
The Imperial Crown of India was used by King George V in his capacity as Emperor of India at the Delhi Durbar of 1911. [1]

The Imperial Crown of India was used by King George V in his capacity as Emperor of India at the Delhi Durbar of 1911. [1]
Tradition prohibits the Crown Jewels from leaving the United Kingdom, a product of the days when kings and queens often pawned the jewels to foreign brokers. There are also considerable risks involved in transporting the historic regalia by sea and land over such a great distance. [2] For these reasons, a new crown was made specially for George V and Queen Mary's trip to India in 1911, where they were proclaimed as Emperor and Empress of India before the princes and rulers of India. [3]
The Crown Jewellers at the time, Garrard & Co, made the crown at a cost of £60,000 (equivalent to £6,500,000in 2021), which was borne by the India Office. [1]
The Imperial Crown of India weighs 920 g (2.03 lb) and is set with 6,170 diamonds, 9 emeralds, 4 rubies, and 4 sapphires. At the front is a very fine emerald weighing 32 carats (6.4 g). [4] (p 169) The King wrote in his diary that it was heavy and uncomfortable to wear: "Rather tired after wearing my crown for 3+1⁄2 hours; it hurt my head, as it is pretty heavy." [5]
Similar to other British crowns, it consists of a circlet with four crosses pattée and four fleurs-de-lis. However, the eight half-arches on top, which join at a typical monde and cross pattée, point upwards in the form of a Gothic ogee arch. [2] The Crown of India is the only crown of a British sovereign to have eight half-arches, in the style of continental European crowns, departing from the tradition of British crowns having two arches or four half-arches.
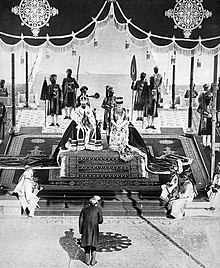
George and Mary were not crowned as emperor and empress at the ceremony; the Archbishop of Canterbury, Randall Davidson, did not think it appropriate for a Christian service to take place in a country where the people were mostly Hindu or Muslim. Instead, the king simply wore the crown as he entered the durbar, and the durbar was styled as an affirmation of the king's coronation, which had already taken place in the United Kingdom six months earlier.
It has not been used since George V returned from India. On 15 August 1947, British rule over India ended and the Dominions of India and Pakistan came into being. George VI and his British Prime Minister, Clement Attlee, agreed that
The Imperial Crown of India is on public display in the Jewel House at the Tower of London. [6]

Crown jewels are the objects of metalwork and jewellery in the regalia of a current or former monarchy. They are often used for the coronation of a monarch and a few other ceremonial occasions. A monarch may often be shown wearing them in portraits, as they symbolize the power and continuity of the monarchy. Additions to them may be made, but since medieval times the existing items are typically passed down unchanged as they symbolize the continuity of the monarchy.

A crown is a traditional form of head adornment, or hat, worn by monarchs as a symbol of their power and dignity. A crown is often, by extension, a symbol of the monarch's government or items endorsed by it. The word itself is used, particularly in Commonwealth countries, as an abstract name for the monarchy itself, as distinct from the individual who inhabits it. A specific type of crown is employed in heraldry under strict rules. Indeed, some monarchies never had a physical crown, just a heraldic representation, as in the constitutional kingdom of Belgium.

Emperor or Empress of India was a title used by British monarchs from 1 May 1876 to 22 June 1948 to signify their sovereignty over the British Raj as its imperial head of state. The image of the emperor or empress appeared on Indian currency, in government buildings, railway stations, courts, on statues etc. Oaths of allegiance were made to the emperor or empress and the lawful successors by the governors-general, princes, governors, commissioners in India in events such as imperial durbars.

The Cullinan Diamond is the largest gem-quality rough diamond ever found, weighing 3,106 carats (621.20 g), discovered at the Premier No.2 mine in Cullinan, South Africa, on 26 January 1905. It was named after Thomas Cullinan, the owner of the mine. In April 1905, it was put on sale in London, but despite considerable interest, it was still unsold after two years. In 1907, the Transvaal Colony government bought the Cullinan and Prime Minister Louis Botha presented it to Edward VII, the British king who reigned over the territory, and it was cut by Joseph Asscher & Co. in Amsterdam.

The Crown Jewels of the United Kingdom, originally the Crown Jewels of England, are a collection of royal ceremonial objects kept in the Jewel House at the Tower of London, which include the coronation regalia and vestments worn by British monarchs.

St Edward's Crown is the centrepiece of the Crown Jewels of the United Kingdom. Named after Saint Edward the Confessor, versions of it have traditionally been used to crown English and British monarchs at their coronations since the 13th century.

The Imperial State Crown is one of the Crown Jewels of the United Kingdom and symbolises the sovereignty of the British monarch. It has existed in various forms since the 15th century. The 1937 version is worn by a new monarch for the first time in the royal procession following their coronation and subsequently used at State Openings of Parliament. The crown is adorned with 2,901 precious stones, including the Cullinan II diamond, St Edward's Sapphire, the Stuart Sapphire, and the Black Prince's Ruby.

The coronation of the monarch of the United Kingdom is an initiation ceremony in which they are formally invested with regalia and crowned at Westminster Abbey. It corresponds to the coronations that formerly took place in other European monarchies, which have all abandoned coronations in favour of inauguration or enthronement ceremonies. A coronation is a symbolic formality and does not signify the official beginning of the monarch's reign; de jure and de facto their reign commences from the moment of the preceding monarch's death or abdication, maintaining legal continuity of the monarchy.

The Delhi Durbar was an Indian imperial-style mass assembly organized by the British at Coronation Park, Delhi, India, to mark the succession of an Emperor or Empress of India. Also known as the Imperial Durbar, it was held three times, in 1877, 1903, and 1911, at the height of the British Empire. The 1911 Durbar was the only one that a sovereign, George V, attended. The term was derived from the common Persian term durbar.

The Imperial crown of Russia, also known as the great imperial crown, was used for the coronation of the monarchs of Russia from 1762 until the Russian monarchy's abolition in 1917. The great imperial crown was first used in the coronation by Catherine the Great, and it was last worn at the coronation of Nicholas II. It was displayed prominently next to Nicholas II on a cushion at the State Opening of the Russian Duma inside the Winter Palace in St. Petersburg in 1906. It survived the 1917 revolution and ensuing civil war and is currently on display in Moscow at the Kremlin Armoury's State Diamond Fund.

An imperial crown is a crown used for the coronation of emperors.
A king-emperor is a sovereign ruler who is simultaneously a king of one territory and emperor of another. This title usually results from a merger of a royal and imperial crown, but recognises the two territories as different politically and culturally as well as in status. It also denotes a king's imperial status through the acquisition of an empire or vice versa.

The State Crown of Mary of Modena is the consort crown made in 1685 for Mary of Modena, queen of England, Scotland and Ireland. It was used by future queens consort until the end of the 18th century.
A half-arch is the piece of gold, silver or platinum, usually decorated with jewels, that links the circlet of a hoop crown to the monde at the top of the crown.

The Small Diamond Crown of Queen Victoria is a miniature imperial and state crown made at the request of Queen Victoria in 1870 to wear over her widow's cap following the death of her husband, Prince Albert. It was perhaps the crown most associated with the queen and is one of the Crown Jewels on public display in the Jewel House at the Tower of London.

Durbar is a Persian-derived term referring to the noble court of a king or ruler or a formal meeting where the king held all discussions regarding the state. It was used in South Asia for a ruler's court or feudal levy as the latter came to be ruled and later administered by foreigners. A durbar may be either a feudal state council for administering the affairs of a princely state, or a purely ceremonial gathering, as was increasingly the case during British rule in India.

Coronation Park is a park located at Burari Road near Nirankari Sarovar in Delhi, India. It was the venue of the Delhi Durbar of 1877 when Queen Victoria was proclaimed the Empress of India. Later it was used to celebrate the accession of King Edward VII in 1903, and, finally, it was here that the Durbar commemorating the coronation of King George V as Emperor of India took place on 12 December 1911, subsequent to his coronation at Westminster Abbey in June 1911. This last celebration had all the princely states in attendance. The decision to hold the Coronation Durbars in Delhi at the vast open ground at Coronation Park was a move to emphasise the historical significance of Delhi as the former capital of the Mughal Empire.

Queen Elizabeth II owned a historic collection of jewels – some as monarch and others as a private individual. They are separate from the gems and jewels of the Royal Collection, and from the coronation and state regalia that make up the Crown Jewels.

The Tudor Crown, also known as Henry VIII's Crown, was the imperial and state crown of English monarchs from around the time of Henry VIII until it was destroyed during the Civil War in 1649. It was described by the art historian Sir Roy Strong as "a masterpiece of early Tudor jeweller's art", and its form has been compared to the crown of the Holy Roman Empire.

The coronation of George V and his wife, Mary, as king and queen of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions took place at Westminster Abbey, London, on Thursday 22 June 1911. This was the second of four such events held during the 20th century and the last to be attended by royal representatives of the great continental European empires.
{{cite book}}: |website= ignored (help){{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)