Related Research Articles

The Tuscarora are an Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands in Canada and the United States. They are an Iroquoian Native American and First Nations people, based in New York and Ontario.

Ashtabula County is the northeasternmost county in the U.S. state of Ohio. As of the 2020 census, the population was 97,574. The county seat is Jefferson, while its largest city is Ashtabula. The county was created in 1808 and later organized in 1811. The name Ashtabula derives from the Lenape language phrase ashte-pihële, which translates to 'always enough (fish) to go around, to be given away' and is a contraction of apchi ('always') + tepi ('enough') + hële. Ashtabula County is part of the Cleveland, OH Metropolitan Statistical Area.
Gallitzin is a borough in Cambria County, Pennsylvania, United States. It is bordered by Gallitzin Township and Tunnelhill, all of which sit astride the Eastern continental divide. Tunnel Hill and Gallitzin both are pierced by railroad tunnels shortening the necessary ascent for rails crossing the Allegheny Front onto the Allegheny Plateau which encompasses the towns' terrains. Topping the gaps of the Allegheny, the area is one of only five major breaks in the Appalachians allowing east–west transportation corridors before the advent of 20th century technologies.

James Mooney was an American ethnographer who lived for several years among the Cherokee. Known as "The Indian Man", he conducted major studies of Southeastern Indians, as well as of tribes on the Great Plains. He did ethnographic studies of the Ghost Dance, a spiritual movement among various Native American culture groups, after Sitting Bull's death in 1890. His works on the Cherokee include The Sacred Formulas of the Cherokees (1891), and Myths of the Cherokee (1900). All were published by the US Bureau of American Ethnology, within the Smithsonian Institution.
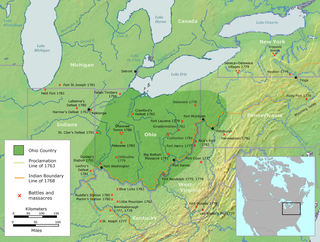
The Ohio Country, was a name used for a loosely defined region of colonial North America west of the Appalachian Mountains and south of Lake Erie.

The Shawnee are an Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands. Their language, Shawnee, is an Algonquian language.

The Kanawha River is a tributary of the Ohio River, approximately 97 mi (156 km) long, in the U.S. state of West Virginia. The largest inland waterway in West Virginia, its watershed has been a significant industrial region of the state since early in the 19th century.

The Akokisa were an Indigenous tribe who lived on Galveston Bay and the lower Trinity and Sabine rivers in Texas, primarily in the present-day Greater Houston area. They were a band of the Atakapa Indians, closely related to the Atakapa of Lake Charles, Louisiana.
The Mdewakanton or Mdewakantonwan are one of the sub-tribes of the Isanti (Santee) Dakota (Sioux). Their historic home is Mille Lacs Lake in central Minnesota. Together with the Wahpekute, they form the so-called Upper Council of the Dakota or Santee Sioux. Today their descendants are members of federally recognized tribes in Minnesota, South Dakota and Nebraska of the United States, and First Nations in Manitoba, Canada.
The Nomlaki are a Wintun people native to the area of the Sacramento Valley, extending westward to the Coast Range in Northern California. Today some Nomlaki people are enrolled in the federally recognized tribes: Round Valley Indian Tribes, Grindstone Indian Rancheria or the Paskenta Band of Nomlaki Indians. The Nomlaki were bordered by the Wintu (Wintun) in the north, the Yana in the northeast and east, the Konkow (Maiduan) in the east, the Patwin (Wintun) in the south, and the Yuki in the west.
The Erie people were Indigenous people historically living on the south shore of Lake Erie. An Iroquoian group, they lived in what is now western New York, northwestern Pennsylvania, and northern Ohio before 1658. Their nation was almost exterminated in the mid-17th century by five years of prolonged warfare with the powerful neighboring Iroquois for helping the Huron in the Beaver Wars for control of the fur trade. Captured survivors were adopted or enslaved by the Iroquois.
The Mosopelea, or Ofo, were a Siouan-speaking Native American people who historically lived near the upper Ohio River. In reaction to Iroquois Confederacy invasions to take control of hunting grounds in the late 17th century, they moved south to the lower Mississippi River. They finally settled in central Louisiana, where they assimilated with the Tunica and the Siouan-speaking Biloxi. They spoke the Ofo language, generally classified as a Siouan language.

The Saponi are a Native American tribe historically based in the Piedmont of North Carolina and Virginia. They spoke a Siouan language, related to the languages of the Tutelo, Biloxi, and Ofo.

Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands include Native American tribes and First Nation bands residing in or originating from a cultural area encompassing the northeastern and Midwest United States and southeastern Canada. It is part of a broader grouping known as the Eastern Woodlands. The Northeastern Woodlands is divided into three major areas: the Coastal, Saint Lawrence Lowlands, and Great Lakes-Riverine zones.

The Native American tribes in Virginia are the Indigenous peoples whose tribal nations historically or currently are based in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States of America.

The Tutelo were Native American people living above the Fall Line in present-day Virginia and West Virginia. They spoke a dialect of the Siouan Tutelo language thought to be similar to that of their neighbors, the Monacan and Manahoac nations.
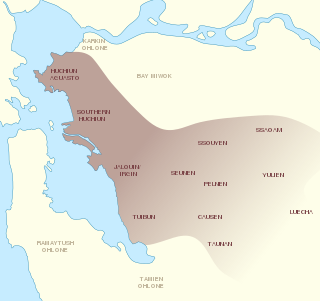
The Chochenyo are one of the divisions of the indigenous Ohlone (Costanoan) people of Northern California. The Chochenyo reside on the east side of the San Francisco Bay, primarily in what is now Alameda County, and also Contra Costa County, from the Berkeley Hills inland to the western Diablo Range.
The Acolapissa were a small tribe of Native Americans of North America, who lived in the Southeast of what is the present-day United States. They lived along the banks of the Pearl River, between present-day Louisiana and Mississippi. They are believed to have spoken a Muskogean language, closely related to the Choctaw and Chickasaw spoken by other Southeast tribes of the Muskogean family.

The protohistoric period of the state of West Virginia in the United States began in the mid-sixteenth century with the arrival of European trade goods. Explorers and colonists brought these goods to the eastern and southern coasts of North America and were brought inland by native trade routes. This was a period characterized by increased intertribal strife, rapid population decline, the abandonment of traditional life styles, and the extinction and migrations of many Native American groups.
The Dhegihan migration and separation was the long journey on foot by the North American Indians in the ancient Hą́ke tribe. During the migration from present-day Illinois/Kentucky and as far as Nebraska, they gradually split up into five groups. Each became an independent and historic tribe. They are the Omaha, Ponca, Kaw or Kansa, Osage and Quapaw.
References
- ↑ Hodge, Frederick Webb, Handbook of American Indians North of Mexico, Smithsonian Institution Bureau of Ethnology, 1910, retrieved January 1, 2017.
- 1 2 Hanna, Charles A. (1911). The Wilderness Trail, Volume 2. G. P. Putnam's sons. pp. 117–119.
- ↑ Swanton, John R., 'The Indian Tribes of North America' , Bureau of American Ethnology Bulletin 145 (1953): 55-57.