
The medical uses of silver include its use in wound dressings, creams, and as an antibiotic coating on medical devices. Wound dressings containing silver sulfadiazine or silver nanomaterials may be used to treat external infections. The limited evidence available shows that silver coatings on endotracheal breathing tubes may reduce the incidence of ventilator-associated pneumonia. There is tentative evidence that using silver-alloy indwelling catheters for short-term catheterizing will reduce the risk of catheter-acquired urinary tract infections.

An ulcer is a sore on the skin or a mucous membrane, accompanied by the disintegration of tissue. Ulcers can result in complete loss of the epidermis and often portions of the dermis and even subcutaneous fat. Ulcers are most common on the skin of the lower extremities and in the gastrointestinal tract. An ulcer that appears on the skin is often visible as an inflamed tissue with an area of reddened skin. A skin ulcer is often visible in the event of exposure to heat or cold, irritation, or a problem with blood circulation.
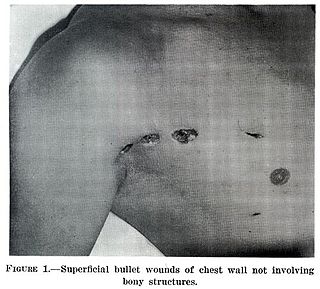
A wound is a rapid onset of injury that involves lacerated or punctured skin, or a contusion from blunt force trauma or compression. In pathology, a wound is an acute injury that damages the epidermis of the skin. To heal a wound, the body undertakes a series of actions collectively known as the wound healing process.
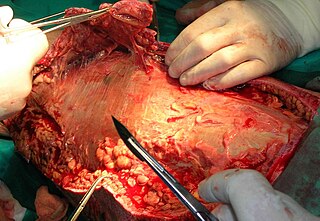
Debridement is the medical removal of dead, damaged, or infected tissue to improve the healing potential of the remaining healthy tissue. Removal may be surgical, mechanical, chemical, autolytic (self-digestion), and by maggot therapy.

Pressure ulcers, also known as pressure sores, bed sores or pressure injuries, are localised damage to the skin and/or underlying tissue that usually occur over a bony prominence as a result of usually long-term pressure, or pressure in combination with shear or friction. The most common sites are the skin overlying the sacrum, coccyx, heels, and hips, though other sites can be affected, such as the elbows, knees, ankles, back of shoulders, or the back of the cranium.
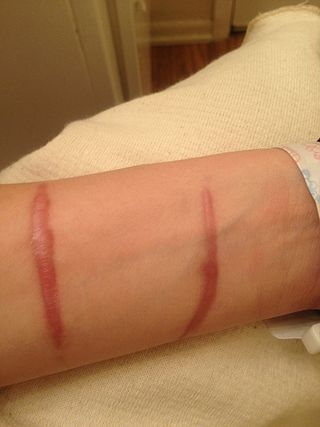
A hypertrophic scar is a cutaneous condition characterized by deposits of excessive amounts of collagen which gives rise to a raised scar, but not to the degree observed with keloids. Like keloids, they form most often at the sites of pimples, body piercings, cuts and burns. They often contain nerves and blood vessels. They generally develop after thermal or traumatic injury that involves the deep layers of the dermis and express high levels of TGF-β.
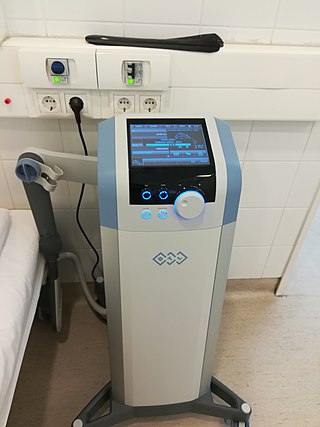
Electrotherapy is the use of electrical energy as a medical treatment. In medicine, the term electrotherapy can apply to a variety of treatments, including the use of electrical devices such as deep brain stimulators for neurological disease. The term has also been applied specifically to the use of electric current to speed wound healing. Additionally, the term "electrotherapy" or "electromagnetic therapy" has also been applied to a range of alternative medical devices and treatments.

Silver sulfadiazine, sold under the brand Silvadene among others, is a topical antibiotic used in partial thickness and full thickness burns to prevent infection. Tentative evidence has found other antibiotics to be more effective, and therefore it is no longer generally recommended for second-degree (partial-thickness) burns, but is still widely used to protect third-degree (full-thickness) burns.
A dressing or compress is a sterile pad applied to a wound to promote healing and protect the wound from further harm. A dressing is designed to be in direct contact with the wound, as distinguished from a bandage, which is most often used to hold a dressing in place. Many modern dressings are self-adhesive.

Maggot therapy is a type of biotherapy involving the introduction of live, disinfected maggots into non-healing skin and soft-tissue wounds of a human or other animal for the purpose of cleaning out the necrotic (dead) tissue within a wound (debridement), and disinfection.

Venous ulcer is defined by the American Venous Forum as "a full-thickness defect of skin, most frequently in the ankle region, that fails to heal spontaneously and is sustained by chronic venous disease, based on venous duplex ultrasound testing." Venous ulcers are wounds that are thought to occur due to improper functioning of venous valves, usually of the legs. They are an important cause of chronic wounds, affecting 1% of the population. Venous ulcers develop mostly along the medial distal leg, and can be painful with negative effects on quality of life.
A chronic wound is a wound that does not heal in an orderly set of stages and in a predictable amount of time the way most wounds do; wounds that do not heal within three months are often considered chronic. Chronic wounds seem to be detained in one or more of the phases of wound healing. For example, chronic wounds often remain in the inflammatory stage for too long. To overcome that stage and jump-start the healing process, a number of factors need to be addressed such as bacterial burden, necrotic tissue, and moisture balance of the whole wound. In acute wounds, there is a precise balance between production and degradation of molecules such as collagen; in chronic wounds this balance is lost and degradation plays too large a role.
Skin care or skincare is a range of practices that support skin integrity, enhance its appearance, and relieve skin conditions. They can include nutrition, avoidance of excessive sun exposure, and appropriate use of emollients. Practices that enhance appearance include the use of cosmetics, botulinum, exfoliation, fillers, laser resurfacing, microdermabrasion, peels, retinol therapy, and ultrasonic skin treatment. Skin care is a routine daily procedure in many settings, such as skin that is either too dry or too moist, and prevention of dermatitis and prevention of skin injuries.

Negative-pressure wound therapy (NPWT), also known as a vacuum assisted closure (VAC), is a therapeutic technique using a suction pump, tubing, and a dressing to remove excess exudate and promote healing in acute or chronic wounds and second- and third-degree burns. The therapy involves the controlled application of sub-atmospheric pressure to the local wound environment using a sealed wound dressing connected to a vacuum pump. The use of this technique in wound management started in the 1990s and this technique is often recommended for treatment of a range of wounds including dehisced surgical wounds, closed surgical wounds, open abdominal wounds, open fractures, pressure injuries or pressure ulcers, diabetic foot ulcers, venous insufficiency ulcers, some types of skin grafts, burns, sternal wounds. It may also be considered after a clean surgery in a person who is obese.

Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) is a non-invasive, out-patient alternative to surgery for those with many joint and tendon disorders. ESWT sends acoustic shock waves into bone or soft tissue, in effect reinjuring the area on a cellular level and breaking up the scarring that has penetrated tendons and ligaments. The controlled reinjuring of tissue allows the body to regenerate blood vessels and bone cells. The resulting revascularization leads to faster healing and often a return to pre-injury activity levels. ESWT is mostly used for kidney stones removal, in physical therapy and orthopedics.
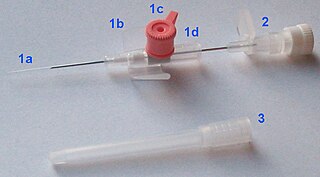
In medicine, a peripheral venous catheter, peripheral venous line, peripheral venous access catheter, or peripheral intravenous catheter, is a catheter placed into a peripheral vein for venous access to administer intravenous therapy such as medication fluids.
An alginate dressing is a natural wound dressing derived from carbohydrate sources released by clinical bacterial species, in the same manner as biofilm formation. These types of dressings are best used on wounds that have a large amount of exudate. They may be used on full-thickness burns, surgical wounds, split-thickness graft donor sites, Mohs surgery defects, refractory decubiti, and chronic ulcers. They can also be applied onto dry wounds after normal saline is first applied to the site of application.
Wound bed preparation (WBP) is a systematic approach to wound management by identifying and removing barriers to healing. The concept was originally developed in plastic surgery. During the year 2000, the concept was applied to systematizing the treatment of chronic wounds. The 2000 proposals recommended that wound management address the identifiable impediments to healing in order to achieve more successful outcomes. Three publications appeared that year that focused on the concept of managing the healing processes of a wound exudate, bioburden and devitalized tissue. Initially, emphasis was placed on debridement, moisture balance and bacterial balance as the three guiding principles of good wound care, while at the same time recognizing that the provision of care includes a vast array of patient, clinical and environmental variables.

Diabetic foot ulcer is a breakdown of the skin and sometimes deeper tissues of the foot that leads to sore formation. It may occur due to a variety of mechanisms. It is thought to occur due to abnormal pressure or mechanical stress chronically applied to the foot, usually with concomitant predisposing conditions such as peripheral sensory neuropathy, peripheral motor neuropathy, autonomic neuropathy or peripheral arterial disease. It is a major complication of diabetes mellitus, and it is a type of diabetic foot disease. Secondary complications to the ulcer, such as infection of the skin or subcutaneous tissue, bone infection, gangrene or sepsis are possible, often leading to amputation.
Hydrogels are three-dimensional networks consisting of chemically or physically cross-linked hydrophilic polymers. The insoluble hydrophilic structures absorb polar wound exudates and allow oxygen diffusion at the wound bed to accelerate healing. Hydrogel dressings can be designed to prevent bacterial infection, retain moisture, promote optimum adhesion to tissues, and satisfy the basic requirements of biocompatibility. Hydrogel dressings can also be designed to respond to changes in the microenvironment at the wound bed. Hydrogel dressings should promote an appropriate microenvironment for angiogenesis, recruitment of fibroblasts, and cellular proliferation.















