlin, is a wholly owned subsidiary of VTech Holdings Limited, since 2016.
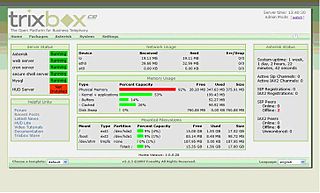
trixbox was a software PBX based on Asterisk.

Issabel is open-source Unified Communications PBX software, providing user-friendly web-based configuration, management, and reporting for telephony. Modules providing predictive dialing can be added. It is a fork of the open-source versions of Elastix, developed by the user/developer community when 3CX acquired Elastix, closed the community, halted distribution and development of the open-source versions, and released a proprietary version.

Elastix is a unified communications server software that brings together IP PBX, email, IM, faxing and collaboration functionality. It has a Web interface and includes capabilities such as a call center software with predictive dialing.

Bharat Operating System Solutions is an Indian Linux distribution based on Debian, with Its latest stable version is 10.0 ("Pragya") which was released in March 2024.

CrunchBang Linux was a Linux distribution derived from Debian by Philip Newborough.

antiX is a Linux distribution, originally based on MEPIS, which itself is based on the Debian stable distribution. antiX initially replaced the MEPIS KDE desktop environment with the Fluxbox and IceWM window managers, making it suitable for older, less powerful x86-based systems. Unlike Debian, antiX does not use the systemd init system, instead, antiX provides images where either SysVinit or Runit are set as the default init system.

Sangoma Technologies Corporation (Sangoma) is a Canadian company that provides Communications as a Service (“CaaS”) products for businesses. It was founded in 1984. It is publicly traded on the Toronto Stock Exchange.
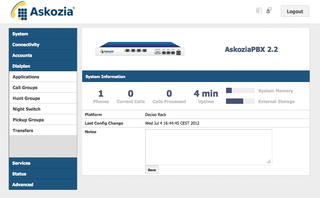
AskoziaPBX is a closed source telephone system firmware. It is a fork of the m0n0wall project and uses the Asterisk private branch exchange (PBX) software to realize all telephony functions.

The FreePBX Distro is a freeware unified communications software system that consists of a graphical user interface (GUI) for configuring, controlling, and managing Asterisk PBX software. The FreePBX Distro includes packages that offer VoIP, PBX, Fax, IVR, voice-mail and email functions.

HandyLinux is a simplified Linux operating system developed in France, derived from the Debian stable branch. It was designed to be easily accessible and downloadable, so that it could be used by people with very little computer experience and on a range of older hardware that was no longer supported by the latest versions of proprietary operating systems. It was particularly aimed at older people with dated hardware who do not need nor possess the skill to use many features afforded by state-of-the-art operating systems.















