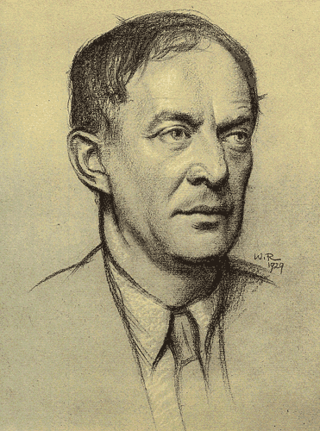Gilbert Keith Chesterton was an English writer, philosopher, Christian apologist, a literary and art critic.
Walter John de la Mare was an English poet, short story writer and novelist. He is probably best remembered for his works for children, for his poem "The Listeners", and for his psychological horror short fiction, including "Seaton's Aunt" and "All Hallows". In 1921, his novel Memoirs of a Midget won the James Tait Black Memorial Prize for fiction, and his post-war Collected Stories for Children won the 1947 Carnegie Medal for British children's books.

George Robert Gissing was an English novelist, who published 23 novels between 1880 and 1903. His best-known works have reappeared in modern editions. They include The Nether World (1889), New Grub Street (1891) and The Odd Women (1893).

Geoffrey Anketell Studdert Kennedy was an English Anglican priest and poet. He was nicknamed "Woodbine Willie" during World War I for giving Woodbine cigarettes to the soldiers he met, as well as spiritual aid to injured and dying soldiers.

Father Brown is a fictional Roman Catholic priest and amateur detective. He features in 53 short stories by English author G. K. Chesterton, published between 1910 and 1936. Father Brown solves mysteries and crimes using his intuition and keen understanding of human nature. Chesterton loosely based him on the Rt Rev. Msgr John O'Connor (1870–1952), a parish priest in Bradford, who was involved in Chesterton's conversion to Catholicism in 1922. Since 2013, the character has been portrayed by Mark Williams in the ongoing BBC Television Series Father Brown.

Cecil Edward Chesterton was an English journalist and political commentator, known particularly for his role as editor of The New Witness from 1912 to 1916, and in relation to its coverage of the Marconi scandal.

Philip Guedalla was an English barrister, and a popular historical and travel writer and biographer. His wit and epigrams are well-known, one example being "Even reviewers read a Preface". He also was the originator of a now-common theory on Henry James, writing that "The work of Henry James has always seemed divisible by a simple dynastic arrangement into three reigns: James I, James II, and the Old Pretender".

Edmund Dulac was a French-British naturalised magazine illustrator, book illustrator and stamp designer. Born in Toulouse he studied law but later turned to the study of art at the École des Beaux-Arts. He moved to London early in the 20th century and in 1905 received his first commission to illustrate the novels of the Brontë Sisters. During World War I, Dulac produced relief books and when after the war the deluxe children's book market shrank he turned to magazine illustrations among other ventures. He designed banknotes during World War II and postage stamps, most notably those that heralded the beginning of Queen Elizabeth II's reign.
G.K.'s Weekly was a British publication founded in 1925 by writer G. K. Chesterton, continuing until his death in 1936. Its articles typically discussed topical cultural, political, and socio-economic issues yet the publication also ran poems, cartoons, and other such material that piqued Chesterton's interest. It contained much of his journalistic work done in the latter part of his life, and extracts from it were published as the book The Outline of Sanity. Precursor publications existed by the names of The Eye-Witness and The New Witness, the former being a weekly newspaper started by Hilaire Belloc in 1911, the latter Belloc took over from Cecil Chesterton, Gilbert's brother, who died in World War I: and a revamped version of G. K.'s Weekly continued some years after Chesterton's death by the name of The Weekly Review.
Émile Leon Cammaerts CBE was a Belgian playwright, poet and author who wrote primarily in English and French.
John Agard FRSL is a Guyanese playwright, poet and children's writer, now living in Britain. In 2012, he was selected for the Queen's Gold Medal for Poetry. He was awarded BookTrust's Lifetime Achievement Award in November 2021.

P. J. Kavanagh FRSL was an English poet, lecturer, actor, broadcaster and columnist. His father was the ITMA scriptwriter Ted Kavanagh.

Lewis Christopher Edward Baumer was best known as an English cartoonist who worked for more than fifty years for the British magazine Punch, from 1897. He was also a portrait and still life painter, pastellist, magazine and book illustrator. His legacy includes many portraits, advertisements and still life paintings in the first half of the 20th century. He contributed to the revival of the tradition of portraiture using pastels, and was accomplished in many other media including oils, watercolours, gouache, and etching.

John Archibald Austen was a British book illustrator.
Jessie Louisa Rickard, also known as Mrs Victor Rickard (1876–1963), was an Irish literary novelist. During her lifetime she became a versatile writer who produced over forty novels, some of which found a large reading public. She preferred to be known as Mrs Victor Richard to avoid association with a young woman called Jessie Rickard, who was brutally murdered in an incident reported in the media as 'The Cornish Tragedy'.

Arthur Stringer was a Canadian novelist, screenwriter, and poet who later moved to the United States.
Patrick Philip William Braybrooke FRSL (1894–1956) was an English literary critic who largely concentrated his attention on English writers of the nineteenth and early twentieth century.

George Edwards Theodore Goodridge Roberts was a Canadian novelist and poet. He was the author of thirty-four novels and over one hundred published stories and poems.

Frances Alice Blogg Chesterton was an English author of verse, songs and school drama. She was the wife of G. K. Chesterton and had a large role in his career as amanuensis and personal manager.
Queenie Scott-Hopper was the pen name of Mabel Olive Scott-Hopper, an English author of children’s stories, poetry, and devotional literature.