Newspaper sections

- Cover News
- Forum & Reflection
- Home News
- International News
- Editorial
- Opinion
- Focus
- Focus: Faith Alive
- Focus: Children
- Focus: Youth
- Chinese
- Bahasa Malaysia
- Weekly reading
- Supplements
- Today's Shalom
| Type | Weekly newspaper |
|---|---|
| Format | Compact |
| Owner(s) | The Titual Archbishop of Kuala Lumpur, on behalf of the Catholic Bishops of Peninsular Malaysia |
| Editor | Father Lawrence Andrew, SJ |
| Founded | 8 September 1994 |
| Headquarters | Archdiocesan Pastoral Centre, 5 Robertson Road, 50150 Kuala Lumpur |
| Circulation | 15,600 |
| Website | Official website |
Herald Malaysia is a multilingual Malaysian Catholic weekly newspaper. It publishes in English with additional language sections inside in Chinese, Tamil and Malaysian languages.
It has a circulation of 15,600 copies in Malaysia. [1] It is printed in English, Malay, Tamil and Chinese, and meant for distribution to Malaysian Catholics. [2]

The Herald newspaper nearly lost its publishing licence for using the word "Allah" as a translation for "God," with authorities saying it should only be used by Muslims. The weekly was warned not to print "Allah" in the future, but instead it mounted an ongoing legal challenge to revoke the ban on the word, which is also used in the Malay-language Bible. [3]

Allah is the common Arabic word for God. In the English language, the word generally refers to God in Islam. The word is thought to be derived by contraction from al-ilāh, which means "the god", and is linguistically related to the Aramaic words Elah and Syriac ܐܲܠܵܗܵܐ (ʼAlāhā) and the Hebrew word El (Elohim) for God.
Manglish is an informal form of Malaysian English with features of an English-based creole principally used in Malaysia. It is heavily influenced by the dominant languages of the country, Malay, Chinese languages, and Tamil. It is not an official language of Malaysia.
Freedom of religion is enshrined in the Malaysian Constitution. First, Article 11 provides that every person has the right to profess and to practice his or her religion and to propagate it. Second, the Constitution also provides that Islam is the religion of the country but other religions may be practised in peace and harmony.
The New Straits Times is an English-language newspaper published in Malaysia. It is Malaysia's oldest newspaper still in print, having been founded as The Straits Times on 15 July 1845. It was relaunched as the New Straits Times on 13 August 1974. The paper served as Malaysia's only broadsheet format English-language newspaper.
Education in Malaysia is overseen by the Ministry of Education. Although education is the responsibility of the Federal Government, each state and federal territory has an Education Department to co-ordinate educational matters in its territory. The main legislation governing education is the Education Act 1996.
Mediacorp Pte. Ltd. is a media conglomerate in Singapore. Owned by Temasek Holdings—the holding company of the Government of Singapore—it owns television, radio, and digital media properties in the country.

Christianity is a minority religion in Malaysia. In the 2020 census, 9.1% of the Malaysian population identified themselves as Christians. About two-thirds of Malaysia's Christian population lives in East Malaysia, in the states of Sabah and Sarawak. Adherents of Christianity represent majority (50.1%) of the population in Sarawak, which is Malaysia's largest state by land area. The major Christian denominations in Malaysia include Roman Catholics, Anglicans, Baptists, Brethren, non-denominational churches, independent Charismatic churches, Lutherans, Methodists, and Presbyterians.

The culture of Malaysia draws on the varied cultures of the different people of Malaysia. The first people to live in the area were indigenous tribes that still remain; they were followed by the Malays, who moved there from mainland Asia in ancient times. Chinese and Indian cultural influences made their mark when trade began with those countries, and increased with immigration to Malaysia. Other cultures that heavily influenced that of Malaysia include Persian, Arabic, British. The many different ethnicities that currently exist in Malaysia have their own unique and distinctive cultural identities, with some crossover.

Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. The federal constitutional monarchy consists of thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two regions, Peninsular Malaysia and Borneo's East Malaysia. Peninsular Malaysia shares a land and maritime border with Thailand and maritime borders with Singapore, Vietnam, and Indonesia. East Malaysia shares land and maritime borders with Brunei and Indonesia and a maritime border with the Philippines and Vietnam. Kuala Lumpur is the national capital, largest city and the seat of the legislative branch of the federal government. The nearby planned capital of Putrajaya is the administrative capital, which represents the seat of both the executive branch and the judicial branch of the federal government. With a population of over 32 million, Malaysia is the world's 45th-most populous country. The southernmost point of continental Eurasia is in Tanjung Piai. In the tropics, Malaysia is one of 17 megadiverse countries, home to numerous endemic species.

A multitude of languages are used in Singapore. It consists of several varieties of languages under the families of the Austronesian languages, Dravidian languages, Indo-European languages and Sino-Tibetan languages. According to the Constitution of Singapore, the national language of Singapore is Malay, which plays a symbolic role, as Malays are constitutionally recognised as the indigenous peoples of Singapore, and it is the government's duty to protect their language and heritage. The constitution also states that the four commonly used languages of Singapore are English, Chinese, Malay and Tamil, with the lingua franca between Singaporeans of different races being English, the de facto main language. Singaporeans often speak Singlish among themselves. Singlish is an informal, colloquial form of English that is used in Singapore. Linguists define it as Singapore Colloquial English.
The mass media in Brunei are strictly controlled by the government under Sultan Hassanal Bolkiah, which has effectively imposed martial law in the country since the Brunei Revolt of 1962. News coverage consists of police-beat reporting, lifestyle features, and community events, with little in the way of diverse viewpoints. Reporters Without Borders reports there is "virtually no criticism of the government". The liberal democracy watchdog Freedom House lists Brunei's media as "not free".
Censorship is a long term issue in Malaysia which has become more apparent as it attempts to adapt to a modern knowledge-based economy. Despite having in its Federal Constitution that subject to certain conditions, "every citizen has the right to freedom of speech and expression", Malaysia has consistently sat low on global indexes related to press and media freedom.

Malaysia is a multireligious country, whose official religion is Islam. As of the 2020 Population and Housing Census, 63.5 percent of the population practices Islam; 18.7 percent Buddhism; 9.1 percent Christianity; 6.1 percent Hinduism; and 2.7 percent other religion or gave no information. The remainder is accounted for by other faiths, including Animism, Folk religion, Sikhism, Baháʼí Faith and other belief systems. The states of Sarawak, Penang and the federal territory of Kuala Lumpur have non-Muslim majorities. Numbers of self-described atheists in Malaysia are few; the state has come under criticism from human rights organisations for the government's discrimination against atheists, with some cabinet members saying that "the freedom of religion is not the freedom from religion".
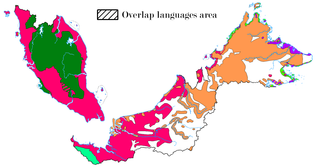
The indigenous languages of Malaysia belong to the Mon-Khmer and Malayo-Polynesian families. The national, or official, language is Malay which is the mother tongue of the majority Malay ethnic group. The main ethnic groups within Malaysia are the Malay people, Han Chinese people and Tamil people, with many other ethnic groups represented in smaller numbers, each with its own languages. The largest native languages spoken in East Malaysia are the Iban, Dusunic, and Kadazan languages. English is widely understood and spoken within the urban areas of the country; the English language is a compulsory subject in primary and secondary education. It is also the main medium of instruction within most private colleges and private universities. English may take precedence over Malay in certain official contexts as provided for by the National Language Act, especially in the states of Sabah and Sarawak, where it may be the official working language. Furthermore, the law of Malaysia is commonly taught and read in English, as the unwritten laws of Malaysia continues to be partially derived from pre-1957 English common law, which is a legacy of past British colonisation of the constituents forming Malaysia. In addition, authoritative versions of constitutional law and statutory law are continuously available in both Malay and English.

Tan Sri Datuk Murphy Nicholas Xavier Pakiam, P.S.M., P.J.N. was the third metropolitan archbishop of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, from 2003 to 2013. He is styled His Grace The Most Reverend Tan Sri Datuk.
Malaysia curbs blasphemy and any insult to religion or to the religious by rigorous control of what people in that country can say or do. Government-funded schools teach young Muslims the principles of Sunni Islam, and instruct young non-Muslims on morals. The government informs the citizenry on proper behavior and attitudes, and ensures that Muslim civil servants take courses in Sunni Islam. The government ensures that the broadcasting and publishing media do not create disharmony or disobedience. If someone blasphemes or otherwise engages in deviant behavior, Malaysia punishes such transgression with Sharia or through legislation such as the Penal Code.
Titular Roman Catholic Archbishop of Kuala Lumpur v. Menteri Dalam Negeri is a court decision by the High Court of Malaya holding that Christians do not have the constitutional right to use the word "Allah" in church newspapers. An appeals court overturned a previous ruling which granted that right. This verdict on appeal was later upheld by the Federal Court of Malaysia.

Dato' Dr. Ibrahim bin Ali is a Malaysian politician. He is informally known as Tok Him. He served as the Member of Parliament (MP) for Pasir Mas from August 1986 to April 1995 and again from March 2008 to May 2013. He is a member of the Parti Bumiputera Perkasa Malaysia (PUTRA), a component party of the Gerakan Tanah Air (GTA) opposition coalition. He has served as the 1st and founding President of PUTRA since May 2019. He is also founding President of the Malay dominance organisation Pertubuhan Pribumi Perkasa (PERKASA).

Pertubuhan Pribumi Perkasa, is a Malay dominance non-governmental organisation (NGO) that was formed by Ibrahim Ali in the aftermath of the 2008 general election (GE12). This conservative, extreme-right, ethnic Malay organisation is led by its president Ibrahim Ali to influence the unity of Malaysian by refusing to accept any decoration of other ethnic group except Malay decoration. The group is reported to have a membership of 700,000.