Related Research Articles

Aten also Aton, Atonu, or Itn was the focus of Atenism, the religious system formally established in ancient Egypt by the late Eighteenth Dynasty pharaoh Akhenaten. Exact dating for the 18th dynasty is contested, though a general date range places the dynasty in the years 1550 to 1292 B.C.E. The worship of Aten and the coinciding rule of Akhenaten are major identifying characteristics of a period within the 18th dynasty referred to as the Amarna Period.

Amarna is an extensive ancient Egyptian archaeological site containing the remains of what was the capital city during the late Eighteenth Dynasty. The city of Akhetaten was established in 1346 BC, built at the direction of the Pharaoh Akhenaten, and abandoned shortly after his death in 1332 BC. The name that the ancient Egyptians used for the city is transliterated as Akhetaten or Akhetaton, meaning "the horizon of the Aten".

Akhenaten, also spelled Akhenaton or Echnaton, was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh reigning c. 1353–1336 or 1351–1334 BC, the tenth ruler of the Eighteenth Dynasty. Before the fifth year of his reign, he was known as Amenhotep IV.

Nefertiti was a queen of the 18th Dynasty of Ancient Egypt, the great royal wife of Pharaoh Akhenaten. Nefertiti and her husband were known for their radical overhaul of state religious policy, in which they promoted the earliest known form of monotheism, Atenism, centered on the sun disc and its direct connection to the royal household. With her husband, she reigned at what was arguably the wealthiest period of ancient Egyptian history. After her husband's death, some scholars believe that Nefertiti ruled briefly as the female king known by the throne name, Neferneferuaten and before the ascension of Tutankhamun, although this identification is a matter of ongoing debate. If Nefertiti did rule as Pharaoh, her reign was marked by the fall of Amarna and relocation of the capital back to the traditional city of Thebes.

Smenkhkare was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh of unknown background who lived and ruled during the Amarna Period of the 18th Dynasty. Smenkhkare was husband to Meritaten, the daughter of his likely co-regent, Akhenaten. Since the Amarna period was subject to a large-scale condemnation of memory by later Pharaohs, very little can be said of Smenkhkare with certainty, and he has hence been subject to immense speculation.

Kiya was one of the wives of the Egyptian Pharaoh Akhenaten. Little is known about her, and her actions and roles are poorly documented in the historical record, in contrast to those of Akhenaten's ‘Great royal wife’, Nefertiti. Her unusual name suggests that she may originally have been a Mitanni princess. Surviving evidence demonstrates that Kiya was an important figure at Akhenaten's court during the middle years of his reign, when she had a daughter with him. She disappears from history a few years before her royal husband's death. In previous years, she was thought to be mother of Tutankhamun, but recent DNA evidence suggests this is unlikely.

Meritaten, also spelled Merytaten, Meritaton or Meryetaten, was an ancient Egyptian royal woman of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt. Her name means "She who is beloved of Aten"; Aten being the sun-deity whom her father, Pharaoh Akhenaten, worshipped. She held several titles, performing official roles for her father and becoming the Great Royal Wife to Pharaoh Smenkhkare, who may have been a brother or son of Akhenaten. Meritaten also may have served as pharaoh in her own right under the name Ankhkheperure Neferneferuaten.

Khakaure Senusret III was a pharaoh of Egypt. He ruled from 1878 BC to 1839 BC during a time of great power and prosperity, and was the fifth king of the Twelfth Dynasty of the Middle Kingdom. He was a great pharaoh of the Twelfth Dynasty and is considered to rule at the height of the Middle Kingdom. Consequently, he is regarded as one of the sources for the legend about Sesostris. His military campaigns gave rise to an era of peace and economic prosperity that reduced the power of regional rulers and led to a revival in craftwork, trade, and urban development. Senusret III was among the few Egyptian kings who were deified and honored with a cult during their own lifetime.

Khasekhemre Neferhotep I was an Egyptian pharaoh of the mid Thirteenth Dynasty ruling in the second half of the 18th century BC during a time referred to as the late Middle Kingdom or early Second Intermediate Period, depending on the scholar. One of the best attested rulers of the 13th Dynasty, Neferhotep I reigned for 11 years.

Khaneferre Sobekhotep IV was one of the more powerful Egyptian kings of the 13th Dynasty, who reigned at least eight years. His brothers, Neferhotep I and Sihathor, were his predecessors on the throne, the latter having only ruled as coregent for a few months.

Sekhemre Khutawy Amenemhat Sobekhotep was an Egyptian pharaoh of the early 13th Dynasty.

David Bourke O'Connor was an Australian-American Egyptologist who primarily worked in the fields of Ancient Egypt and Nubia.
This page list topics related to ancient Egypt.

Menwadjre Sihathor was an ephemeral ruler of the 13th Dynasty during the late Middle Kingdom. Sihathor may never have enjoyed an independent reign, possibly only ruling for a few months as a coregent with his brother Neferhotep I.

Woseribre Senebkay was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh during the Second Intermediate Period. The discovery of his tomb in January 2014 supports the existence of an independent Abydos Dynasty, contemporary with the Fifteenth and Sixteenth Dynasties during the Second Intermediate Period.

The Abydos Dynasty is hypothesized to have been a short-lived local dynasty ruling over parts of Middle and Upper Egypt during the Second Intermediate Period in Ancient Egypt. The Abydos Dynasty would have been contemporaneous with the Fifteenth and Sixteenth Dynasties, from approximately 1650 to 1600 BC. It would have been based in or around Abydos and its royal necropolis might have been located at the foot of the Mountain of Anubis, a hill resembling a pyramid in the Abydene desert, close to a rock-cut tomb built for pharaoh Senusret III.

S 10 is the modern name given to a monumental ancient Egyptian tomb complex at Abydos in Egypt. The tomb is most likely royal and dates to the mid-13th Dynasty. Finds from nearby tombs indicate that S10 suffered extensive state-sanctioned stone and grave robbing during the Second Intermediate Period, only a few decades after its construction, as well as during the later Roman and Coptic periods. These finds also show that S10 was used for an actual burial and belonged to a king "Sobekhotep", now believed to be pharaoh Sobekhotep IV. According to the Egyptologist Josef W. Wegner who excavated S10, the tomb might originally have been capped by a pyramid, although Aidan Dodson states that it is still unclear whether S10 was a pyramid or a mastaba.
Wah-Sut is a town located south of Abydos in Middle Egypt. The name of the town indicates that it was originally built as an outlying part of Abydos, set up by the Egyptian state as housing for the people working in and around the funerary complex of pharaoh Senusret III of the Twelfth Dynasty, at the peak of the Middle Kingdom.
David P. Silverman is an American archaeologist and Egyptologist. He received an undergraduate degree from Rutgers University where he majored in art history. He later studied Egyptology as a graduate student at the University of Chicago where he received his PhD. Shortly after, he took a position at the international Treasures of Tutankhamun exhibit which originally ran from 1977 to 1982, and continued to work as curator on subsequent exhibits. Following this, he continued working at a variety of institutions including the Field Museum in Chicago. Since 1996, he has been Eckley Brinton Coxe, Jr. Professor of Egyptology at the University of Pennsylvania and head curator of the University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology's Egyptian section. Alongside this, he currently teaches an online course through Coursera called Introduction to Ancient Egypt and Its Civilization. Some of his archaeological work has included excavations at Bersheh and Saqqara.
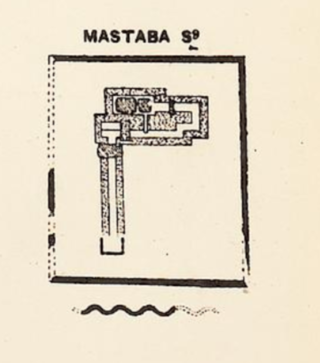
S 9 is the modern name given to a monumental ancient Egyptian tomb complex at Abydos in Egypt. The tomb is most likely royal and dates to the mid-13th Dynasty, during the late Middle Kingdom. Finds from the area of the tomb indicate that S9 suffered extensive, state-sanctioned stone and grave robbing during the Second Intermediate Period, only a few decades after its construction, as well as during the later Roman and Coptic periods. Although no direct evidence was found to determine the tomb owner, strong indirect evidence suggest that the neighbouring and slightly smaller tomb S10 belongs to pharaoh Sobekhotep IV. Consequently, S9 has been tentatively attributed by the Egyptologist Josef W. Wegner to Sobekhotep IV's predecessor and brother, Neferhotep I . According to Wegner, the tomb might originally have been capped by a pyramid.
References
- ↑ "Great Pyramid Mystery to Be Solved by Hidden Room?". National Geographic. March 24, 2010. Archived from the original on December 4, 2008. Retrieved June 18, 2010.
- ↑ "Josef W. Wegner | Near Eastern Languages and Civilizations". nelc.sas.upenn.edu. Retrieved 2022-11-14.
- ↑ "Student Dies in Hiking Accident". Harvard Crimson . October 23, 2007. Retrieved June 18, 2010.
- ↑ "Josef W. Wegner | Near Eastern Languages and Civilizations". nelc.sas.upenn.edu. Retrieved 2022-10-10.
- ↑ Wegner, J.; Cahail, K. (2015). "Royal Funerary Equipment of a King Sobekhotep at South Abydos: Evidence for the Tombs of Sobekhotep IV and Neferhotep I?". JARCE. 15.
- ↑ Discovery of the tomb and nomen of the pharaoh on the Luxor Times.
- ↑ "Mystery pharaoh and his tomb identified in Egypt". NBC News . Archived from the original on 2023-06-24.
- ↑ Wegner, Josef W. (2015). "A royal necropolis at south Abydos: New Light on Egypt's Second Intermediate Period". Near Eastern Archaeology. 78 (2): 69–70. doi:10.5615/neareastarch.78.2.0068. S2CID 163519900.
- ↑ The Sunshade Chapel of Meritaten from the House-of-Waenre of Akhenaten.
- ↑ "Josef W. Wegner | Near Eastern Languages and Civilizations". nelc.sas.upenn.edu. Retrieved 2022-10-10.
- ↑ "Josef W. Wegner | Near Eastern Languages and Civilizations". nelc.sas.upenn.edu. Retrieved 2022-11-23.
- ↑ Olszewski, Deborah. "Meet the Curators: Josef Wegner" (PDF). Expedition Magazine. 47 (2): 4–5 – via Penn Museum.
- ↑ "Josef W. Wegner | Near Eastern Languages and Civilizations". nelc.sas.upenn.edu. Retrieved 2022-11-23.
- ↑ Wegner, Josef (2021). "A Late Middle Kingdom Temple Bakery at South Abydos". Journal of the American Research Center in Egypt. 57 (1): 287–328 – via Lockwood Online Journals.