Biography
Born in Peacham,Vermont,he was educated at Peacham Academy. At the age of 18,he became a reporter on the Springfield (Massachusetts) Republican and later on the New York World,where he reported on New Jersey politics. He was appointed by Governor Robert Stockton Green of New Jersey as aide-de-camp on his staff,and was reappointed by Governor Leon Abbett. The latter also made him insurance commissioner of New Jersey in 1890. A protégéof publisher Joseph Pulitzer,at the age of twenty-seven he became managing editor of the New York World (1891-4). It was the flagship newspaper of the Democratic Party;its editorials were widely reprinted by the party press. [2]
Harvey then became associated with Thomas Fortune Ryan and William C. Whitney,leading Democrats who were millionaire promoters of street railways. In 1898 Harvey organized a syndicate which acquired the lines in Havana,Cuba. Having accumulated a great fortune,he purchased prestige magazines,including the North American Review in 1899. It had long been the leading national magazine in arts,letters,and politics,but it was soon overshadowed and outsold by muckraking magazines of which Harvey disapproved. [3] In 1901 he also purchased Harper's Weekly ,which he edited until 1913. He was president of Harper and Company until 1915. In 1903,Harvey purchased the Metropolitan Magazine .
Politics
A conservative Democrat,Harvey was a top advisor to New Jersey governor Woodrow Wilson. As early as 1906 he became the first leader to suggest Wilson,then president of Princeton University,would be a strong presidential possibility. According to Arthur Link,"More than any other single individual,he was responsible for Wilson's political career." [4] In the run-up to the start of the 1912 campaign he gave Wilson strong support. But Wilson was moving left and needed to shake off the image that he was under the thumb of Wall Street. Wilson sensed he was jeopardized by Harvey's officiousness and conservatism,while Harvey was alarmed by Wilson's move to the left of the party. Their breakup was the talk of the hour in the national press,and helped Wilson gain support among liberal Democrats. [5]
In 1916 Harvey urged the election of Charles E. Hughes,the Republican candidate for president. [2]
Despite retiring from Harper's Weekly as editor in 1913,Harvey returned in 1918 to use it as a medium for attacking the policies of President Wilson. [6] In 1918 he established The North American Review's War Weekly,later called Harvey's Weekly,which bitterly denounced Wilson's foreign policy. [2]
Harvey was a central figure in the "smoke-filled room" that played a major role in the GOP national convention in Chicago in 1920. The politicians there recognized that the three leading contenders were stalemated and that a dark horse like Warren G. Harding was needed as the Republican nominee. Harvey himself favored Will H. Hays,another dark horse but one with less support. [7] When Harding was elected,he appointed Harvey to the highly prestigious post of Ambassador to the Court of St. James's (perhaps better known as Ambassador to Great Britain). Harvey served from 1921 until 1923 but was not comfortable in the role. He gained a reputation for being acid-tongued and was quoted in 1923 as saying that "the national American foreign policy is to have no foreign policy." [8]
From 1906 until 1908,Harvey promoted the artificial language Esperanto in the North American Review. In 1908 and 1909 he was president of Esperanto-Asocio de Norda Ameriko (Esperanto Association of North America). He was a strong proponent of womens suffrage,speaking often upon the subject until the US Constitution was amended to require it in 1920. [9] He was strongly opposed to the League of Nations in 1919 and 1920 on the ground that it involved the yielding of national sovereignty. [2]
Harvey published a number of works during his life,most notably Women in 1908 and Henry Clay Frick,the Man (1928),a biography of the industrialist,art collector,and philanthropist. [10] He died on August 20,1928,at his home in Dublin,New Hampshire. [11] Harvey was buried in Peacham Village Cemetery.

Warren Gamaliel Harding was the 29th president of the United States, serving from 1921 until his death in 1923. A member of the Republican Party, he was one of the most popular sitting U.S. presidents. After his death, a number of scandals were exposed, including Teapot Dome, as well as an extramarital affair with Nan Britton, which diminished his reputation.
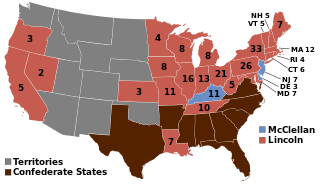
The 1864 United States presidential election was the 20th quadrennial presidential election. It was held on Tuesday, November 8, 1864. Near the end of the American Civil War, incumbent President Abraham Lincoln of the National Union Party easily defeated the Democratic nominee, former General George B. McClellan, by a wide margin of 212–21 in the electoral college, with 55% of the popular vote. For the election, the Republican Party and some Democrats created the National Union Party, especially to attract War Democrats.

The 1920 United States presidential election was the 34th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 2, 1920. In the first election held after the end of World War I and the first election after the ratification of the Nineteenth Amendment, Republican Senator Warren G. Harding of Ohio defeated Democratic Governor James M. Cox of Ohio. The vice presidential nominees Calvin Coolidge and Franklin D. Roosevelt would be the separate successors of Harding and 1928 Republican nominee Herbert Hoover.

George Brinton McClellan was an American soldier, Civil War Union general, civil engineer, railroad executive, and politician who served as the 24th governor of New Jersey. A graduate of West Point, McClellan served with distinction during the Mexican–American War (1846–1848), and later left the Army to serve as an executive and engineer on railroads until the outbreak of the American Civil War (1861–1865). Early in the conflict, McClellan was appointed to the rank of major general and played an important role in raising a well-trained and disciplined army, which would become the Army of the Potomac in the Eastern Theater; he served a brief period as Commanding General of the United States Army of the Union Army.

Andrew William Mellon, sometimes A. W. Mellon, was an American banker, businessman, industrialist, philanthropist, art collector, and politician. From the wealthy Mellon family of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, he established a vast business empire before moving into politics. He served as United States Secretary of the Treasury from March 9, 1921 to February 12, 1932, presiding over the boom years of the 1920s and the Wall Street crash of 1929. A conservative Republican, Mellon favored policies that reduced taxation and the national debt in the aftermath of World War I.

Harper's Weekly, A Journal of Civilization was an American political magazine based in New York City. Published by Harper & Brothers from 1857 until 1916, it featured foreign and domestic news, fiction, essays on many subjects, and humor, alongside illustrations. It carried extensive coverage of the American Civil War, including many illustrations of events from the war. During its most influential period, it was the forum of the political cartoonist Thomas Nast.

Philander Chase Knox was an American lawyer, bank director and politician. A member of the Republican Party, Knox served in the Cabinet of three different presidents and represented Pennsylvania in the United States Senate.

George Brinton McClellan Jr., was an American statesman, author, historian, and educator. The son of the American Civil War general and presidential candidate George B. McClellan, he was the 93rd Mayor of New York City, serving from 1904 to 1909.

John Franklin Fort was an American Republican Party politician, who served as the 33rd governor of New Jersey, from 1908 to 1911. His uncle, George Franklin Fort, was a Democratic Governor of New Jersey from 1851 to 1854.
Frank Tenney Johnson was a painter of the Old American West, and he popularized a style of painting cowboys which became known as "The Johnson Moonlight Technique". Somewhere on the Range is an example of Johnson's moonlight technique. To paint his paintings he used knives, fingers and brushes.

Blau gas is an artificial illuminating gas, similar to propane, named after its inventor, Hermann Blau of Augsburg, Germany. Not or rarely used or produced today, it was manufactured by decomposing mineral oils in retorts by heat, and compressing the resulting naphtha until it liquefied. It was transported in liquid condition, and, like LPG, when released returns to a gaseous state.
George Harvey may refer to:

George Wingfield was a Nevada cattleman and gambler who became a financier, investor and one of the state's most powerful economic and political figures during the period from 1909 to 1932. With future senator George S. Nixon as his mentor after he settled in Winnemucca in 1899, and fellow gambler John Hennessy as his partner in the mining boomtown of Tonopah after 1901, Wingfield rose from faro-dealer to become richest man in Nevada in less than five years.

The 1920 United States presidential election in New York took place on November 2, 1920. All contemporary 48 states were part of the 1920 United States presidential election. Voters chose 45 electors to the Electoral College, which selected the president and vice president.

The 1920 United States presidential election in Massachusetts took place on November 2, 1920, as part of the 1920 United States presidential election, which was held throughout all contemporary 48 states. Voters chose 18 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 1920 United States presidential election in New Jersey took place on November 2, 1920. All contemporary 48 states were part of the 1920 United States presidential election. Voters chose 14 electors to the Electoral College, which selected the president and vice president.

The 1910 New Jersey gubernatorial election was held on November 8, 1910. Democratic nominee and future President Woodrow Wilson defeated Republican Assemblyman Vivian M. Lewis with 53.93% of the vote. During the campaign, Wilson underwent a political transformation from a symbol of conservative Wall Street reaction into one of the leading members of his party's progressive faction. His victory was widely understood to be the prelude to his campaign for the presidency in 1912.

In the 1864 U.S. presidential election, the Democrats nominated Union Army General George McClellan for U.S. President and Ohio U.S. Representative George Pendleton for U.S. Vice President. During the campaign, McClellan vowed to do a better job of prosecuting the Union Army effort in the American Civil War than incumbent U.S. President Abraham Lincoln did. Ultimately, the McClellan-Pendleton ticket lost to the National Union ticket of Abraham Lincoln and former U.S. Senator Andrew Johnson.

James Horace Harding was an American banker, financier and art collector.
Victor Herbert Smalley was a writer, reporter and promoter who worked at newspapers, songwriting, and playwriting in the United States. In 1907 he wrote "That Lovin' Rag" with music by Bernie Adler. He died at age 32 of appendicitis. Victor Records recorded The Peerless Quartet performing their song "That Fussy Rag" in 1910. Lou Busch recorded the song "Dat Lovin' Rag" he wrote with Adler on the 1950 album Honky-Tonk Piano, re-titled as "That Everlovin' Rag" and rearranged. It was also recorded by Dick Hyman in 1958 his a honky-tonk album as "Knuckles O'Toole". It and "That Fussy Rag" continue to be performed in the 21st century at various ragtime events.

















