Related Research Articles

The Document Object Model (DOM) is a cross-platform and language-independent interface that treats an XML or HTML document as a tree structure wherein each node is an object representing a part of the document. The DOM represents a document with a logical tree. Each branch of the tree ends in a node, and each node contains objects. DOM methods allow programmatic access to the tree; with them one can change the structure, style or content of a document. Nodes can have event handlers attached to them. Once an event is triggered, the event handlers get executed.

The HyperText Markup Language or HTML is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It can be assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScript.

Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) is an XML-based vector image format for defining two-dimensional graphics, having support for interactivity and animation. The SVG specification is an open standard developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) since 1999.
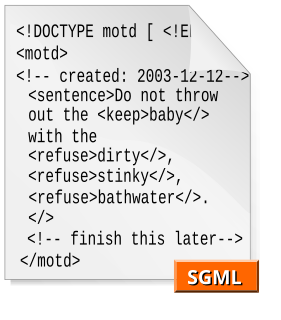
The Standard Generalized Markup Language is a standard for defining generalized markup languages for documents. ISO 8879 Annex A.1 states that generalized markup is "based on two postulates":

The World Wide Web (WWW), commonly known as the Web, is an information system enabling documents and other web resources to be accessed over the Internet.

Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language and file format for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing arbitrary data. It defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. The World Wide Web Consortium's XML 1.0 Specification of 1998 and several other related specifications—all of them free open standards—define XML.
Mathematical Markup Language (MathML) is a mathematical markup language, an application of XML for describing mathematical notations and capturing both its structure and content. It aims at integrating mathematical formulae into World Wide Web pages and other documents. It is part of HTML5 and is a ISO/IEC standard ISO/IEC 40314 since 2015.
The symbol # is known variously in English-speaking regions as the number sign, hash, or pound sign. The symbol has historically been used for a wide range of purposes including the designation of an ordinal number and as a ligatured abbreviation for pounds avoirdupois – having been derived from the now-rare ℔.

The Unicode Consortium is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization incorporated and based in Mountain View, California. Its primary purpose is to maintain and publish the Unicode Standard which was developed with the intention of replacing existing character encoding schemes which are limited in size and scope, and are incompatible with multilingual environments. The consortium describes its overall purpose as:
...enabl[ing] people around the world to use computers in any language, by providing freely-available specifications and data to form the foundation for software internationalization in all major operating systems, search engines, applications, and the World Wide Web. An essential part of this purpose is to standardize, maintain, educate and engage academic and scientific communities, and the general public about, make publicly available, promote, and disseminate to the public a standard character encoding that provides for an allocation for more than a million characters.
Web standards are the formal, non-proprietary standards and other technical specifications that define and describe aspects of the World Wide Web. In recent years, the term has been more frequently associated with the trend of endorsing a set of standardized best practices for building web sites, and a philosophy of web design and development that includes those methods.
In computer programming, whitespace is any character or series of characters that represent horizontal or vertical space in typography. When rendered, a whitespace character does not correspond to a visible mark, but typically does occupy an area on a page. For example, the common whitespace symbol U+0020 SPACE represents a blank space punctuation character in text, used as a word divider in Western scripts.
RDFa or Resource Description Framework in Attributes is a W3C Recommendation that adds a set of attribute-level extensions to HTML, XHTML and various XML-based document types for embedding rich metadata within Web documents. The Resource Description Framework (RDF) data-model mapping enables its use for embedding RDF subject-predicate-object expressions within XHTML documents. It also enables the extraction of RDF model triples by compliant user agents.
In computer science and web development, XML Events is a W3C standard for handling events that occur in an XML document. These events are typically caused by users interacting with the web page using a device, such as a web browser on a personal computer or mobile phone.

HTML5 is a markup language used for structuring and presenting content on the World Wide Web. It is the fifth and final major HTML version that is a World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) recommendation. The current specification is known as the HTML Living Standard. It is maintained by the Web Hypertext Application Technology Working Group (WHATWG), a consortium of the major browser vendors.

Lojban is a logical, constructed, syntactically unambiguous human language created by the Logical Language Group. It succeeds the Loglan project.
Extensible HyperText Markup Language (XHTML) is part of the family of XML markup languages. It mirrors or extends versions of the widely used HyperText Markup Language (HTML), the language in which Web pages are formulated.
Animation of Scalable Vector Graphics, an open XML-based standard vector graphics format is possible through various means:

EPUB is an e-book file format that uses the ".epub" file extension. The term is short for electronic publication and is sometimes styled ePub. EPUB is supported by many e-readers, and compatible software is available for most smartphones, tablets, and computers. EPUB is a technical standard published by the International Digital Publishing Forum (IDPF). It became an official standard of the IDPF in September 2007, superseding the older Open eBook (OEB) standard.
Microdata is a WHATWG HTML specification used to nest metadata within existing content on web pages. Search engines, web crawlers, and browsers can extract and process Microdata from a web page and use it to provide a richer browsing experience for users. Search engines benefit greatly from direct access to this structured data because it allows them to understand the information on web pages and provide more relevant results to users. Microdata uses a supporting vocabulary to describe an item and name-value pairs to assign values to its properties. Microdata is an attempt to provide a simpler way of annotating HTML elements with machine-readable tags than the similar approaches of using RDFa and microformats.
References
- ↑ The Unicode Consortium: “The Unicode Consortium Members" https://www.unicode.org/consortium/memblogo.html (accessed 24 October 2013)
- ↑ World Wide Web Consortium: "Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.1 (Second Edition)" http://www.w3.org/TR/xml11/ (accessed 24 October 2013)
- ↑ scheme-reports.org: "Scheme Working Group 2" http://scheme-reports.org/2012/working-group-2.html (accessed 24 October 2013)
- ↑ William Strunk, Jr, and John Woldemar Cowan, The Elements of Style. On Cowan's website.
- ↑ John Woldemar Cowan, The Complete Lojban Language . Logical Language Group, 1997, ISBN 0-9660283-0-9.