
Burkina Faso is a landlocked Sahel country that shares borders with six nations. It lies between the Sahara desert and the Gulf of Guinea, south of the loop of the Niger River, mostly between latitudes 9° and 15°N, and longitudes 6°W and 3°E. The land is green in the south, with forests and fruit trees, and semi-arid in the north. Most of central Burkina Faso lies on a savanna plateau, 198–305 metres (650–1,001 ft) above sea level, with fields, brush, and scattered trees. Burkina Faso's game preserves – the most important of which are Arly, Nazinga, and W National Park—contain lions, elephants, hippopotamus, monkeys, common warthogs, and antelopes. Previously the endangered painted hunting dog, Lycaon pictus occurred in Burkina Faso, but, although the last sightings were made in Arli National Park, the species is considered extirpated from Burkina Faso.
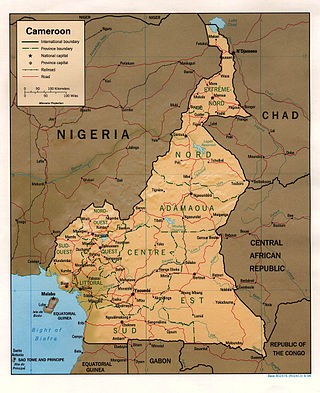
At 475,440 km2 (183,570 sq mi), Cameroon is the world's 53rd largest country. It is slightly larger than the nation of Sweden and the US state of California. It is comparable in size to Papua New Guinea. Cameroon's landmass is 472,710 km2 (182,510 sq mi), with 2,730 km2 (1,050 sq mi) of water.

Cape Verde is a group of arid Atlantic islands which are home to distinct communities of plants, birds, and reptiles. The islands constitute the unique Cape Verde Islands dry forests ecoregion, according to the World Wildlife Fund.

The Republic of Equatorial Guinea is located in west central Africa. Bioko Island lies about 40 kilometers (24.9 mi) from Cameroon. Annobón Island lies about 595 kilometres (370 mi) southwest of Bioko Island. The larger continental region of Río Muni lies between Cameroon and Gabon on the mainland; it includes the islands of Corisco, Elobey Grande, Elobey Chico, and adjacent islets. The total land area is 28,051 km2 (10,831 sq mi). It has an Exclusive Economic Zone of 303,509 km2 (117,185 sq mi).

The Geography of Kenya is diverse, varying amongst its 47 counties. Kenya has a coastline on the Indian Ocean, which contains swamps of East African mangroves. Inland are broad plains and numerous hills. Kenya borders South Sudan to the northwest, Uganda to the west, Somalia to the east, Tanzania to the south, and Ethiopia to the north. Kenya currently faces border disputes with South Sudan over the Ilemi Triangle and with Somalia over Jubbaland where, if the Somalian Government gives it up, it could be a new part of Kenya, which would bring the total land area of Kenya to approximately 692,939 sq km.

Kiribati consists of 32 atolls and one island in an expanse of ocean equivalent in size to the contiguous United States. The islands are scattered such that Kiribati has territory located in each of the four hemispheres. The islands of Kiribati lie roughly halfway between Hawaii and Australia in the Micronesian and Polynesian regions of the South Pacific. The three main island groupings are the Gilbert Islands, Phoenix Islands, and Line Islands. On 1 January 1995 Kiribati moved the International Date Line to include its easternmost islands and make it the same day throughout the country.

Morocco is the northwesternmost country which spans from the Mediterranean Sea and Atlantic Ocean on the north and the west respectively, into large mountainous areas in the interior, to the Sahara desert in the far south. Morocco is a Northern African country, located in the extreme northwest of Africa on the edge of continental Europe. The Strait of Gibraltar separates Spain from Morocco with a 13 kilometres (8.1 mi) span of water. Morocco borders the North Atlantic Ocean to the west, and the western Mediterranean Sea to the north, and has borders with Algeria and disputed Western Sahara.

The geography of Mozambique consists mostly of coastal lowlands with uplands in its center and high plateaus in the northwest. There are also mountains in the western portion. The country is located on the east coast of southern Africa, directly west of the island of Madagascar. Mozambique has a tropical climate with two seasons, a wet season from October to March and a dry season from April to September.

The Republic of the Congo is located in the western part of central Africa. Situated on the Equator, it is bordered by the Angolan exclave of Cabinda to the south (231 km), the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north and east (1,229 km), the Central African Republic (487 km) and Cameroon (494 km) to the north and Gabon to the west (2,567 km). Congo has a 169 km long Atlantic coast with several important ports. The Republic of the Congo covers an area of 342,000 km², of which 341,500 km² is land while 500 km² is water. Congo claims 200 nautical miles (370 km) of territorial sea.

São Tomé and Príncipe is a small island country composed of an archipelago located in the Gulf of Guinea of the equatorial Atlantic Ocean. The nation's main islands are São Tomé Island and Príncipe Island, for which the country is named. These are located about 300 and 250 kilometres, respectively, off the northwest coast of Gabon in Central Africa.

Sierra Leone is a country in West Africa with a North Atlantic Ocean coastline to the west. It lies on the African Plate. The country's main geographical features include wooded hill country, an upland plateau, and mountains in the east. The highest peak is Mount Bintumani, which is 1,948 meters (6,391 ft) above sea level. The coastline has a belt of mangrove swamps. Freetown, the nation's capital city, has one of the world's largest natural harbours. The Rokel River is the largest river in Sierra Leone. It is 400 kilometres (250 mi) long and has a basin with a total area of 10,622 square kilometres (4,101 sq mi).

Solomon Islands is an island country in the South Pacific Ocean, that lies east of Papua New Guinea.

Tanzania comprises many lakes, national parks, and Africa's highest point, Mount Kilimanjaro. Northeast Tanzania is mountainous, while the central area is part of a large plateau covered in grasslands. The country also contains the southern portion of Lake Victoria on its northern border with Uganda and Kenya.

Togo is a small Sub-Saharan state, comprising a long strip of land in West Africa. Togo's geographic coordinates are a latitude of 8° north and a longitude of 1°10′ east. It is bordered by three countries: Benin to the east, with 644 km (400 mi) of border; Burkina Faso to the north, with 126 km (78 mi) of border; and Ghana, with 877 km (545 mi) of border. To the south Togo has 56 km (35 mi) of coastline along the Bight of Benin of the Gulf of Guinea in the North Atlantic Ocean. Togo stretches 579 km (360 mi) north from the Gulf and is only 160 km (99 mi) wide at the broadest point. In total, Togo has an area of 56,785 km2 (21,925 sq mi), of which 54,385 km2 (20,998 sq mi) is land and 2,400 km2 (927 sq mi) is water.

Western Sahara is a territory in Northern Africa, bordered by the North Atlantic Ocean, Morocco proper, Algeria, and Mauritania. Geographic coordinates: 24°30′N13°00′W

Mali is a landlocked nation in West Africa, located southwest of Algeria, extending south-west from the southern Sahara Desert through the Sahel to the Sudanian savanna zone. Mali's size is 1,240,192 square kilometers.

Benin, a narrow, key-shaped, north–south strip of land in West Africa, lies between the Equator and the Tropic of Cancer. Its latitude ranges from 6°30′ N to 12°30′ N and its longitude from 1° E to 3°40′ E. It is bounded by Togo to the west, Burkina Faso and Niger to the north, Nigeria to the east, and the Bight of Benin to the south.
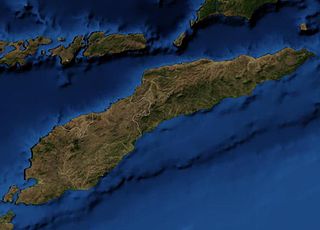
East Timor includes the mountainous eastern half of Timor, the Ocussi-Ambeno region on the northwest portion of the island of Timor, and the islands of Atauro and Jaco. The country is located northwest of Australia in the Lesser Sunda Islands at the eastern end of the Indonesian Archipelago. 'Timor' is a Portuguese derivation of 'Timor', the Malay word for "Orient"; the island of Timor is part of the Malay Archipelago and is the largest and easternmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands. East Timor is the only Asian nation to lie entirely within the Southern Hemisphere. The Loes River is the longest with a length of 80 km (50 mi). This river system covers an area of 2,184 km2 (843 sq mi). It is a small country with a land size of 14,919 km2 (5,760 sq mi). The exclusive economic zone is 70,326 km2 (27,153 sq mi).

Madang is the capital of Madang Province and is a town with a population of 27,420 on the north coast of Papua New Guinea. It was first settled by the Germans in the 19th century.
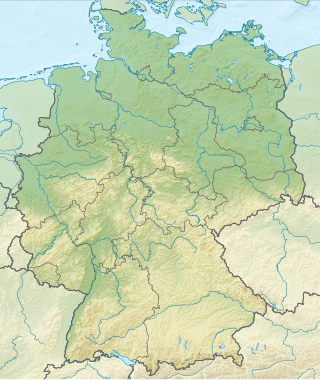
Germany is a country in Central and Western Europe that stretches from the Alps, across the North European Plain to the North Sea and the Baltic Sea. It is the second-most populous country in Europe after Russia, and is seventh-largest country by area in the continent. The area of Germany ranked 63rd and covers 357,021 km2 (137,847 sq mi), consisting of 349,223 km2 (134,836 sq mi) of land and 7,798 km2 (3,011 sq mi) of waters, smaller than Japan but larger than Republic of the Congo.
























