Conjugation or conjugate may refer to:

In mathematics, a holomorphic function is a complex-valued function of one or more complex variables that is complex differentiable in a neighbourhood of each point in a domain in complex coordinate space Cn. The existence of a complex derivative in a neighbourhood is a very strong condition: it implies that a holomorphic function is infinitely differentiable and locally equal to its own Taylor series (analytic). Holomorphic functions are the central objects of study in complex analysis.

In mathematics and physics, Laplace's equation is a second-order partial differential equation named after Pierre-Simon Laplace, who first studied its properties. This is often written as
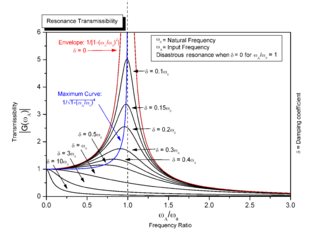
Resonance describes the phenomenon of increased amplitude that occurs when the frequency of an applied periodic force is equal or close to a natural frequency of the system on which it acts. When an oscillating force is applied at a resonant frequency of a dynamic system, the system will oscillate at a higher amplitude than when the same force is applied at other, non-resonant frequencies.

In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is an equation which imposes relations between the various partial derivatives of a multivariable function.

In mathematics, mathematical physics and the theory of stochastic processes, a harmonic function is a twice continuously differentiable function where U is an open subset of that satisfies Laplace's equation, that is,

In physics, a phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter, specifically in solids and some liquids. A type of quasiparticle, a phonon is an excited state in the quantum mechanical quantization of the modes of vibrations for elastic structures of interacting particles. Phonons can be thought of as quantized sound waves, similar to photons as quantized light waves.
Normal(s) or The Normal(s) may refer to:
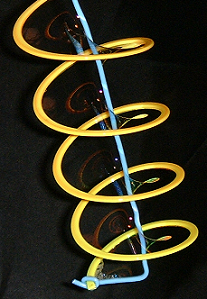
In mathematics, a minimal surface is a surface that locally minimizes its area. This is equivalent to having zero mean curvature.
In mathematics, a closed-form expression is a mathematical expression that uses a finite number of standard operations. It may contain constants, variables, certain well-known operations, and functions, but usually no limit, differentiation, or integration. The set of operations and functions may vary with author and context.

Amongst the lay public of non-mathematicians and non-scientists, trigonometry is known chiefly for its application to measurement problems, yet is also often used in ways that are far more subtle, such as its place in the theory of music; still other uses are more technical, such as in number theory. The mathematical topics of Fourier series and Fourier transforms rely heavily on knowledge of trigonometric functions and find application in a number of areas, including statistics.
In mathematics, a real-valued function defined on a connected open set is said to have a conjugate (function) if and only if they are respectively the real and imaginary parts of a holomorphic function of the complex variable That is, is conjugate to if is holomorphic on As a first consequence of the definition, they are both harmonic real-valued functions on . Moreover, the conjugate of if it exists, is unique up to an additive constant. Also, is conjugate to if and only if is conjugate to .

In mathematics, a differential equation is an equation that relates one or more unknown functions and their derivatives. In applications, the functions generally represent physical quantities, the derivatives represent their rates of change, and the differential equation defines a relationship between the two. Such relations are common; therefore, differential equations play a prominent role in many disciplines including engineering, physics, economics, and biology.
In mathematics and mathematical physics, potential theory is the study of harmonic functions.
In mathematics, the Sommerfeld radiation condition is a concept from theory of differential equations and scattering theory used for choosing a particular solution to the Helmholtz equation. It was introduced by Arnold Sommerfeld in 1912 and is closely related to the limiting absorption principle (1905) and the limiting amplitude principle (1948).
Algebra is one of the broad areas of mathematics. Roughly speaking, algebra is the study of mathematical symbols and the rules for manipulating these symbols in formulas; it is a unifying thread of almost all of mathematics.

Vibration is a mechanical phenomenon whereby oscillations occur about an equilibrium point. The word comes from Latin vibrationem. The oscillations may be periodic, such as the motion of a pendulum—or random, such as the movement of a tire on a gravel road.
Special functions are particular mathematical functions that have more or less established names and notations due to their importance in mathematical analysis, functional analysis, geometry, physics, or other applications.
In mathematics, a real differential one-form ω on a surface is called a harmonic differential if ω and its conjugate one-form, written as ω∗, are both closed.






