Related Research Articles

In mathematics, differential topology is the field dealing with the topological properties and smooth properties of smooth manifolds. In this sense differential topology is distinct from the closely related field of differential geometry, which concerns the geometric properties of smooth manifolds, including notions of size, distance, and rigid shape. By comparison differential topology is concerned with coarser properties, such as the number of holes in a manifold, its homotopy type, or the structure of its diffeomorphism group. Because many of these coarser properties may be captured algebraically, differential topology has strong links to algebraic topology.

Differential geometry is a mathematical discipline that studies the geometry of smooth shapes and smooth spaces, otherwise known as smooth manifolds. It uses the techniques of differential calculus, integral calculus, linear algebra and multilinear algebra. The field has its origins in the study of spherical geometry as far back as antiquity. It also relates to astronomy, the geodesy of the Earth, and later the study of hyperbolic geometry by Lobachevsky. The simplest examples of smooth spaces are the plane and space curves and surfaces in the three-dimensional Euclidean space, and the study of these shapes formed the basis for development of modern differential geometry during the 18th and 19th centuries.
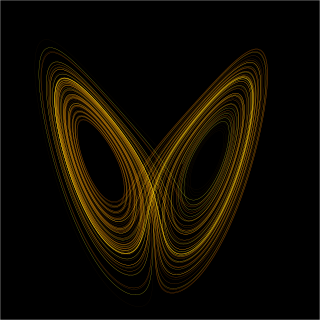
In mathematics, a dynamical system is a system in which a function describes the time dependence of a point in an ambient space, such as in a parametric curve. Examples include the mathematical models that describe the swinging of a clock pendulum, the flow of water in a pipe, the random motion of particles in the air, and the number of fish each springtime in a lake. The most general definition unifies several concepts in mathematics such as ordinary differential equations and ergodic theory by allowing different choices of the space and how time is measured. Time can be measured by integers, by real or complex numbers or can be a more general algebraic object, losing the memory of its physical origin, and the space may be a manifold or simply a set, without the need of a smooth space-time structure defined on it.

Sir Michael Francis Atiyah was a British-Lebanese mathematician specialising in geometry. His contributions include the Atiyah–Singer index theorem and co-founding topological K-theory. He was awarded the Fields Medal in 1966 and the Abel Prize in 2004.

In mathematics, topology is concerned with the properties of a geometric object that are preserved under continuous deformations, such as stretching, twisting, crumpling, and bending; that is, without closing holes, opening holes, tearing, gluing, or passing through itself.

Vector calculus, or vector analysis, is concerned with differentiation and integration of vector fields, primarily in 3-dimensional Euclidean space The term "vector calculus" is sometimes used as a synonym for the broader subject of multivariable calculus, which spans vector calculus as well as partial differentiation and multiple integration. Vector calculus plays an important role in differential geometry and in the study of partial differential equations. It is used extensively in physics and engineering, especially in the description of electromagnetic fields, gravitational fields, and fluid flow.

Algebraic topology is a branch of mathematics that uses tools from abstract algebra to study topological spaces. The basic goal is to find algebraic invariants that classify topological spaces up to homeomorphism, though usually most classify up to homotopy equivalence.

In abstract algebra, group theory studies the algebraic structures known as groups. The concept of a group is central to abstract algebra: other well-known algebraic structures, such as rings, fields, and vector spaces, can all be seen as groups endowed with additional operations and axioms. Groups recur throughout mathematics, and the methods of group theory have influenced many parts of algebra. Linear algebraic groups and Lie groups are two branches of group theory that have experienced advances and have become subject areas in their own right.
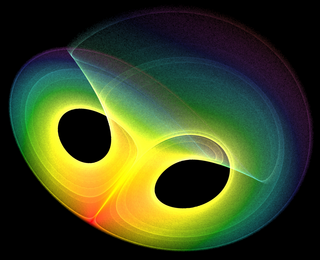
Analysis is the branch of mathematics dealing with continuous functions, limits, and related theories, such as differentiation, integration, measure, infinite sequences, series, and analytic functions.

Shing-Tung Yau is a Chinese-American mathematician and the William Caspar Graustein Professor of Mathematics at Harvard University. In April 2022, Yau announced retirement from Harvard to become Chair Professor of mathematics at Tsinghua University.
In the mathematical field of differential geometry, Ricci-flatness is a condition on the curvature of a (pseudo-)Riemannian manifold. Ricci-flat manifolds are a special kind of Einstein manifold. In theoretical physics, Ricci-flat Lorentzian manifolds are of fundamental interest, as they are the solutions of Einstein's field equations in vacuum with vanishing cosmological constant.
In mathematics, a pseudogroup is a set of diffeomorphisms between open sets of a space, satisfying group-like and sheaf-like properties. It is a generalisation of the concept of a group, originating however from the geometric approach of Sophus Lie to investigate symmetries of differential equations, rather than out of abstract algebra. The modern theory of pseudogroups was developed by Élie Cartan in the early 1900s.
A stochastic differential equation (SDE) is a differential equation in which one or more of the terms is a stochastic process, resulting in a solution which is also a stochastic process. SDEs have many applications throughout pure mathematics and are used to model various behaviours of stochastic models such as stock prices, random growth models or physical systems that are subjected to thermal fluctuations.

Louis Nirenberg was a Canadian-American mathematician, considered one of the most outstanding mathematicians of the 20th century.

In mathematics, a manifold is a topological space that locally resembles Euclidean space near each point. More precisely, an -dimensional manifold, or -manifold for short, is a topological space with the property that each point has a neighborhood that is homeomorphic to an open subset of -dimensional Euclidean space.

Geometric analysis is a mathematical discipline where tools from differential equations, especially elliptic partial differential equations (PDEs), are used to establish new results in differential geometry and differential topology. The use of linear elliptic PDEs dates at least as far back as Hodge theory. More recently, it refers largely to the use of nonlinear partial differential equations to study geometric and topological properties of spaces, such as submanifolds of Euclidean space, Riemannian manifolds, and symplectic manifolds. This approach dates back to the work by Tibor Radó and Jesse Douglas on minimal surfaces, John Forbes Nash Jr. on isometric embeddings of Riemannian manifolds into Euclidean space, work by Louis Nirenberg on the Minkowski problem and the Weyl problem, and work by Aleksandr Danilovich Aleksandrov and Aleksei Pogorelov on convex hypersurfaces. In the 1980s fundamental contributions by Karen Uhlenbeck, Clifford Taubes, Shing-Tung Yau, Richard Schoen, and Richard Hamilton launched a particularly exciting and productive era of geometric analysis that continues to this day. A celebrated achievement was the solution to the Poincaré conjecture by Grigori Perelman, completing a program initiated and largely carried out by Richard Hamilton.
In mathematics, topological dynamics is a branch of the theory of dynamical systems in which qualitative, asymptotic properties of dynamical systems are studied from the viewpoint of general topology.

Geometry is a branch of mathematics concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. Geometry is, along with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is called a geometer. Until the 19th century, geometry was almost exclusively devoted to Euclidean geometry, which includes the notions of point, line, plane, distance, angle, surface, and curve, as fundamental concepts.

Leon Melvyn Simon, born in 1945, is a Leroy P. Steele Prize and Bôcher Prize-winning mathematician, known for deep contributions to the fields of geometric analysis, geometric measure theory, and partial differential equations. He is currently Professor Emeritus in the Mathematics Department at Stanford University.
Mathematics is a broad subject that is commonly divided in many areas that may be defined by their objects of study, by the used methods, or by both. For example, analytic number theory is a subarea of number theory devoted to the use of methods of analysis for the study of natural numbers.
References
- ↑ Smale, S. (January 1969). "What is Global Analysis". American Mathematical Monthly. 76 (1): 4–9. doi:10.2307/2316777.
- ↑ Richard S. Palais (1968). Foundations of Global Non-Linear Analysis (PDF). W.A. Benjamin, Inc.
- ↑ Andreas Kriegl and Peter W. Michor (1991). The Convenient Setting of Global Analysis (PDF). American Mathematical Society. pp. 1–7. ISBN 0-8218-0780-3.
- ↑ Marsden, Jerrold E. (1974). Applications of global analysis in mathematical physics . Berkeley, CA.: Publish or Perish, Inc. p. Chapter 2. ISBN 0-914098-11-X.