
Tinea cruris, also known as jock itch, is a common type of contagious, superficial fungal infection of the groin and buttocks region, which occurs predominantly but not exclusively in men and in hot-humid climates.
Irritant diaper dermatitis is a generic term applied to skin rash in the diaper area that are caused by various skin disorders and/or irritants.

Contact dermatitis is a type of acute or chronic inflammation of the skin caused by exposure to chemical or physical agents. Symptoms of contact dermatitis can include itchy or dry skin, a red rash, bumps, blisters, or swelling. These rashes are not contagious or life-threatening, but can be very uncomfortable.

The axilla is the area on the human body directly under the shoulder joint. It includes the axillary space, an anatomical space within the shoulder girdle between the arm and the thoracic cage, bounded superiorly by the imaginary plane between the superior borders of the first rib, clavicle and scapula, medially by the serratus anterior muscle and thoracolumbar fascia, anteriorly by the pectoral muscles and posteriorly by the subscapularis, teres major and latissimus dorsi muscle.

Athlete's foot, known medically as tinea pedis, is a common skin infection of the feet caused by a fungus. Signs and symptoms often include itching, scaling, cracking and redness. In rare cases the skin may blister. Athlete's foot fungus may infect any part of the foot, but most often grows between the toes. The next most common area is the bottom of the foot. The same fungus may also affect the nails or the hands. It is a member of the group of diseases known as tinea.
Dermatophyte is a common label for a group of fungus of Arthrodermataceae that commonly causes skin disease in animals and humans. Traditionally, these anamorphic mold genera are: Microsporum, Epidermophyton and Trichophyton. There are about 40 species in these three genera. Species capable of reproducing sexually belong in the teleomorphic genus Arthroderma, of the Ascomycota. As of 2019 a total of nine genera are identified and new phylogenetic taxonomy has been proposed.

Miliaria, commonly known as heat rash, sweat rash, or prickly heat, is a skin disease marked by small, itchy rashes due to sweat trapped under the skin by clogged sweat-gland ducts. Miliaria is a common ailment in hot and humid conditions, such as in the tropics and during the summer. Although it affects people of all ages, it is especially common in children and infants due to their underdeveloped sweat glands.

Fungal infection, also known as mycosis, is a disease caused by fungi. Different types are traditionally divided according to the part of the body affected; superficial, subcutaneous, and systemic. Superficial fungal infections include common tinea of the skin, such as tinea of the body, groin, hands, feet and beard, and yeast infections such as pityriasis versicolor. Subcutaneous types include eumycetoma and chromoblastomycosis, which generally affect tissues in and beneath the skin. Systemic fungal infections are more serious and include cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, pneumocystis pneumonia, aspergillosis and mucormycosis. Signs and symptoms range widely. There is usually a rash with superficial infection. Fungal infection within the skin or under the skin may present with a lump and skin changes. Pneumonia-like symptoms or meningitis may occur with a deeper or systemic infection.
Skin disorders are among the most common health problems in dogs, and have many causes. The condition of a dog's skin and coat is also an important indicator of its general health. Skin disorders of dogs vary from acute, self-limiting problems to chronic or long-lasting problems requiring life-time treatment. Skin disorders may be primary or secondary in nature, making diagnosis complicated.
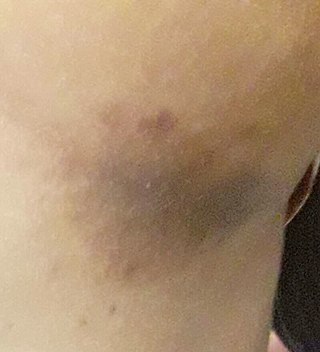
Erythrasma is a superficial skin infection that causes brown, scaly skin patches. It is caused by Corynebacterium minutissimum bacteria, a normal part of skin flora.

Corynebacterium minutissimum is a species of Corynebacterium associated with erythrasma, a type of skin rash. It can be distinguished from similar-appearing rashes by exposing the area to the light of a Wood's lamp; C. minutissimum produces porphyrins that fluoresce coral-red.
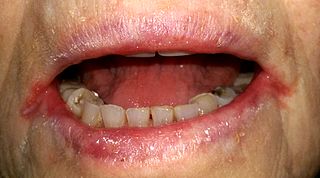
Angular cheilitis (AC) is inflammation of one or both corners of the mouth. Often the corners are red with skin breakdown and crusting. It can also be itchy or painful. The condition can last for days to years. Angular cheilitis is a type of cheilitis.

Hailey–Hailey disease (HHD), or familial benign chronic pemphigus or familial benign pemphigus, was originally described by the Hailey brothers in 1939. It is a genetic disorder that causes blisters to form on the skin.

Erythema annulare centrifugum (EAC), is a descriptive term for a class of skin lesion presenting redness (erythema) in a ring form (anulare) that spreads from a center (centrifugum). It was first described by Darier in 1916. Many different terms have been used to classify these types of lesions and it is still controversial on what exactly defines EAC. Some of the types include annular erythema, erythema perstans, erythema gyratum perstans, erythema gyratum repens, darier erythema and erythema figuratum perstans.

Malassezia furfur is a species of yeast that is naturally found on the skin surfaces of humans and some other mammals. It is associated with a variety of dermatological conditions caused by fungal infections, notably seborrhoeic dermatitis and tinea versicolor. As an opportunistic pathogen, it has further been associated with dandruff, malassezia folliculitis, pityriasis versicolor (alba), and malassezia intertrigo, as well as catheter-related fungemia and pneumonia in patients receiving hematopoietic transplants.

Streptococcal intertrigo is a skin condition that is secondary to a streptococcal bacterial infection. It is often seen in infants and young children and can be characterized by a fiery-red color of the skin, foul odor with an absence of satellite lesions, and skin softening in the neck, armpits or folds of the groin. Newborn children and infants commonly develop intertrigo because of physical features such as deep skin folds, short neck, and flexed posture. Prompt diagnosis by a medical professional and treatment with topical and/or oral antibiotics can effectively relieve symptoms.
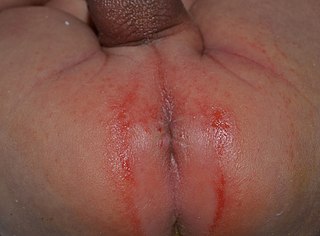
Perianal cellulitis, also known as perianitis or perianal streptococcal dermatitis, is a bacterial infection affecting the lower layers of the skin (cellulitis) around the anus. It presents as bright redness in the skin and can be accompanied by pain, difficulty defecating, itching, and bleeding. This disease is considered a complicated skin and soft tissue infection (cSSTI) because of the involvement of the deeper soft tissues.
Two feet-one hand syndrome(TFOHS), is a long-term fungal condition where athlete's foot or fungal toe nail infections in both feet is associated with tinea manuum in one hand. Often the feet are affected for several years before symptoms of a diffuse scaling rash on the palm of one hand appear, which is when most affected people then seek medical help.














