
Lake Malawi, also known as Lake Nyasa in Tanzania and Lago Niassa in Mozambique, is an African Great Lake and the southernmost lake in the East African Rift system, located between Malawi, Mozambique and Tanzania.

Mouthbrooding, also known as oral incubation and buccal incubation, is the care given by some groups of animals to their offspring by holding them in the mouth of the parent for extended periods of time. Although mouthbrooding is performed by a variety of different animals, such as the Darwin's frog, fish are by far the most diverse mouthbrooders. Mouthbrooding has evolved independently in several different families of fish.

Mbuna is the common name for a large group of African cichlids from Lake Malawi, and are members of the haplochromine family. The name mbuna means "rockfish" in the language of the Tonga people of Malawi. As the name implies, most mbuna are cichlids that live among the piles of rocks and along the rocky shores of Lake Malawi, as opposed to the utaka, cichlids that live in the open water or on sandy shores or soft substrates. Some species of mbuna are highly sexually dimorphic, although many are not. Among biologists, almost all of the cichlid species of Lake Malawi, including mbuna and non mbuna such as the utaka, are believed to have descended from one or a very few species that became isolated in the lake. With rising water levels, new habitats could be colonized and the many isolated rocky outcrops allowed new mbuna species to form. Their striking colors, intriguing behavioral characteristics, and relative hardiness make them very popular despite their unique demands for the home aquarist.

Maylandia estherae is a haplochromine cichlid. It is a rock dwelling fish or mbuna from Lake Malawi. This fish, like most cichlids from Lake Malawi, is a mouthbrooder - females hold their fertilized eggs then fry in their mouths until they are released after about 21 days.

Aulonocara is a genus of haplochromine cichlids endemic to Lake Malawi in East Africa. All Aulonocara species are maternal mouth brooders. Particularly in the aquarium hobby, Aulonocara species are also known as peacock cichlids, aulonocaras or simply "peacocks". This genus is strongly sexually dichromic, even by haplochromine standards.

Maylandia or Metriaclima is a genus of haplochromine cichlids endemic to Lake Malawi in East Africa. They belong to the mbuna (rock-dwelling) haplochromines.

Melanochromis is a genus of haplochromine cichlids endemic to Lake Malawi in Eastern Africa. Ecologically, they belong to the rock-dwelling mbuna cichlids of Lake Malawi.

Sciaenochromis is a genus of haplochromine cichlids endemic to Lake Malawi in East Africa. The species are popular in the aquarium hobby, most notably S. fryeri.

Iodotropheus is a small genus of cichlids endemic to Lake Malawi in east Africa. The genus is distinguished from other genera of mbuna by the upper lip which is usually connected medially to the skin of the snout by a frenum; by its small, terminal mouth; by the outer teeth of both jaws, which are unequally bicuspid and loosely spaced, the tooth shafts inclined slightly toward the jaw symphysis; by the anterior teeth of the upper jaw being much longer and more robust than the lateral and posterior teeth. The rusty cichlid or lavender mbuna, Iodotropheus sprengerae is the most commonly encountered member of the genus in the aquarium trade.

Iodotropheus sprengerae, the rusty cichlid, lavender mbuna or lavender cichlid, is a species of cichlid endemic to the Boadzulu and Chinyankwazi Islands and Chinyamwezi Island regions of Lake Malawi. It prefers a temperature range of 24-26 °C.

Haplochromis is a ray-finned fish genus in the family Cichlidae. It has been used as the default "wastebin taxon" for Pseudocrenilabrinae cichlids of the East African Rift, and as such became the "largest" fish "genus". Many of these cichlids are popular aquarium fishes; like similar Haplochromini they are known as "haplos", "happies" or "haps" among aquarium enthusiasts.

Copadichromis borleyi is a species of haplochromine cichlid fish endemic to Lake Malawi in East Africa. The species is popular in the fishkeeping hobby where it is frequently kept in aquariums. The species has numerous common names, including redfin hap and goldfin hap.

The nkhomo-benga peacock, also known as the new yellow regal peacock, is a species of haplochromine cichlid which is endemic to Lake Malawi. This species is threatened by capture for the aquarium trade.
Aulonocara guentheri is a species of haplochromine cichlid endemic to Lake Malawi, where they are restricted to the south eastern arm, and Lake Malombe, meaning that as far as is known this fish is endemic to Malawi. It prefers shallow sandy habitat where it forages in small schools, males in breeding colours have been caught by fishermen in November and December suggesting that is when they breed. The specific name honours the German born British herpetologist and ichthyologist Albert Günther (1830-1914), who was one of the first scientists to recognise the diversity of te cichlids in Lake Malawi.

The sulfurhead aulonocara or sulfurhead peacock is a species of haplochromine cichlid which is endemic to Lake Malawi in the country of Malawi and has only been observed on West Reef and Eccles Reef. It is threatened by collection for the aquarium trade and this has caused a 70% reduction in numbers. In this mouthbrooding species, the eggs are cared for by the females only, and it is found over mixed sand and rocky areas where they hunt small invertebrates in the sand. It closely resembles the blue orchid aulonocara though it develops a yellow blaze across its dorsal In the past these two taxa have been considered to be subspecies. The specific name honours Hans-Joachim Mayland, an author on cichlids and a fishkeeper, brought the species to the attention of Ethelwynn Trewavas.
The greenface aulonocara is a species of haplochromine cichlid which is endemic to Lake Malawi.

The flavescent peacock, also known as Grant's peacock, is a species of haplochromine cichlid. Its common name refers to its "flavescent" (yellowish) colour.
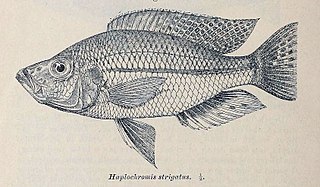
Dimidiochromis strigatus is a species of haplochromine cichlid endemic to Malawi. It was formerly placed in the genus Haplochromis and known as Haplochromis 'sunset' in the aquarium fish trade.

Melanochromis loriae is a species of cichlid in the Cichlidae endemic to Lake Malawi. This species can reach a length of 12.5 centimetres (4.9 in) TL.

The Pseudocrenilabrinae are a subfamily in the cichlid family of fishes to which, according to a study from 2004, includes all the Middle Eastern and African cichlids with the exception of the unusual Heterochromis multidens and the Malagasy species. This subfamily includes more than 1,100 species. Previous authors recognized additional African subfamilies, e.g. the Tilapiinae of Hoedeman (1947), Tylochrominae of Poll (1986), or Boulengerochrominae of Tawil (2001).





















