
Changsha is the capital and the largest city of Hunan Province of China. Changsha is the 17th most populous city in China with a population of over 10 million, and the third-most populous city in Central China, located in the lower reaches of the Xiang River in northeastern Hunan. Changsha is also called Xingcheng and was once named Linxiang, Tanzhou, and Qingyang (青阳) in ancient times. It is also known as Shanshuizhoucheng (山水洲城), with the Xiang River flowing through it, containing Mount Yuelu and Orange Isle. The city forms a part of the Greater Changsha Metropolitan Region along with Zhuzhou and Xiangtan, also known as Changzhutan City Cluster. Greater Changsha was named one of the 13 emerging mega-cities in China in 2012 by the Economist Intelligence Unit. It is also a National Comprehensive Transportation Hub, and one of the first National Famous Historical and Cultural Cities in China. Changshanese, a kind of Xiang Chinese, is spoken in the downtown, while Ningxiangnese and Liuyangnese are also spoken in the counties and cities under its jurisdiction. As of the 2020 Chinese census, the prefecture-level city of Changsha had a population of 10,047,914 inhabitants.

In probability theory and statistics, the gamma distribution is a versatile two-parameter family of continuous probability distributions. The exponential distribution, Erlang distribution, and chi-squared distribution are special cases of the gamma distribution. There are two equivalent parameterizations in common use:
- With a shape parameter k and a scale parameter θ
- With a shape parameter and an inverse scale parameter , called a rate parameter.
In biology and biochemistry, protease inhibitors, or antiproteases, are molecules that inhibit the function of proteases. Many naturally occurring protease inhibitors are proteins.

The Structural Classification of Proteins (SCOP) database is a largely manual classification of protein structural domains based on similarities of their structures and amino acid sequences. A motivation for this classification is to determine the evolutionary relationship between proteins. Proteins with the same shapes but having little sequence or functional similarity are placed in different superfamilies, and are assumed to have only a very distant common ancestor. Proteins having the same shape and some similarity of sequence and/or function are placed in "families", and are assumed to have a closer common ancestor.

A global city, also known as a power city, world city, alpha city, or world center, is a city that serves as a primary node in the global economic network. The concept originates from geography and urban studies, based on the thesis that globalization has created a hierarchy of strategic geographic locations with varying degrees of influence over finance, trade, and culture worldwide. The global city represents the most complex and significant hub within the international system, characterized by links binding it to other cities that have direct, tangible effects on global socioeconomic affairs.

The Taipei–Keelung metropolitan area also commonly known as Greater Taipei Area is the largest metropolitan area in Taiwan. It is composed of 3 administrative divisions: Taipei, New Taipei City and Keelung. The region encompasses an area of 2,457.13 square kilometers (948.70 sq mi) and a population of 7,034,084 as of 2019. It is the most populous and the most densely populated metropolitan area in Taiwan, with one-third of Taiwanese people living and working there. In some sources, Taoyuan City is considered as part of the metropolitan area on a broader extent, but is usually considered as a metropolitan area of its own.
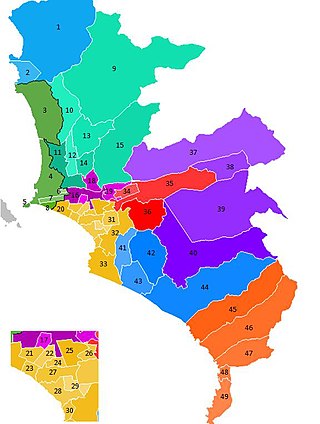
The Lima Metropolitan Area is an area formed by the conurbation of the Peruvian provinces of Lima and Callao. It is the largest of the metropolitan areas of Peru, the seventh largest in the Americas, the fourth largest in Latin America, and among the thirty largest in the world. The conurbation process started to be evident in the 1980s.
The following are the international rankings of Jordan.
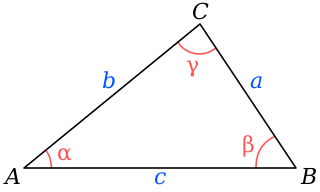
In trigonometry, the law of cosines relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. For a triangle with sides and opposite respective angles and , the law of cosines states:

NyLon is the concept of New York City and London as twin cities—the financial, commercial and cultural capitals of the Anglo-American world. There is a community of high-earning professionals who commute between these cities on the busy transatlantic air route. To satisfy the tastes of this common community, businesses such as Time Out and Conran establish branches in both cities.

There are eleven metropolitan regions in Germany consisting of the country's most densely populated cities and their catchment areas. They represent Germany's political, commercial and cultural centres. The eleven metropolitan regions in Germany were organised into political units for planning purposes.
Loughborough Lightning is an English netball team based at Loughborough University. Their senior team plays in the Netball Superleague. In 2005–06 they were founder members of the league. They also enter under-19 and under-21 teams in the National Performance League. Using the name Loughborough Students, Loughborough University also enter teams in intervarsity leagues organised by British Universities and Colleges Sport. Together with the women's cricket team, the women's rugby union team, the women's cycling team, the women's football team and the women's wheelchair basketball team, the netball team is one of five women's sports teams based at Loughborough University that use the Loughborough Lightning name.

Athletic Club Chalkis, also known as A.C. Chalkida, is an association football club based in Chalkida, Greece. The club was founded in 1967 upon the merger of Olympiakos Chalkida and Evrypos Chalkida. Its colours are black and blue and its symbol is the nymph Arethusa.

Triglia Rafinas is a Greek amateur association football club located in Rafina, Attica, Greece. It was founded in 1931 by a particular union of amateur clubs. The original symbol of the team was the barbouna or red Mullet (trigli). Its colors are black and yellow, which are the colors of the Byzantine flag. Today, the club keeps its colors, but the symbol has been changed to a two-headed eagle, the Byzantine symbol.

Americium-241 is an isotope of americium. Like all isotopes of americium, it is radioactive, with a half-life of 432.2 years. 241
Am
is the most common isotope of americium as well as the most prevalent isotope of americium in nuclear waste. It is commonly found in ionization type smoke detectors and is a potential fuel for long-lifetime radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs). Its common parent nuclides are β− from 241
Pu
, EC from 241
Cm
, and α from 245
Bk
. 241
Am
is not fissile, but is fissionable, and the critical mass of a bare sphere is 57.6–75.6 kilograms (127.0–166.7 lb) and a sphere diameter of 19–21 centimetres (7.5–8.3 in). Americium-241 has a specific activity of 3.43 Ci/g (126.91 GBq/g). It is commonly found in the form of americium-241 dioxide. This isotope also has one meta state, 241m
Am
, with an excitation energy of 2.2 MeV (0.35 pJ) and a half-life of 1.23 μs. The presence of americium-241 in plutonium is determined by the original concentration of plutonium-241 and the sample age. Because of the low penetration of alpha radiation, americium-241 only poses a health risk when ingested or inhaled. Older samples of plutonium containing 241
Pu
contain a buildup of 241
Am
. A chemical removal of americium-241 from reworked plutonium may be required in some cases.
The following are international rankings of Shanghai by categories.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Milan:

The Moderus Gamma is an articulated tram manufactured in Biskupice, Poland, since 2016 by Modertrans Poznań, a subsidiary of transport operator MPK Poznań. Planning began in 2008 and the prototype was completed in 2016.

The term variant of concern (VOC) for SARS-CoV-2, which causes COVID-19, is a category used for variants of the virus where mutations in their spike protein receptor binding domain (RBD) substantially increase binding affinity in RBD-hACE2 complex, while also being linked to rapid spread in human populations.

















