Related Research Articles

The World Summit on the Information Society (WSIS) was a two-phase United Nations-sponsored summit on information, communication and, in broad terms, the information society that took place in 2003 in Geneva and in 2005 in Tunis. WSIS Forums have taken place periodically since then. One of the Summit's chief aims is to bridge the global digital divide separating rich countries from poor countries by increasing internet accessibility in the developing world. The conferences established 17 May as World Information Society Day.

The International Day of Peace, also officially known as World Peace Day, is a United Nations-sanctioned holiday observed annually on 21 September. It is dedicated to world peace, and specifically the absence of war and violence, such as might be occasioned by a temporary ceasefire in a combat zone for humanitarian aid access. The day was first established in 1981 and first observed in September 1982 and is kept by many nations, political groups, military groups, and people.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1325 (S/RES/1325), on women, peace, and security, was adopted unanimously by the UN Security Council on 31 October 2000, after recalling resolutions 1261 (1999), 1265 (1999), 1296 (2000), and 1314 (2000). The resolution acknowledged the disproportionate and unique impact of armed conflict on women and girls. It calls for the adoption of a gender perspective to consider the special needs of women and girls during conflict, repatriation and resettlement, rehabilitation, reintegration, and post-conflict reconstruction.

The World Federation of United Nations Associations (WFUNA) was founded in 1946 as a Federation of national associations. Its objectives are to promote the values of the UN Charter, defend multilateralism, work towards a better United Nations Organisation and raise awareness on the main pillars of work of the United Nations—peace and security, sustainable development, and human rights.

Federico Mayor Zaragoza is a scientist, scholar, politician, diplomat, and poet from Spain. He served as the Director-General of the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) from 1987 to 1999. After his tenure as Director-General, he continued to participate in various peace-related organizations such as the Foundation for a Culture of Peace and the International Decade for the Promotion of a Culture of Peace and Non-Violence for the Children of the World, as a member of their honorary boards. Additionally, he serves as the honorary chairman of the Académie de la Paix.

The Fourth World Conference on Women: Action for Equality, Development and Peace was the name given for a conference convened by the United Nations during 4–15 September 1995 in Beijing, China.
The Vienna Declaration and Programme of Action (VDPA) is a human rights declaration adopted by consensus at the World Conference on Human Rights on 25 June 1993 in Vienna, Austria. The position of United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights was recommended by this Declaration and subsequently created by General Assembly Resolution 48/141.

Human rights are largely respected in Switzerland, one of Europe's oldest democracies. Switzerland is often at or near the top in international rankings of civil liberties and political rights observance. Switzerland places human rights at the core of the nation's value system, as represented in its Federal Constitution. As described in its FDFA's Foreign Policy Strategy 2016-2019, the promotion of peace, mutual respect, equality and non-discrimination are central to the country's foreign relations.
On 10 November 1998, the United Nations General Assembly proclaimed the first decade of the 21st century and the third millennium, the years 2001 to 2010, as the International Decade for the Promotion of a Culture of Peace and Non-Violence for the Children of the World.
The United Nations Division for Palestinian Rights (UNDPR) is a part of the Department of Political Affairs of the United Nations Secretariat.
The International Action Network on Small Arms (IANSA) was incorporated on 30 May 2002 under the laws of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. The IANSA London office was closed in 2015, but it has an active UN liaison office in New York. IANSA has had registration as an NGO in Ghana since 2014 to reflect the organizations commitments to bringing voices from the global south to the United Nations small arms disarmament process.
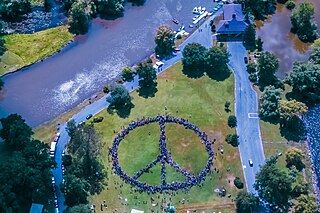
Peacebuilding is an activity that aims to resolve injustice in nonviolent ways and to transform the cultural and structural conditions that generate deadly or destructive conflict. It revolves around developing constructive personal, group, and political relationships across ethnic, religious, class, national, and racial boundaries. The process includes violence prevention; conflict management, resolution, or transformation; and post-conflict reconciliation or trauma healing before, during, and after any given case of violence.
The International Year for the Culture of Peace was designated by the United Nations as the year 2000, with the aim of celebrating and encouraging a culture of peace.
Elaine Valdov is President and Founder of The International Institute for a Culture of Peace As a peace and human rights activist and conflict resolution specialist, Valdov lectures internationally and is best known for her work in championing and building initiatives worldwide, in support of the UN Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) and UNESCO’s International Decade for the Promotion of a Culture of Peace and Non-Violence for the Children of the World. She has chaired task forces for women empowerment and gender equality; and founded “Yoga Peace Ambassadors” to teach MDG humanitarian service options in Yoga Ashrams worldwide.
In December 2009, the United Nations General Assembly adopted resolution 64/134 proclaiming the year commencing 12 August 2010 as the International Year of Youth.
The United Nations Non-Governmental Liaison Service is a programme of the United Nations mandated to promote and develop constructive relations between the United Nations and civil society organizations. UN-NGLS operates autonomously across the United Nations system and with civil society constituencies and social movements on cross-cutting and emerging issues on the UN agenda. For example, UN-NGLS currently focuses on the UN General Assembly preparatory process for negotiations of a global compact on migration, and high-level events organized by the President of the UN General Assembly. UN-NGLS advises civil society organizations on opportunities to engage with the UN and facilitates their participation in various UN processes and events. UN-NGLS has offices at UN headquarters in New York and is part of the United Nations Department of Global Communications.
United Nations General Assembly Resolution 30/3520 (XXX.) was a resolution adopted by the UN General Assembly on 15 December 1975. The resolution adopted the World Plan of Action and related resolutions from the International Women's Year World Conference on Women which was held in Mexico City earlier in the year.
Declaration of Mexico on the Equality of Women and their Contribution to Development and Peace 66/34 was a United Nations resolution that was adopted on July 2, 1975, at the close of the International Women's Year World Conference on Women held in Mexico City. The resolution was adopted to promulgate a set of principles concerning the equality of men and women. The Declaration called for action to immediately address the burdens and discrimination women experienced in the labor market, as primary childcare providers, and as political participants around the world.
International Year of Volunteers was designated for 2001 by the United Nations General Assembly. The initiative aimed at increased recognition, facilitation, networking and promotion of volunteering, to highlight the achievements of the millions of volunteers worldwide who devote their time to serving others, and to encourage more people globally to engage in volunteering.
The Declaration and Programme of Action on a Culture of Peace was adopted by the United Nations General Assembly on September 13, 1999. This occurred after ten months of negotiations in the context of preparations for the International Year for the Culture of Peace.
References
- ↑ United Nations General Assembly Session 53 Resolution A/RES/53/25 10 November 1998. Retrieved 2007-08-10.
- ↑ 2005 International Decade for a Culture of Peace and Non-Violence for the Children of the World, 2001-2010
- ↑ 2005 Report of Civil Society
- ↑ 2010 Report from the Civil Society
- ↑ Paxchristi.org.uk Archived 2006-10-14 at the Wayback Machine