
The Zachman Framework is an enterprise ontology and is a fundamental structure for Enterprise Architecture which provides a formal and structured way of viewing and defining an enterprise. The ontology is a two dimensional classification schema that reflects the intersection between two historical classifications. The first are primitive interrogatives: What, How, When, Who, Where, and Why. The second is derived from the philosophical concept of reification, the transformation of an abstract idea into an instantiation. The Zachman Framework reification transformations are: Identification, Definition, Representation, Specification, Configuration and Instantiation.

CIMOSA, standing for "Computer Integrated Manufacturing Open System Architecture", is an enterprise modeling framework, which aims to support the enterprise integration of machines, computers and people. The framework is based on the system life cycle concept, and offers a modelling language, methodology and supporting technology to support these goals.
ISO 10303 is an ISO standard for the computer-interpretable representation and exchange of product manufacturing information. Its official title is: Automation systems and integration — Product data representation and exchange. It is known informally as "STEP", which stands for "STandard for the Exchange of Product model data". ISO 10303 can represent 3D objects in Computer-aided design (CAD) and related information.

Enterprise integration is a technical field of enterprise architecture, which is focused on the study of topics such as system interconnection, electronic data interchange, product data exchange and distributed computing environments.

An enterprise architecture framework defines how to create and use an enterprise architecture. An architecture framework provides principles and practices for creating and using the architecture description of a system. It structures architects' thinking by dividing the architecture description into domains, layers, or views, and offers models - typically matrices and diagrams - for documenting each view. This allows for making systemic design decisions on all the components of the system and making long-term decisions around new design requirements, sustainability, and support.

Enterprise modelling is the abstract representation, description and definition of the structure, processes, information and resources of an identifiable business, government body, or other large organization.
John A. Zachman is an American business and IT consultant, early pioneer of enterprise architecture, Chief Executive Officer of Zachman International, and originator of the Zachman Framework.

Jean Leonardus Gerardus (Jan) Dietz is a Dutch Information systems researcher, Emeritus Professor of Information Systems Design, and part-time Professor of Enterprise Engineering at the Delft University of Technology, known for the development of the Design & Engineering Methodology for Organizations. and his work on enterprise ontology.

STEP-NC is a machine tool control language that extends the ISO 10303 STEP standards with the machining model in ISO 14649, adding geometric dimension and tolerance data for inspection, and the STEP PDM model for integration into the wider enterprise. The combined result has been standardized as ISO 10303-238.
Enterprise engineering is the body of knowledge, principles, and practices used to design all or part of an enterprise. An enterprise is a complex socio-technical system that comprises people, information, and technology that interact with each other and their environment in support of a common mission. One definition is: "an enterprise life-cycle oriented discipline for the identification, design, and implementation of enterprises and their continuous evolution", supported by enterprise modelling. The discipline examines each aspect of the enterprise, including business processes, information flows, material flows, and organizational structure. Enterprise engineering may focus on the design of the enterprise as a whole, or on the design and integration of certain business components.

Enterprise life cycle (ELC) in enterprise architecture is the dynamic, iterative process of changing the enterprise over time by incorporating new business processes, new technology, and new capabilities, as well as maintenance, disposition and disposal of existing elements of the enterprise.

NIST Enterprise Architecture Model is a late-1980s reference model for enterprise architecture. It defines an enterprise architecture by the interrelationship between an enterprise's business, information, and technology environments.

Generalised Enterprise Reference Architecture and Methodology (GERAM) is a generalised enterprise architecture framework for enterprise integration and business process engineering. It identifies the set of components recommended for use in enterprise engineering.
François B. Vernadat is a French and Canadian computer scientist, who has contributed to Enterprise Modelling, Integration and Networking over the last 25 years specialising in enterprise architectures, business process modelling, information systems design and analysis, systems integration and interoperability and systems analysis using Petri nets.
Peter Bernus is a Hungarian Australian scientist and Associate Professor of Enterprise Architecture at the School of Information and Communication Technology, Griffith University, Brisbane, Australia.
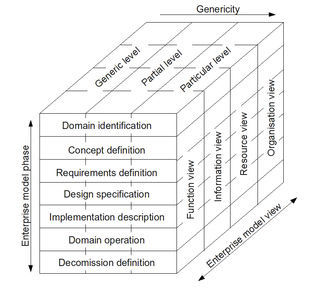
ISO 19439:2006 Enterprise integration—Framework for enterprise modelling, is an international standard for enterprise modelling and enterprise integration developed by the International Organization for Standardization, based on CIMOSA and GERAM.
Mark Stephen Fox is a Canadian computer scientist, Professor of Industrial Engineering and Distinguished Professor of Urban Systems Engineering at the University of Toronto, known for the development of Constraint Directed Scheduling in the 1980s and the TOVE Project to develop an ontological framework for enterprise modeling and enterprise integration in the 1990s.
Kurt Kosanke is a German engineer, retired IBM manager, director of the AMICE Consortium and consultant, known for his work in the field of enterprise engineering, Enterprise integration and CIMOSA.
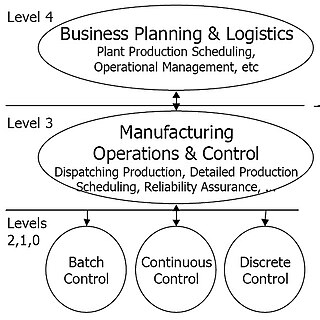
Purdue Enterprise Reference Architecture (PERA) is a 1990s reference model for enterprise architecture, developed by Theodore J. Williams and members of the Industry-Purdue University Consortium for Computer Integrated Manufacturing.
The history of business architecture has its origins in the 1980s. In the next decades business architecture has developed into a discipline of "cross-organizational design of the business as a whole" closely related to enterprise architecture. The concept of business architecture has been proposed as a blueprint of the enterprise, as a business strategy, and also as the representation of a business design.













