
Network address translation (NAT) is a method of mapping an IP address space into another by modifying network address information in the IP header of packets while they are in transit across a traffic routing device. The technique was originally used to bypass the need to assign a new address to every host when a network was moved, or when the upstream Internet service provider was replaced, but could not route the network's address space. It has become a popular and essential tool in conserving global address space in the face of IPv4 address exhaustion. One Internet-routable IP address of a NAT gateway can be used for an entire private network.

GNUnet is a software framework for decentralized, peer-to-peer networking and an official GNU package. The framework offers link encryption, peer discovery, resource allocation, communication over many transports and various basic peer-to-peer algorithms for routing, multicast and network size estimation.

GNU Wget is a computer program that retrieves content from web servers. It is part of the GNU Project. Its name derives from "World Wide Web" and "get". It supports downloading via HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP.
A BNC is a piece of software that is used to relay traffic and connections in computer networks, much like a proxy. Using a BNC allows a user to hide the original source of the user's connection, providing privacy as well as the ability to route traffic through a specific location. A BNC can also be used to hide the true target to which a user connects.
OpenVPN is a virtual private network (VPN) system that implements techniques to create secure point-to-point or site-to-site connections in routed or bridged configurations and remote access facilities. It implements both client and server applications.
IPFilter is an open-source software package that provides firewall services and network address translation (NAT) for many Unix-like operating systems. The author and software maintainer is Darren Reed. IPFilter supports both IPv4 and IPv6 protocols, and is a stateful firewall.
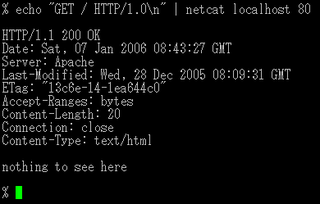
netcat is a computer networking utility for reading from and writing to network connections using TCP or UDP. The command is designed to be a dependable back-end that can be used directly or easily driven by other programs and scripts. At the same time, it is a feature-rich network debugging and investigation tool, since it can produce almost any kind of connection its user could need and has a number of built-in capabilities.
Netfilter is a framework provided by the Linux kernel that allows various networking-related operations to be implemented in the form of customized handlers. Netfilter offers various functions and operations for packet filtering, network address translation, and port translation, which provide the functionality required for directing packets through a network and prohibiting packets from reaching sensitive locations within a network.
The 389 Directory Server is a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) server developed by Red Hat as part of the community-supported Fedora Project. The name "389" derives from the port number used by LDAP.
An H.323 Gatekeeper serves the purpose of Call Admission Control and translation services from E.164 IDs to IP addresses in an H.323 telephony network. Gatekeepers can be combined with a gateway function to proxy H.323 calls and are sometimes referred to as session border controllers (SBC). A gatekeeper can also deny access or limit the number of simultaneous connections to prevent network congestion.

Ekiga is a VoIP and video conferencing application for GNOME and Microsoft Windows. It was distributed as free software under the terms of the GNU GPL-2.0-or-later. It was the default VoIP client in Ubuntu until October 2009, when it was replaced by Empathy. Ekiga supports both the SIP and H.323 protocols and is fully interoperable with any other SIP compliant application and with Microsoft NetMeeting. It supports many high-quality audio and video codecs.
This article presents a comparison of the features, platform support, and packaging of many independent implementations of Domain Name System (DNS) name server software.
Quagga is a network routing software suite providing implementations of Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), Routing Information Protocol (RIP), Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) and IS-IS for Unix-like platforms, particularly Linux, Solaris, FreeBSD and NetBSD.

H.323 is a recommendation from the ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) that defines the protocols to provide audio-visual communication sessions on any packet network. The H.323 standard addresses call signaling and control, multimedia transport and control, and bandwidth control for point-to-point and multi-point conferences.
In the field of VoIP networking, the Open Phone Abstraction Library (OPAL) continues the open-source openh323 project to support a wide range of commonly used protocols used to send voice, video and fax data over IP networks rather than being tied to the H.323 protocol. Initially, from 2007, OPAL supported the H.323 and Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) protocols, but it has grown to include Asterisk IAX2.

Drizzle is a discontinued free software/open-source relational database management system (DBMS) that was forked from the now-defunct 6.0 development branch of the MySQL DBMS.
The OpenH323 project had as its goal the development of a full featured, open source (MPL) implementation of the H.323 Voice over IP protocol. The code was written in C++ and, through the development effort of numerous people around the world, supported a broad subset of the H.323 protocol. The software has since been integrated into a number of open source and commercial software products.
Chih-Wei Huang is a developer and promoter of free software who lives in Taiwan. He is famous for his work in the VoIP and internationalization and localization fields in Greater China. The user name he usually uses is cwhuang.

Polipo is a discontinued lightweight caching and forwarding web proxy server. It has a wide variety of uses, from aiding security by filtering traffic; to caching web, DNS and other computer network lookups for a group of people sharing network resources; to speeding up a web server by caching repeated requests. It can be configured to use on-disk cache and serve cached content when offline and perform various forms of content filtering.






