
Concorde is a retired Franco-British supersonic airliner jointly developed and manufactured by Sud Aviation and the British Aircraft Corporation (BAC). Studies started in 1954, and France and the UK signed a treaty establishing the development project on 29 November 1962, as the programme cost was estimated at £70 million . Construction of the six prototypes began in February 1965, and the first flight took off from Toulouse on 2 March 1969. The market was predicted for 350 aircraft, and the manufacturers received up to 100 option orders from many major airlines. On 9 October 1975, it received its French Certificate of Airworthiness, and from the UK CAA on 5 December.

Supersonic speed is the speed of an object that exceeds the speed of sound (Mach 1). For objects traveling in dry air of a temperature of 20 °C (68 °F) at sea level, this speed is approximately 343.2 m/s. Speeds greater than five times the speed of sound (Mach 5) are often referred to as hypersonic. Flights during which only some parts of the air surrounding an object, such as the ends of rotor blades, reach supersonic speeds are called transonic. This occurs typically somewhere between Mach 0.8 and Mach 1.2.
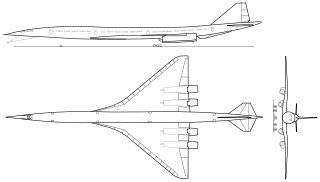
The Boeing 2707 was an American supersonic passenger airliner project during the 1960s. After winning a competition for a government-funded contract to build an American supersonic airliner, Boeing began development at its facilities in Seattle, Washington. The design emerged as a large aircraft with seating for 250 to 300 passengers and cruise speeds of approximately Mach 3. It was intended to be much larger and faster than competing supersonic transport (SST) designs such as Concorde.

A sonic boom is a sound associated with shock waves created when an object travels through the air faster than the speed of sound. Sonic booms generate enormous amounts of sound energy, sounding similar to an explosion or a thunderclap to the human ear.

A supersonic transport (SST) or a supersonic airliner is a civilian supersonic aircraft designed to transport passengers at speeds greater than the speed of sound. To date, the only SSTs to see regular service have been Concorde and the Tupolev Tu-144. The last passenger flight of the Tu-144 was in June 1978 and it was last flown in 1999 by NASA. Concorde's last commercial flight was in October 2003, with a November 26, 2003 ferry flight being its last airborne operation. Following the permanent cessation of flying by Concorde, there are no remaining SSTs in commercial service. Several companies have each proposed a supersonic business jet, which may bring supersonic transport back again.

The Lockheed L-2000 was Lockheed Corporation's entry in a government-funded competition to build the United States' first supersonic airliner in the 1960s. The L-2000 lost the contract to the Boeing 2707, but that competing design was ultimately canceled for political, environmental and economic reasons.
Supercruise is sustained supersonic flight of a supersonic aircraft without using afterburner. Many supersonic military aircraft are not capable of supercruise and can maintain Mach 1+ flight only in short bursts with afterburners. Aircraft such as the SR-71 Blackbird are designed to cruise at supersonic speed with afterburners enabled.
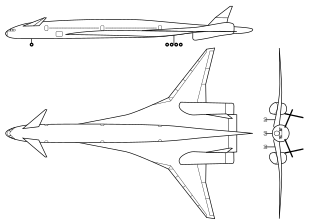
The Boeing Sonic Cruiser was a concept jet airliner with a delta wing–canard configuration. It was distinguished from conventional airliners by its delta wing and high-subsonic cruising speed of up to Mach 0.98. Boeing first proposed it in 2001, but airlines generally preferred lower operating costs over higher speed. Boeing ended the Sonic Cruiser project in December 2002 and shifted to the slower, but more fuel-efficient 7E7 airliner.

The General Dynamics F-16XL is a derivative of the F-16 Fighting Falcon with a cranked-arrow delta wing. It entered the United States Air Force's (USAF) Enhanced Tactical Fighter (ETF) competition in 1981 but lost to the F-15E Strike Eagle. The two prototypes were shelved until being turned over to NASA for additional aeronautical research in 1988. Both aircraft were fully retired in 2009 and stored at Edwards Air Force Base.

A supersonic aircraft is an aircraft capable of supersonic flight, that is, flying faster than the speed of sound. Supersonic aircraft were developed in the second half of the twentieth century. Supersonic aircraft have been used for research and military purposes, but only two supersonic aircraft, the Tupolev Tu-144 and the Concorde, ever entered service for civil use as airliners. Fighter jets are the most common example of supersonic aircraft.

An oblique wing is a variable geometry wing concept. On an aircraft so equipped, the wing is designed to rotate on center pivot, so that one tip is swept forward while the opposite tip is swept aft. By changing its sweep angle in this way, drag can be reduced at high speed without sacrificing low speed performance. This is a variation on the classic swing-wing design, intended to simplify construction and retain the center of gravity as the sweep angle is changed.

A supersonic business jet (SSBJ) is a business jet travelling above the speed of sound: a supersonic aircraft. Some manufacturers are designing or have been designing SSBJs, but none are currently available. Usually intended to transport about ten passengers, proposed SSBJs would be about the same size as subsonic business jets.

Quiet Spike was a collaborative program between Gulfstream Aerospace and NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center to investigate the suppression of sonic booms. The patent was published with the United States Patent and Trademark Office in 2004 and is owned by Gulfstream Aerospace.
The Avion de Transport Supersonique Futur (ATSF) also known as Alliance, was a concept design for supersonic transport that was being worked on by both British Aerospace and Aérospatiale. The aircraft was to be based on the experience learned from the supersonic Concorde, and was to fly at a top speed of roughly Mach 2. Preliminary designs were produced, with some wind-tunnel testing of small-scale models, but development apparently stalled in the early 2000s.
The Next Generation Supersonic Transport is a supersonic transport (SST) being developed by the Japanese Space Agency JAXA. By comparison to the Concorde this new design will carry three times as many passengers and fly roughly at the same speed 1,522.4 mph (2,450.1 km/h). It also has twice the range. The goal is to achieve a ticket price comparable to that of commercial business class. JAXA had expected to launch the plane by 2015. An 11.5-meter prototype was tested on October 10, 2005.
The Gulfstream X-54 is a proposed research and demonstration aircraft, under development in the United States by Gulfstream Aerospace for NASA, that is planned for use in sonic boom and supersonic transport research.
The Zero Emission Hyper Sonic Transport or ZEHST is a planned hypersonic passenger jet airliner project by the multinational aerospace conglomerate EADS and the Japanese national space agency JAXA.

The Aerion AS2 was a proposed supersonic business jet that was being developed by Aerion Corporation. In May 2014, it was announced that the Aerion AS2 would be part of a larger Aerion SBJ redesign, which aimed for release after a seven-year developmental period. Aerion partnered with Airbus in September the same year. In December 2017, Airbus was replaced by Lockheed Martin. Its General Electric Affinity engine was unveiled in October 2018. In February 2019, Boeing replaced Lockheed Martin. Development stopped when Aerion ceased operations in May 2021.

The Lockheed Martin X-59 Quesst, sometimes styled QueSST, is an American experimental supersonic aircraft being developed at Skunk Works for NASA's Low-Boom Flight Demonstrator project. Preliminary design started in February 2016, with the X-59 to be delivered to NASA in 2021 for flight testing in 2023. It is expected to cruise at Mach 1.42 at an altitude of 55,000 ft (16,800 m), creating a low 75 Perceived Level decibel (PLdB) thump to evaluate supersonic transport acceptability.

The Boom Overture is a proposed Mach 1.7, 64–80 passenger supersonic airliner with 4,250 nmi of range, which is planned to be introduced in 2029 by Boom Technology. The company claims that with 500 viable routes, there could be a market for 1,000 supersonic airliners with business class fares. It had gathered 76 commitments by December 2017. The aircraft is planned to have a delta wing configuration, but will be built with composite materials. Following a redesign revealed in 2022 it is intended to be powered by four dry (non-afterburning) 35,000 lbf (160 kN) turbofans. Regulations for takeoff noise or overland boom can be met or changed.
















