Related Research Articles

Democracy is a system of government in which state power is vested in the people or the general population of a state. According to the United Nations, democracy "provides an environment that respects human rights and fundamental freedoms, and in which the freely expressed will of people is exercised."
Politics is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studies politics and government is referred to as political science.
In political science, Duverger's law holds that in political systems with only one winner, two main parties tend to emerge with minor parties typically splitting votes away from the most similar major party. In contrast, systems with proportional representation usually have more representation of minor parties in government.
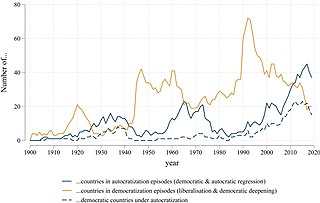
Democratization, or democratisation, is the democratic transition to a more democratic political regime, including substantive political changes moving in a democratic direction.
In general, liberalism in Europe is a political movement that supports a broad tradition of individual liberties and constitutionally-limited and democratically accountable government. These European derivatives of classical liberalism are found in centrist movements and parties as well as some parties on the centre-left and the centre-right.

The Centre Democrats were a Danish political party.
Arend d'Angremond Lijphart is a Dutch-American political scientist specializing in comparative politics, elections and voting systems, democratic institutions, and ethnicity and politics. He is Research Professor Emeritus of Political Science at the University of California, San Diego. He is influential for his work on consociational democracy and his contribution to the new Institutionalism in political science.
Modernization theory holds that as societies become more economically modernized, wealthier and more educated, their political institutions become increasingly liberal democratic. The "classical" theories of modernization of the 1950s and 1960s, most influentially articulated by Seymour Lipset, drew on sociological analyses of Karl Marx, Emile Durkheim, Max Weber, and Talcott Parsons. Modernization theory was a dominant paradigm in the social sciences in the 1950s and 1960s, and saw a resurgence after 1991, when Francis Fukuyama wrote about the end of the Cold War as confirmation on modernization theory.

Political culture describes how culture impacts politics. Every political system is embedded in a particular political culture.

Comparative politics is a field in political science characterized either by the use of the comparative method or other empirical methods to explore politics both within and between countries. Substantively, this can include questions relating to political institutions, political behavior, conflict, and the causes and consequences of economic development. When applied to specific fields of study, comparative politics may be referred to by other names, such as comparative government.

Democratic and Social Centre was a liberal political party in Spain, founded in 1982 by former Prime Minister Adolfo Suárez. The party was a member of the Liberal Democratic and Reformist Group in the European Parliament and the Liberal International. In 2006, most of its remaining members merged into the People's Party, though a reduced faction continued the party, which won some seats in the 2007 local elections.
Michael Gallagher is a political scientist. He is Professor of Comparative Politics and head of the Department of Political Science at the Trinity College Dublin.

A democratic transition describes a phase in a countries political system as a result of an ongoing change from an authoritarian regime to a democratic one The process is known as democratisation, political changes moving in a democratic direction. Democratization waves have been linked to sudden shifts in the distribution of power among the great powers, which created openings and incentives to introduce sweeping domestic reforms. Although transitional regimes experience more civil unrest, they may be considered stable in a transitional phase for decades at a time. Since the end of the Cold War transitional regimes have become the most common form of government. Scholarly analysis of the decorative nature of democratic institutions concludes that the opposite democratic backsliding (autocratization), a transition to authoritarianism is the most prevalent basis of modern hybrid regimes.
Manfred G. Schmidt is professor of political science at the Faculty of Economic and Social Sciences of the University of Heidelberg.
Authoritarianism is a political system characterized by the rejection of democracy and political plurality. It involves the use of strong central power to preserve the political status quo, and reductions in the rule of law, separation of powers, and democratic voting. Political scientists have created many typologies describing variations of authoritarian forms of government. Authoritarian regimes may be either autocratic or oligarchic and may be based upon the rule of a party or the military. States that have a blurred boundary between democracy and authoritarianism have some times been characterized as "hybrid democracies", "hybrid regimes" or "competitive authoritarian" states.

António Costa Pinto is a research professor at the Institute of Social Sciences, University of Lisbon, and Professor of Politics and Contemporary European History at ISCTE – Lisbon University Institute, Portugal.
A hybrid regime is a type of political system often created as a result of an incomplete democratic transition from an authoritarian regime to a democratic one. Hybrid regimes are categorized as having a combination of autocratic features with democratic ones and can simultaneously hold political repressions and regular elections. Hybrid regimes are commonly found in developing countries with abundant natural resources such as petro-states. Although these regimes experience civil unrest, they may be relatively stable and tenacious for decades at a time. There has been a rise in hybrid regimes since the end of the Cold War.
Staffan I. Lindberg, is a Swedish political scientist, Principal Investigator for Varieties of Democracy (V-Dem) Institute and Director of the V-Dem Institute at the University of Gothenburg. He is a professor in the Department of Political Science, and member of the Board of University of Gothenburg, Sweden member of the Young Academy of Sweden, Wallenberg Academy Fellow, Research Fellow at the Quality of Government Institute; and senior advisor for the Oslo Analytica.

Julio Cabral Teehankee is a Filipino political scientist. He is Full Professor of Political Science and International Studies at De La Salle University (DLSU) where he served as Chair of the Political Science Department (1994–2007); Chair of the International Studies Department (2008–2013); and Dean of the College of Liberal Arts (2013–2017).

Daniele Caramani is a comparative political scientist.
References
- "Academy of Europe: Colomer Josep". www.ae-info.org.
- "Faculty". gufaculty360.georgetown.edu.