
Mabo v Queensland is a landmark decision of the High Court of Australia that recognised the existence of Native Title in Australia. It was brought by Eddie Mabo against the State of Queensland and decided on 3 June 1992. The case is notable for being the first in Australia to recognise pre-colonial land interests of Indigenous Australians within the common law of Australia.

A treaty is a formal, legally binding written contract between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal persons.

There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territory, and an experience of subjugation and discrimination under a dominant cultural model.
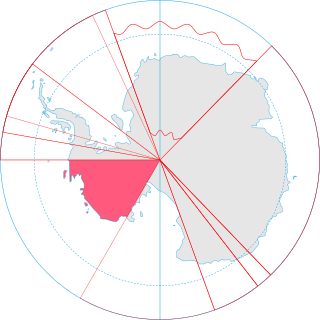
Terra nullius is a Latin expression meaning "nobody's land". It was a principle sometimes used in international law to justify claims that territory may be acquired by a state's occupation of it. There are currently three territories sometimes claimed to be terra nullius: Bir Tawil, four pockets of land near the Danube due to the Croatia–Serbia border dispute, and parts of Antarctica, principally Marie Byrd Land.

Australian Indigenous sovereignty, also recently termed Blak sovereignty, encompasses the various rights claimed by Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples within Australia. Such rights are said to derive from Indigenous peoples' occupation and ownership of Australia prior to colonisation and through their continuing spiritual connection to land. Indigenous sovereignty is not recognised in the Australian Constitution or under Australian law.
Native title refers to rights, recognised by Australian law, held by Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander groups or individuals to land that derive from their maintenance of their traditional laws and customs. These Aboriginal title rights were first recognised as a part of Australian common law with the decision of Mabo v Queensland in 1992. The doctrine was subsequently implemented and modified via statute with the Native Title Act 1993.
Paul Gerrard McHugh is a New Zealand academic lawyer. He teaches at the University of Cambridge where he is a Professor in Law and Legal History and Fellow of Sidney Sussex College.

Aboriginal title is a common law doctrine that the land rights of indigenous peoples to customary tenure persist after the assumption of sovereignty to that land by another colonising state. The requirements of proof for the recognition of aboriginal title, the content of aboriginal title, the methods of extinguishing aboriginal title, and the availability of compensation in the case of extinguishment vary significantly by jurisdiction. Nearly all jurisdictions are in agreement that aboriginal title is inalienable, and that it may be held either individually or collectively.

Canadian Aboriginal law is the body of law of Canada that concerns a variety of issues related to Indigenous peoples in Canada. Canadian Aboriginal Law is different from Canadian Indigenous law: In Canada, Indigenous Law refers to the legal traditions, customs, and practices of Indigenous peoples and groups. Aboriginal peoples as a collective noun is a specific term of art used in legal documents, including the Constitution Act, 1982, and includes First Nations, Inuit and Métis people. Canadian Aboriginal law provides certain constitutionally recognized rights to land and traditional practices. Canadian Aboriginal Law enforces and interprets certain treaties between the Crown and Indigenous people, and manages much of their interaction. A major area of Aboriginal law involves the duty to consult and accommodate.
In Australia, Canada, New Zealand and the United States the term treaty rights specifically refers to rights for indigenous peoples enumerated in treaties with settler societies that arose from European colonization.
Indigenous rights are those rights that exist in recognition of the specific condition of the Indigenous peoples. This includes not only the most basic human rights of physical survival and integrity, but also the rights over their land, language, religion, and other elements of cultural heritage that are a part of their existence and identity as a people. This can be used as an expression for advocacy of social organizations, or form a part of the national law in establishing the relation between a government and the right of self-determination among its Indigenous people, or in international law as a protection against violation of Indigenous rights by actions of governments or groups of private interests.
Aboriginal child protection describes services designed specifically for protection of the children of "aboriginal" or indigenous peoples, particularly where they are a minority within a country. This may differ at international, national, legal, cultural, social, professional and program levels from general or mainstream child protection services. Fundamental human rights are a source of many of the differences. Aboriginal child protection may be an integral or a distinct aspect of mainstream services or it may be exercised formally or informally by an aboriginal people itself. There has been controversy about systemic genocide in child protection systems enforced with aboriginal children in post-colonial societies.
The Indigenous Law Centre (ILC), formerly the Aboriginal Law Research Unit and Aboriginal Law Centre, is part of the Law Faculty at the University of New South Wales. It develops and coordinates research, teaching and information services in the multi-disciplinary area of Indigenous peoples and the law, and publishes two major journals: the Australian Indigenous Law Review and the Indigenous Law Bulletin. It is the only Indigenous law research centre in Australia.
Pan-Indianism is a philosophical and political approach promoting unity, and to some extent cultural homogenization, among different Indigenous groups in the Americas regardless of tribal distinctions and cultural differences.

The Aboriginal Provisional Government (APG) is an Indigenous Australian independence movement.
Ancestral domain or ancestral lands refers to the lands, territories and resources of indigenous peoples, particularly in the Asia-Pacific region. The term differs from indigenous land rights, Aboriginal title or Native Title by directly indicating relationship to land based on ancestry, while domain indicates relationships beyond material lands and territories, including spiritual and cultural aspects that may not be acknowledged in land titles and legal doctrine about trading ownership.
Free, prior and informed consent (FPIC) is aimed to establish bottom-up participation and consultation of an indigenous population prior to the beginning of development on ancestral land or using resources in an indigenous population's territory. Indigenous people have a special connection to their land and resources and inhabit one fifth of the earth's surface. Such areas are environmentally rich in both renewable and non-renewable resources. The collective ownership style of most Indigenous Peoples conflicts with the modern global market and its continuous need for resources and land. To protect Indigenous Peoples' rights, international human rights law has created processes and standards to safeguard their way of life and to encourage participation in the decision-making process. One such method is the process of FPIC. There is criticism that many international conventions and treaties require consultation, not consent, which is a much higher threshold. Without the requirement for consent, indigenous people cannot veto government projects and developments in their area that directly affect their lives and cultures. FPIC allows Indigenous Peoples to have the right to self-determination and self-governance in national and local government decision-making processes over projects that concern their lives and resources.

The judiciary of New Zealand is responsible for the system of courts that interprets and applies the laws of New Zealand. It has four primary functions: to provide a mechanism for dispute resolution; to deliver authoritative rulings on the meaning and application of legislation; to develop case law; and to uphold the rule of law, personal liberty and human rights. The judiciary is supported in its work by an executive department, the Ministry of Justice.
Indigenous or Aboriginal self-government refers to proposals to give governments representing the Indigenous peoples in Canada greater powers of government. These proposals range from giving Aboriginal governments powers similar to that of local governments in Canada to demands that Indigenous governments be recognized as sovereign, and capable of "nation-to-nation" negotiations as legal equals to the Crown, as well as many other variations.








