John Carroll (born 1944) is an Australian retired academic sociologist. He is Emeritus Professor of Sociology at La Trobe University in Melbourne.
John Carroll (born 1944) is an Australian retired academic sociologist. He is Emeritus Professor of Sociology at La Trobe University in Melbourne.
John Carroll is the author of Puritan, Paranoid, Remissive (1977), Guilt (1983), Ego and Soul (1998), Humanism: The Wreck of Western Culture (1993; updated as The Wreck of Western culture: Humanism Revisited, 2004) and Intruders In The Bush: The Australian Quest For Identity (1992). His Cambridge doctoral dissertation on epistemological anarchistic and anti-rationalist themes in Max Stirner, Nietzsche and Dostoyevsky was published as Breakout from the Crystal Palace (1974). It was supervised by George Steiner. Puritan, Paranoid, Remissive (1977) echoed and developed upon themes in Philip Rieff's Triumph of the Therapeutic: Uses of Faith after Freud (1966).
Humanism (1993; 2004) is Carroll's most ambitious work. Predicated on the view that Western high culture is in a declining if not nihilistic mode, Humanism traces this decline to an epistemic tyranny of reason and its subjection of other forms of knowing and understanding being. Carroll's often bleak diagnosis is primarily based on unique readings of canonic theological, philosophical and artistic texts including those by Sophocles, Calvin, Holbein, Donatello, Shakespeare, Rembrandt, Poussin, Henry James and John Ford. The heart of the book's analysis is highly indebted to Nietzsche's critique of "Socratic" culture in The Birth of Tragedy . Terror: a Meditation on the Meaning of September 11 (2004) is an application of many of the themes in the former work.
In The Western Dreaming and The Existential Jesus, Carroll rereads Gospel narratives and the ontology of Christ through a Heideggerian and non-theistic lens. [1] Greek Pilgrimage is an unabashedly hellenophilic meditation on the nature of ancient Greek aesthetics and culture and what remains of the archaeological sites themselves. [2] Land of the Golden Cities, on the sources of Australia's current prosperity, was published by Connor Court in 2017. Carroll has published two works which draw on and deepen his prior interests: On Guilt (2020) and The Saviour Syndrome (2023).
A book of essays about his work, Metaphysical Sociology: On the Work of John Carroll (edited by Sara James), was published by Routledge in 2018. It includes Carroll's response to the contributions. [3]

Existentialism is a form of philosophical inquiry that explores the issue of human existence. Existentialist philosophers explore questions related to the meaning, purpose, and value of human existence. Common concepts in existentialist thought include existential crisis, dread, and anxiety in the face of an absurd world and free will, as well as authenticity, courage, and virtue.

Friedrich Wilhelm Nietzsche was a German philosopher. He began his career as a classical philologist before turning to philosophy. He became the youngest person to hold the Chair of Classical Philology at the University of Basel in 1869 at the age of 24, but resigned in 1879 due to health problems that plagued him most of his life; he completed much of his core writing in the following decade. In 1889, at age 44, he suffered a collapse and afterward a complete loss of his mental faculties, with paralysis and probably vascular dementia. He lived his remaining years in the care of his mother until her death in 1897 and then with his sister Elisabeth Förster-Nietzsche. Nietzsche died in 1900, after experiencing pneumonia and multiple strokes.
Individualist anarchism is the branch of anarchism that emphasizes the individual and their will over external determinants such as groups, society, traditions, and ideological systems. Although usually contrasted with social anarchism, both individualist and social anarchism have influenced each other. Mutualism, an economic theory sometimes considered a synthesis of communism and property, has been considered individualist anarchism and other times part of social anarchism. Many anarcho-communists regard themselves as radical individualists, seeing anarcho-communism as the best social system for the realization of individual freedom. Some anarcho-capitalists claim anarcho-capitalism is part of the individualist anarchist tradition, while others disagree and claim individualist anarchism is only part of the socialist movement and part of the libertarian socialist tradition. Economically, while European individualist anarchists are pluralists who advocate anarchism without adjectives and synthesis anarchism, ranging from anarcho-communist to mutualist economic types, most American individualist anarchists of the 19th century advocated mutualism, a libertarian socialist form of market socialism, or a free-market socialist form of classical economics. Individualist anarchists are opposed to property that violates the entitlement theory of justice, that is, gives privilege due to unjust acquisition or exchange, and thus is exploitative, seeking to "destroy the tyranny of capital, — that is, of property" by mutual credit.
Individualism is the moral stance, political philosophy, ideology and social outlook that emphasizes the intrinsic worth of the individual. Individualists promote realizing one's goals and desires, valuing independence and self-reliance, and advocating that the interests of the individual should gain precedence over the state or a social group, while opposing external interference upon one's own interests by society or institutions such as the government. Individualism makes the individual its focus, and so starts "with the fundamental premise that the human individual is of primary importance in the struggle for liberation".
Nihilism is a family of views within philosophy that rejects generally accepted or fundamental aspects of human existence, such as knowledge, morality, or meaning. The term was popularized by Ivan Turgenev and more specifically by his character Bazarov in the novel Fathers and Sons.

Johann Kaspar Schmidt, known professionally as Max Stirner, was a German post-Hegelian philosopher, dealing mainly with the Hegelian notion of social alienation and self-consciousness. Stirner is often seen as one of the forerunners of nihilism, existentialism, psychoanalytic theory, postmodernism and individualist anarchism.

Karl Theodor Jaspers was a German-Swiss psychiatrist and philosopher who had a strong influence on modern theology, psychiatry, and philosophy.

Polemic is contentious rhetoric intended to support a specific position by forthright claims and to undermine the opposing position. The practice of such argumentation is called polemics, which are seen in arguments on controversial topics. A person who writes polemics, or speaks polemically, is called a polemicist. The word derives from Ancient Greek πολεμικός 'warlike, hostile', from πόλεμος 'war'.

John Hurrell Crook was a British ethologist who filled a pivotal role in British primatology.

In social theory and philosophy, antihumanism or anti-humanism is a theory that is critical of traditional humanism, traditional ideas about humanity and the human condition. Central to antihumanism is the view that philosophical anthropology and its concepts of "human nature", "man" or "humanity" should be rejected as historically relative, ideological or metaphysical.

The Good Shepherd is an image used in the pericope of John 10:1–21, in which Jesus Christ is depicted as the Good Shepherd who lays down his life for his sheep. Similar imagery is used in Psalm 23 and Ezekiel 34:11–16. The Good Shepherd is also discussed in the other gospels, the Epistle to the Hebrews, the First Epistle of Peter and the Book of Revelation.

Humanism is a democratic and ethical life stance, which affirms that human beings have the right and responsibility to give meaning and shape to their own lives.
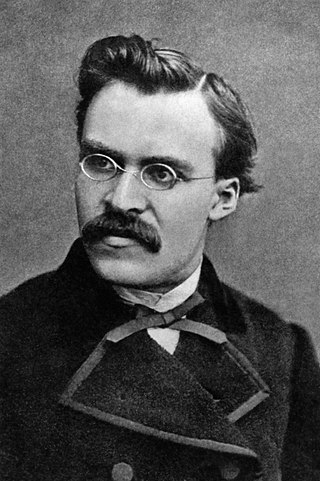
Friedrich Nietzsche's influence and reception varied widely and may be roughly divided into various chronological periods. Reactions were anything but uniform, and proponents of various ideologies attempted to appropriate his work quite early.
Roberto Rino Magliola is an Italian-American academic specializing in European hermeneutics and deconstruction, comparative philosophy, and inter-religious dialogue. He is retired from the National Taiwan University and Assumption University of Thailand.
David Edward Cooper is Emeritus Professor of Philosophy at Durham University.

The ideas of the 19th century German philosophers Max Stirner and Friedrich Nietzsche have been compared frequently. Many authors have discussed apparent similarities in their writings, sometimes raising the question of influences. In Germany, during the early years of Nietzsche's emergence as a well-known figure, the only thinker who discussed his ideas more often than Stirner was Arthur Schopenhauer. It is certain that Nietzsche read about Stirner's book The Ego and Its Own, which was mentioned in Friedrich Albert Lange's History of Materialism and Critique of its Present Importance (1866) and Eduard von Hartmann's Philosophy of the Unconscious (1869), both of which young Nietzsche knew well. However, there is no irrefutable indication that he actually read it as no mention of Stirner is known to exist anywhere in Nietzsche's publications, papers or correspondence.
Jewish existentialism is a category of work by Jewish authors dealing with existentialist themes and concepts, and intended to answer theological questions that are important in Judaism. The existential angst of Job is an example from the Hebrew Bible of the existentialist theme. Theodicy and post-Holocaust theology make up a large part of 20th century Jewish existentialism.
This is a list of articles in continental philosophy.

On the Genealogy of Morality: A Polemic is an 1887 book by German philosopher Friedrich Nietzsche. It consists of a preface and three interrelated treatises that expand and follow through on concepts Nietzsche sketched out in Beyond Good and Evil (1886). The three treatises trace episodes in the evolution of moral concepts with a view to confronting "moral prejudices", specifically those of Christianity and Judaism.
Self-cultivation or personal cultivation is the development of one's mind or capacities through one's own efforts. Self-cultivation is the cultivation, integration, and coordination of mind and body. Although self-cultivation may be practiced as a form of psychotherapy, it goes beyond healing and self-help to also encompass self-development and self-improvement. It is associated with attempts to go beyond normal states of being, enhancing and polishing one's capacities and developing innate human potential.