
Bowling, in cricket, is the action of propelling the ball toward the wicket defended by a batter. A player skilled at bowling is called a bowler; a bowler who is also a competent batter is known as an all-rounder. Bowling the ball is distinguished from throwing the ball by a strictly specified biomechanical definition, which restricts the angle of extension of the elbow. A single act of bowling the ball towards the batsman is called a ball or a delivery. Bowlers bowl deliveries in sets of six, called an over. Once a bowler has bowled an over, a teammate will bowl an over from the other end of the pitch. The Laws of Cricket govern how a ball must be bowled. If a ball is bowled illegally, an umpire will rule it a no-ball. If a ball is bowled too wide of the striker for the batsman to be able to play at it with a proper cricket shot, the bowler's end umpire will rule it a wide.

Leg before wicket (lbw) is one of the ways in which a batsman can be dismissed in the sport of cricket. Following an appeal by the fielding side, the umpire may rule a batter out lbw if the ball would have struck the wicket but was instead intercepted by any part of the batter's body. The umpire's decision will depend on a number of criteria, including where the ball pitched, whether the ball hit in line with the wickets, the ball's expected future trajectory after hitting the batsman, and whether the batter was attempting to hit the ball.
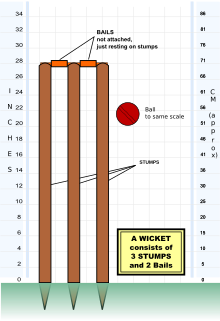
In the sport of cricket, a bail is one of the two smaller sticks placed on top of the three stumps to form a wicket. The bails are used to determine when the wicket is broken or put down, which in turn is one of the critical factors in determining whether a batsman is out bowled, stumped, run out or hit wicket.
The Laws of Cricket is a code which specifies the rules of the game of cricket worldwide. The earliest known code was drafted in 1744 and, since 1788, it has been owned and maintained by its custodian, the Marylebone Cricket Club (MCC) in London. There are currently 42 Laws which outline all aspects of how the game is to be played. MCC has re-coded the Laws six times, the seventh and latest code being released in October 2017. The 2nd edition of the 2017 Code came into force on 1 April 2019. The first six codes prior to 2017 were all subject to interim revisions and so exist in more than one version.

In cricket, the term wicket has several meanings:

This is a general glossary of the terminology used in the sport of cricket. Where words in a sentence are also defined elsewhere in this article, they appear in italics. Certain aspects of cricket terminology are explained in more detail in cricket statistics and the naming of fielding positions is explained at fielding (cricket).

Hawk-Eye is a computer vision system used in numerous sports such as cricket, tennis, Gaelic football, badminton, hurling, rugby union, association football and volleyball, to visually track the trajectory of the ball and display a profile of its statistically most likely path as a moving image. The onscreen representation of the trajectory results is called Shot Spot.
Fast bowling is one of two main approaches to bowling in the sport of cricket, the other being spin bowling. Practitioners of pace bowling are usually known as fast bowlers, quicks, or pacemen. They can also be referred to as a seam bowler, a swing bowler or a fast bowler who can swing it to reflect the predominant characteristic of their deliveries. Strictly speaking, a pure swing bowler does not need to have a high degree of pace, though dedicated medium-pace swing bowlers are rarely seen at Test level in modern times.

In cricket, a dismissal occurs when a batsman's period of batting is brought to an end by the opposing team. It is also known as the batsman being out, the batting side losing a wicket, and the fielding side taking a wicket. The ball becomes dead, and the dismissed batsman must leave the field of play permanently for the rest of their team's innings, and is replaced by a teammate. A team's innings ends if 10 of the 11 team members are dismissed—as players bat in pairs, when only one player is not out it is not possible for the team to bat any longer. This is known as bowling out the batting team, who are said to be all out.
Obstructing the field is one of the ten methods of dismissing a batsman in the sport of cricket. Either batsman can be given out if he wilfully attempts to obstruct or distract the fielding side by word or action. It is Law 37 of the Laws of cricket, and is a rare way for a batsman to be dismissed; in the history of cricket, there has been only one instance in Test matches, six occasions in One Day International (ODI) games, and only one instance in Twenty20 International matches. There have also been seven instances in Test cricket, and two in ODIs, where a batsman has been dismissed handled the ball, a mode of dismissal now folded into obstructing the field.

In cricket, the term bowled has several meanings. First, is the act of propelling the ball towards the wicket defended by a batsman.

In cricket, a scorer is someone appointed to record all runs scored, all wickets taken and, where appropriate, the number of overs bowled. In professional games, in compliance with Law 3 of the Laws of Cricket, two scorers are appointed, most often one provided by each team.

A Snickometer, commonly known as Snicko, is used in televising cricket to graphically analyse sound and video, and show whether a fine noise, or snick, occurs as ball passes bat. It was invented by English computer scientist Allan Plaskett in the mid-1990s. The snickometer was introduced by Channel 4 in the UK, who also introduced the Hawk-Eye and the Red Zone, in 1999.
Crocker is a team sport played between two large teams. Its origins are in cricket and baseball. It also makes the use of a rugby ball, or a soccer ball which may explain its name. It is a casual sport not played formally, but often found on British summer camps.

Owzthat is a dice-based cricket simulation. In its non-commercial form it is often called pencil cricket as in pre-war Britain six-sided pencils, shaved back to bare wood with the numbers and words written on them, were used. Today the game is supplied by a variety of manufacturers, including William Lindop Ltd. The name is derived from a verbal cricket appeal regarding whether a batsman is out.

The Decision Review System (DRS), formerly known as the Umpire Decision Review System(UDRS), is a technology-based system used in cricket to assist the match officials in their decision-making. On-field umpires may choose to consult with the third umpire, and players may request that the third umpire consider a decision of the on-field umpires.
The England team were unhappy with the umpiring in the 1946–47 Ashes series, in particular when Don Bradman was not given out when caught by Jack Ikin for 28 in the First Test and 22 in the Second. Test cricket was not filmed except for highlights and the notion of Test umpires using slow-motion replays or other modern techniques would have been considered absurd. Instead the umpires had to make judgements based on what they saw in a split-second, and honest mistakes were accepted as part and parcel of the game. However, touring teams sometimes felt that there was a natural bias towards the home team which led to some acrimony if important decisions always went against them. The Australian Ray Robinson wrote in The Cricketer:
Usually debatable decisions work out fairly evenly over a Test rubber, but weight of evidence suggests that the umpires were mistaken in giving Bradman not out caught for 28 in the First Test, Edrich out leg-before-wicket for 89 in the Third Test, and Washbrook out caught behind the wicket for 39 in the Fourth Test. These decisions came at such points in England's bids to gain an advantage that they could almost be termed turning-points of the three games.

The 1974–75 Ashes series consisted of six cricket Test matches, each match lasted five days with six hours of play each day and eight ball overs. It formed part of the MCC tour of Australia in 1974–75 and the matches outside the Tests were played in the name of the Marylebone Cricket Club. Ian Chappell's Australians won the series 4–1 and "brutally and unceremoniously wrenched the Ashes" from Mike Denness's England team. It was Australia's first series victory over England for ten years and the experience proved popular as 777,563 spectators came through the gates and paid nearly a million Australian dollars for the privilege. For the first time the first day of the Third Test at Melbourne was held on Boxing Day in an Ashes series, now a cricketing tradition.

The 2019 Ashes series was a series of Test cricket matches played between England and Australia for The Ashes in August and September 2019. The venues were Edgbaston, Lord's, Headingley, Old Trafford and The Oval. Australia were the defending holders of the Ashes going into the series, having won in 2017–18. It was the first Test series of the inaugural 2019–2021 ICC World Test Championship. During the second Test match a concussion substitute was used for the first time in international cricket. Ben Stokes' game-winning 135* in the third Test has been hailed by many as the greatest Test innings of all time. Australia retained the Ashes after winning the fourth Test, with England levelling the series 2–2 in the final test, resulting in the first drawn Ashes series since 1972.

A stump microphone, informally known as a stump mic, is a microphone embedded in a cricket stump. It was originally developed by Kerry Packer for World Series Cricket in the 1970s. At first it was primarily for entertainment value: "television audiences could hear the rattle of stumps".















