
A refreshable braille display or braille terminal is an electro-mechanical device for displaying braille characters, usually by means of round-tipped pins raised through holes in a flat surface. Visually impaired computer users who cannot use a standard computer monitor can use it to read text output. Deafblind computer users may also use refreshable braille displays.

A Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter is a computer hardware device for asynchronous serial communication in which the data format and transmission speeds are configurable. It sends data bits one by one, from the least significant to the most significant, framed by start and stop bits so that precise timing is handled by the communication channel. The electric signaling levels are handled by a driver circuit external to the UART. Common signal levels are RS-232, RS-485, and raw TTL for short debugging links. Early teletypewriters used current loops.
The NewTek Video Toaster is a combination of hardware and software for the editing and production of NTSC standard-definition video. The plug-in expansion card initially worked with the Amiga 2000 computer and provides a number of BNC connectors on the exposed rear edge that provide connectivity to common analog video sources like VHS VCRs. The related software tools support video switching, luma keying, character generation, animation, and image manipulation.

SATA is a computer bus interface that connects host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives, optical drives, and solid-state drives. Serial ATA succeeded the earlier Parallel ATA (PATA) standard to become the predominant interface for storage devices.

The 7400 series is a popular logic family of transistor–transistor logic (TTL) integrated circuits (ICs).

An electronic control unit (ECU), also known as an electronic control module (ECM), is an embedded system in automotive electronics that controls one or more of the electrical systems or subsystems in a car or other motor vehicle.

The Roland MT-32 Multi-Timbre Sound Module is a MIDI synthesizer module first released in 1987 by Roland Corporation. It was originally marketed to amateur musicians as a budget external synthesizer with an original list price of $695. However, it became more famous along with its compatible modules as an early de facto standard in computer music. Since it was made prior to the release of the General MIDI standard, it uses its own proprietary format for MIDI file playback.
A general-purpose input/output (GPIO) is an uncommitted digital signal pin on an integrated circuit or electronic circuit board which may be used as an input or output, or both, and is controllable by software.

Arduino is an Italian open-source hardware and software company, project, and user community that designs and manufactures single-board microcontrollers and microcontroller kits for building digital devices. Its hardware products are licensed under a CC BY-SA license, while the software is licensed under the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) or the GNU General Public License (GPL), permitting the manufacture of Arduino boards and software distribution by anyone. Arduino boards are available commercially from the official website or through authorized distributors.
Soundcraft is a British designer and importer of mixing consoles and other professional audio equipment. It is a subsidiary of Harman International Industries, which is owned by South Korean company Samsung Electronics. It was founded by sound engineer Phil Dudderidge and electronics designer Graham Blyth in 1973.

iRobot Create is a hobbyist robot manufactured by iRobot that was introduced in 2007 and based on their Roomba vacuum cleaning platform. The iRobot Create is explicitly designed for robotics development and improves the experience beyond simply hacking the Roomba. The Create replaces its Roomba predecessor's vacuum cleaner hardware with a cargo bay that also houses a DB-9 port providing serial communication, digital input & output, analog input & output, and an electric power supply. The Create also has a 7-pin Mini-DIN serial port through which sensor data can be read and motor commands can be issued using the iRobot Roomba Open Interface (ROI) protocol.

The IBM System/7 was a computer system designed for industrial control, announced on October 28, 1970 and first shipped in 1971. It was a 16-bit machine and one of the first made by IBM to use novel semiconductor memory, instead of magnetic core memory conventional at that date.

Digi XBee is the brand name of a popular family of form factor compatible wireless connectivity modules from Digi International. The first XBee modules were introduced under the MaxStream brand in 2005 and were based on the IEEE 802.15.4-2003 standard designed for point-to-point and star communications. Since the initial introduction, the XBee family has grown and a complete ecosystem of wireless modules, gateways, adapters and software has evolved.

Hackaday is a hardware hacking website. It was founded in 2004 as a web magazine. Since 2014, Hackaday also hosts a community database of open-source hardware designs.

The Intel Edison is a computer-on-module that was offered by Intel as a development system for wearable devices and Internet of Things devices. The system was initially announced to be the same size and shape as an SD card and containing a dual-core Intel Quark x86 CPU at 400 MHz communicating via Bluetooth and Wi-Fi. A later announcement changed the CPU to a 500 MHz Silvermont dual-core Intel Atom CPU, and in September 2014 a second version of Edison was shown at IDF, which was bigger and thicker than a standard SD card.

NodeMCU is a low-cost open source IoT platform. It initially included firmware which runs on the ESP8266 Wi-Fi SoC from Espressif Systems, and hardware which was based on the ESP-12 module. Later, support for the ESP32 32-bit MCU was added.

The ESP8266 is a low-cost Wi-Fi microchip, with built-in TCP/IP networking software, and microcontroller capability, produced by Espressif Systems in Shanghai, China.
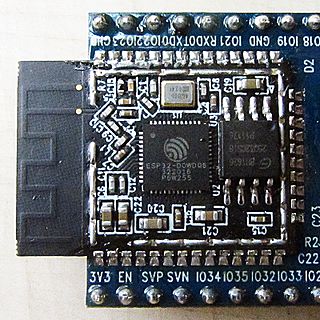
ESP32 is a series of low-cost, low-power system on a chip microcontrollers with integrated Wi-Fi and dual-mode Bluetooth. The ESP32 series employs either a Tensilica Xtensa LX6 microprocessor in both dual-core and single-core variations, Xtensa LX7 dual-core microprocessor or a single-core RISC-V microprocessor and includes built-in antenna switches, RF balun, power amplifier, low-noise receive amplifier, filters, and power-management modules. ESP32 is created and developed by Espressif Systems, a Chinese company based in Shanghai, and is manufactured by TSMC using their 40 nm process. It is a successor to the ESP8266 microcontroller.
IO-Link is a short distance, bi-directional, digital, point-to-point, wired, industrial communications networking standard used for connecting digital sensors and actuators to either a type of industrial fieldbus or a type of industrial Ethernet. Its objective is to provide a technological platform that enables the development and use of sensors and actuators that can produce and consume enriched sets of data that in turn can be used for economically optimizing industrial automated processes and operations. The technology standard is managed by the industry association Profibus and Profinet International.

Flipper Zero is a portable Tamagotchi-like multi-functional device developed for interaction with access control systems. The device is able to read, copy, and emulate RFID and NFC tags, radio remotes, iButton, and digital access keys, along with a GPIO interface. It was first announced in August 2020 through the Kickstarter crowdfunding campaign, which raised $4.8 million. The first devices were delivered to backers 18 months after completion of the crowdfunding campaign. The device's user interface embodies a pixel-art dolphin virtual pet. The interaction with the virtual pet is the device's core game mechanic. The usage of the device's functions defines the appearance and emotions of the pet.
















