John Philippe Rushton was a Canadian psychologist and author. He taught at the University of Western Ontario until the early 1990s, and became known to the general public during the 1980s and 1990s for research on race and intelligence, race and crime, and other purported racial correlations.
Emotional intelligence (EI) is most often defined as the ability to perceive, use, understand, manage, and handle emotions. People with high emotional intelligence can recognize their own emotions and those of others, use emotional information to guide thinking and behavior, discern between different feelings and label them appropriately, and adjust emotions to adapt to environments. Although the term first appeared in 1964, it gained popularity in the 1995 best-selling book Emotional Intelligence, written by science journalist Daniel Goleman. Goleman defined EI as the array of skills and characteristics that drive leadership performance.

Creativity is a phenomenon whereby something new and valuable is formed. The created item may be intangible or a physical object.
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. More generally, it can be described as the ability to perceive or infer information, and to retain it as knowledge to be applied towards adaptive behaviors within an environment or context.

Raymond Bernard Cattell was a British-American psychologist, known for his psychometric research into intrapersonal psychological structure. His work also explored the basic dimensions of personality and temperament, the range of cognitive abilities, the dynamic dimensions of motivation and emotion, the clinical dimensions of abnormal personality, patterns of group syntality and social behavior, applications of personality research to psychotherapy and learning theory, predictors of creativity and achievement, and many multivariate research methods including the refinement of factor analytic methods for exploring and measuring these domains. Cattell authored, co-authored, or edited almost 60 scholarly books, more than 500 research articles, and over 30 standardized psychometric tests, questionnaires, and rating scales. According to a widely cited ranking, Cattell was the 16th most eminent, 7th most cited in the scientific journal literature, and among the most productive psychologists of the 20th century. He was, however, a controversial figure, due in part to his alleged friendships with, and accusations about possible intellectual respect for, white supremacists and neo-Nazis.

Sexual jealousy is a special form of jealousy in sexual relationships, based on suspected or imminent sexual infidelity. The concept is studied in the field of evolutionary psychology.
Emotional competence and Emotional capital refer to the essential set of personal and social skills to recognize, interpret, and respond constructively to emotions in oneself and others. The term implies an ease around others and determines one's ability to effectively and successfully lead and express.
Peter Salovey is an American social psychologist and current president of Yale University. He previously served as Yale's provost, dean of Yale Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, and dean of Yale College. Salovey is one of the early pioneers in emotional intelligence.

Emotional aperture has been defined as the ability to perceive features of group emotions. This skill involves the perceptual ability to adjust one's focus from a single individual's emotional cues to the broader patterns of shared emotional cues that comprise the emotional composition of the collective.
Meta-mood is a term used by psychologists to refer to an individual's awareness of their emotions. The term was first utilized by John D. Mayer and Peter Salovey who believed the experience of mood involved "direct" and "indirect" components. While the direct level refers to the simple appearance of mood - happiness, fear, anger, sadness, and surprise, the indirect level, or the meta-mood experience, does not solely consist of the emotions experienced by an individual in the moment. Rather, it is a reflective state which involves additional thoughts and feelings about the mood itself. "I shouldn’t feel this way" or "I am thinking of ways to improve my mood" are examples of reflective thoughts during a meta-mood experience.

Steven L. Neuberg is an experimental social psychologist whose research has contributed to topics pertaining to person perception, impression formation, stereotyping, prejudice, self-fulfilling prophecies, stereotype threat, and prosocial behavior. His research can be broadly characterized as exploring the ways motives and goals shape social thought processes; extending this approach, his later work employs the adaptationist logic of evolutionary psychology to inform the study of social cognition and social behavior. Neuberg has published over sixty scholarly articles and chapters, and has co-authored a multi-edition social psychology textbook with his colleagues Douglas Kenrick and Robert Cialdini.
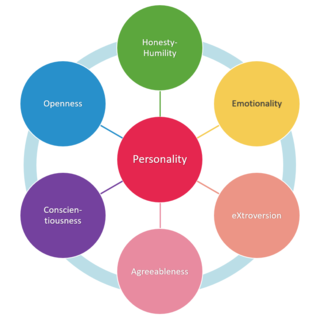
The HEXACO model of personality structure is a six-dimensional model of human personality that was created by Ashton and Lee and explained in their book, The H Factor of Personality, based on findings from a series of lexical studies involving several European and Asian languages. The six factors, or dimensions, include Honesty-Humility (H), Emotionality (E), Extraversion (X), Agreeableness (A), Conscientiousness (C), and Openness to Experience (O). Each factor is composed of traits with characteristics indicating high and low levels of the factor. The HEXACO model was developed through similar methods as other trait taxonomies and builds on the work of Costa and McCrae and Goldberg. The model, therefore, shares several common elements with other trait models. However, the HEXACO model is unique mainly due to the addition of the Honesty-Humility dimension.

Subjective well-being (SWB) is a self-reported measure of well-being, typically obtained by questionnaire.
Marc A. Brackett is a research psychologist and the Founding Director of the Yale Center for Emotional Intelligence and Professor in the Child Study Center at Yale University.

Dr. Anabel L. Jensen is an American educator and author best known for her work with curriculum utilizing emotional intelligence. A former director of the Nueva Learning Center in the 1980s and 1990s, she became president of Six Seconds in 1997 and CEO of Synapse School in 2009. She currently is a professor at Notre Dame de Namur University.
Intelligence and personality have traditionally been studied as separate entities in psychology, but more recent work has increasingly challenged this view. An increasing number of studies have recently explored the relationship between intelligence and personality, in particular the Big Five personality traits.
The Mayer-Salovey-Caruso Emotional Intelligence Test (MSCEIT) is an ability-based measure of emotional intelligence. The test was constructed by academics John D. Mayer, Peter Salovey, and David R. Caruso at Yale and the University of New Hampshire in cooperation with Multi-Health Systems Inc. The test measures emotional intelligence through a series of questions and tests the participant's ability to perceive, use, understand, and regulate emotions. Using questions based on everyday scenarios, the MSCEIT measures how well people respond to social tasks, read facial expressions, and solve emotional problems. The MSCEIT is used in corporate, educational, research, and therapeutic settings.

Reuven Bar-On is an Israeli psychologist and one of the leading pioneers, theorists and researchers in emotional intelligence. Bar-On is thought to be the first to introduce the concept of an “EQ” to measure “emotional and social competence”, although the acronym was used earlier to describe ideas that were not associated with emotional intelligence per se. In the first copy of his doctoral dissertation, which was submitted in 1985, Bar-On proposed a quantitative approach to creating “an EQ analogous to an IQ score”.
A self-test of intelligence is a psychological test that someone can take to purportedly measure one's own intelligence.
Adrian Frank Furnham is a South African-born British BPS chartered occupational psychologist and chartered health psychologist. He is currently an adjunct professor at BI Norwegian Business School and professor at University College London. Throughout his career, he has lectured in the following post-secondary institutions: Pembroke College, Oxford, University of New South Wales, University of West Indies, Hong Kong University Business School, and the Henley Management College.








