
A server farm or server cluster is a collection of computer servers, usually maintained by an organization to supply server functionality far beyond the capability of a single machine. They often consist of thousands of computers which require a large amount of power to run and to keep cool. At the optimum performance level, a server farm has enormous financial and environmental costs. They often include backup servers that can take over the functions of primary servers that may fail. Server farms are typically collocated with the network switches and/or routers that enable communication between different parts of the cluster and the cluster's users. Server "farmers" typically mount computers, routers, power supplies and related electronics on 19-inch racks in a server room or data center.

A data center or data centre is a building, a dedicated space within a building, or a group of buildings used to house computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems.

An evaporative cooler is a device that cools air through the evaporation of water. Evaporative cooling differs from other air conditioning systems, which use vapor-compression or absorption refrigeration cycles. Evaporative cooling exploits the fact that water will absorb a relatively large amount of heat in order to evaporate. The temperature of dry air can be dropped significantly through the phase transition of liquid water to water vapor (evaporation). This can cool air using much less energy than refrigeration. In extremely dry climates, evaporative cooling of air has the added benefit of conditioning the air with more moisture for the comfort of building occupants.

Computer cooling is required to remove the waste heat produced by computer components, to keep components within permissible operating temperature limits. Components that are susceptible to temporary malfunction or permanent failure if overheated include integrated circuits such as central processing units (CPUs), chipsets, graphics cards, hard disk drives, and solid state drives.
Green computing, green IT, or ICT sustainability, is the study and practice of environmentally sustainable computing or IT.
Economizers, or economisers (UK), are mechanical devices intended to reduce energy consumption, or to perform useful function such as preheating a fluid. The term economizer is used for other purposes as well. Boiler, power plant, heating, refrigeration, ventilating, and air conditioning (HVAC) uses are discussed in this article. In simple terms, an economizer is a heat exchanger.

Water efficiency is the practice of reducing water consumption by measuring the amount of water required for a particular purpose and is proportionate to the amount of essential water used. Water efficiency differs from water conservation in that it focuses on reducing waste, not restricting use. Solutions for water efficiency not only focus on reducing the amount of potable water used but also on reducing the use of non-potable water where appropriate. It also emphasizes the influence consumers can have on water efficiency by making small behavioral changes to reduce water wastage, and by choosing more water-efficient products.
The Climate Savers Computing Initiative was a nonprofit group of consumers, businesses and conservation organizations dedicated to promoting smart technologies that improve power efficiency and reduce energy consumption of computers. Formed in 2007, it was based in Portland, Oregon. In July 2012, Climate Savers Computing Initiative combined with The Green Grid and its programs continue within that organization.

A server room is a room, usually air-conditioned, devoted to the continuous operation of computer servers. An entire building or station devoted to this purpose is a data center.
In computing, performance per watt is a measure of the energy efficiency of a particular computer architecture or computer hardware. Literally, it measures the rate of computation that can be delivered by a computer for every watt of power consumed. This rate is typically measured by performance on the LINPACK benchmark when trying to compare between computing systems: an example using this is the Green500 list of supercomputers. Performance per watt has been suggested to be a more sustainable measure of computing than Moore's Law.
The Green Grid is a nonprofit, industry consortium of end-users, policy-makers, technology providers, facility architects, and utility companies collaborating to improve the resource efficiency of data centers.
Power usage effectiveness (PUE) is a ratio that describes how efficiently a computer data center uses energy; specifically, how much energy is used by the computing equipment.
Data center infrastructure efficiency (DCIE), is a performance improvement metric used to calculate the energy efficiency of a data center. DCIE is the percentage value derived, by dividing information technology equipment power by total facility power.
Green Power Usage Effectiveness (GPUE) is a proposed measurement of both how much sustainable energy a computer data center uses, its carbon footprint per usable kilowatt hour (kWh) and it uses its power; specifically, how much of the power is actually used by the computing equipment. It is an addition to the power usage effectiveness (PUE) definition and was first proposed by Greenqloud.
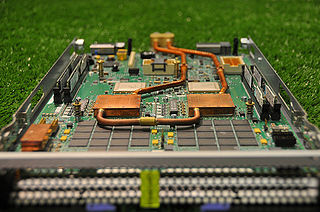
Aquasar is a supercomputer prototype created by IBM Labs in collaboration with ETH Zurich in Zürich, Switzerland and ETH Lausanne in Lausanne, Switzerland. While most supercomputers use air as their coolant of choice, the Aquasar uses hot water to achieve its great computing efficiency. Along with using hot water as the main coolant, an air-cooled section is also included to be used to compare the cooling efficiency of both coolants. The comparison could later be used to help improve the hot water coolant's performance. The research program was first termed to be: "Direct use of waste heat from liquid-cooled supercomputers: the path to energy saving, emission-high performance computers and data centers." The waste heat produced by the cooling system is able to be recycled back in the building's heating system, potentially saving money. Beginning in 2009, the three-year collaborative project was introduced and developed in the interest of saving energy and being environmentally-safe while delivering top-tier performance.

The HP Performance Optimized Datacenter (POD) is a range of three modular data centers manufactured by HP.

Mechanical, electrical and plumbing (MEP) refers to the installation of services which provide a functional and comfortable space for the building occupants. In residential and commercial buildings, these elements are often designed by specialized MEP engineers. MEP's design is important for planning, decision-making, accurate documentation, performance- and cost-estimation, construction, and operating/maintaining the resulting facilities.
Water Usage Effectiveness (WUE) is a sustainability metric created by The Green Grid in 2011 to attempt to measure the amount of water used by datacenters to cool their IT assets. To calculate simple WUE, a data center manager divides the annual site water usage in liters by the IT equipment energy usage in kilowatt hours (Kwh). Water usage includes water used for cooling, regulating humidity and producing electricity on-site. More complex WUE calculations are available from The Green Grid website.

Immersion cooling is an IT cooling practice by which complete servers are immersed in a dielectric, electrically non-conductive fluid that has significantly higher thermal conductivity than air. Heat is removed from a system by putting the coolant in direct contact with hot components, and circulating the heated liquid through heat exchangers. This practice is highly effective because liquid coolants can absorb more heat from the system, and are more easily circulated through the system, than air. Immersion cooling has many benefits, including but not limited to: sustainability, performance, reliability and cost
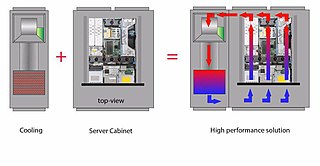
Close Coupled Cooling is a last generation cooling system particularly used in data centers. The goal of close coupled cooling is to bring heat transfer closest to its source: the equipment rack. By moving the air conditioner closer to the equipment rack a more precise delivery of inlet air and a more immediate capture of exhaust air is ensured.





















