Involuntary commitment, civil commitment, or involuntary hospitalization/hospitalisation is a legal process through which an individual who is deemed by a qualified agent to have symptoms of severe mental disorder is detained in a psychiatric hospital (inpatient) where they can be treated involuntarily. This treatment may involve the administration of psychoactive drugs, including involuntary administration. In many jurisdictions, people diagnosed with mental health disorders can also be forced to undergo treatment while in the community; this is sometimes referred to as outpatient commitment and shares legal processes with commitment.
Paraphilia is the experience of intense sexual arousal to atypical objects, situations, fantasies, behaviors, or individuals. It has also been defined as sexual interest in anything other than a consenting human partner.
Kleptomania is the inability to resist the urge to steal items, usually for reasons other than personal use or financial gain. First described in 1816, kleptomania is classified in psychiatry as an impulse control disorder. Some of the main characteristics of the disorder suggest that kleptomania could be an obsessive-compulsive spectrum disorder, but also share similarities with addictive and mood disorders.
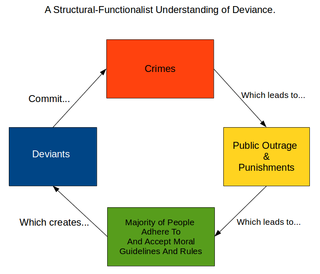
Forensic psychiatry is a subspeciality of psychiatry and is related to criminology. It encompasses the interface between law and psychiatry. According to the American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law, it is defined as "a subspecialty of psychiatry in which scientific and clinical expertise is applied in legal contexts involving civil, criminal, correctional, regulatory, or legislative matters, and in specialized clinical consultations in areas such as risk assessment or employment." A forensic psychiatrist provides services – such as determination of competency to stand trial – to a court of law to facilitate the adjudicative process and provide treatment, such as medications and psychotherapy, to criminals.
Elissa Panush Benedek is an American psychiatrist specializing in child and adolescent psychiatry and forensic psychiatry. She is an adjunct clinical professor of psychiatry at the University of Michigan Medical Center. She served as director of research and training at the Center for Forensic Psychiatry in Ann Arbor for 25 years and was president of the American Psychiatric Association from 1990 to 1991. She is regarded as an expert on child abuse and trauma, and has testified in high-profile court cases. She also focuses on ethics, psychiatric aspects of disasters and terrorism, and domestic violence. In addition to her own books, book chapters, and articles, she has collaborated with her husband, attorney Richard S. Benedek, on studies of divorce, child custody, and child abuse.
Pathological lying, also known as mythomania and pseudologia fantastica, is a chronic behavior in which the person habitually or compulsively lies. These lies often serve no obvious purpose other than to paint oneself as a hero or victim, depending on the circumstance. Pathological lying has been defined as: "a persistent, pervasive, and often compulsive pattern of excessive lying behavior that leads to clinically significant impairment of functioning in social, occupational, or other areas; causes marked distress; poses a risk to the self or others; and occurs for longer than six months." Others have defined pathological lying as "falsification entirely disproportionate to any discernible end in view, may be extensive and very complicated, and may manifest over a period of years or even a lifetime."
Child and adolescent psychiatry is a branch of psychiatry that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of mental disorders in children, adolescents, and their families. It investigates the biopsychosocial factors that influence the development and course of psychiatric disorders and treatment responses to various interventions. Child and adolescent psychiatrists primarily use psychotherapy and/or medication to treat mental disorders in the pediatric population.
In criminal law, a mitigating factor, also known as an extenuating circumstance, is any information or evidence presented to the court regarding the defendant or the circumstances of the crime that might result in reduced charges or a lesser sentence. Unlike a legal defense, the presentation of mitigating factors will not result in the acquittal of a defendant. The opposite of a mitigating factor is an aggravating factor.
Alan Abraham Stone was an American psychiatrist who was the Touroff-Glueck Professor of Law and Psychiatry (Emeritus) at the Harvard Law School. His writing and teaching has focused on professional medical ethics, issues at the intersection of law and psychiatry, and the topic of violence in both law and in psychiatry. Stone served as president of the American Psychiatric Association. He also served for a number of years as the film critic for the Boston Review.

Necrophilia, also known as necrophilism, necrolagnia, necrocoitus, necrochlesis, and thanatophilia, is sexual attraction or act involving corpses. It is classified as a paraphilia by the World Health Organization (WHO) in its International Classification of Diseases (ICD) diagnostic manual, as well as by the American Psychiatric Association in its Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM).
Adjudicative competence, also referred to as competence to stand trial, is a legal construct describing the criminal defendant's ability to understand and participate in legal proceedings. This includes the defendant's current ability to participate in various pleas and waivers of rights. It is unrelated to any possibility of an insanity plea. It is also unrelated to the ability of the defendant to represent himself, or to any evaluation of mitigation factors. The definition of adjudicative competence was provided by the United States Supreme Court in Dusky v. United States.
Psychiatry is the medical specialty devoted to the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of mental conditions. These include various issues related to mood, behaviour, cognition, and perceptions.
Paul Rodney McHugh is an American psychiatrist, researcher, and educator. He is currently the University Distinguished Service Professor of Psychiatry at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and the author, co-author, or editor of seven books in his field. McHugh is a vocal proponent of Catholic-informed and socially conservative stances relating to sexual orientation and transgender people. Several Johns Hopkins staffers and geneticists Dean Hammer accused McHugh of misrepresenting scientific research relating to sexual orientation.
Addiction psychiatry is a medical subspecialty within psychiatry that focuses on the evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment of people who have one or more disorders related to addiction. This may include disorders involving legal and illegal drugs, gambling, sex, food, and other impulse control disorders. Addiction psychiatrists are substance use disorder experts. Growing amounts of scientific knowledge, such as the health effects and treatments for substance use disorders, have led to advancements in the field of addiction psychiatry. These advancements in understanding the neurobiology of rewarding behavior, along with federal funding, has allowed for ample opportunity for research in the discipline of addiction psychiatry. Addiction psychiatry is an expanding field, and currently there is a high demand for substance use disorder experts in both the private and public sector.

Semen Fisheliovych Hluzman is a Ukrainian psychiatrist and human rights activist.
The American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (AACAP) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit professional association in the United States dedicated to facilitating psychiatric care for children and adolescents. The Academy is headquartered in Washington, D.C. Various levels of membership are available to physicians specialized in child psychiatry or pediatrics, as well as medical students interested in the field, in the United States and abroad.
The American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law (AAPL) is a professional organization in the field of forensic psychiatry.
In forensic psychiatry, a pseudocommando is a mass murderer who commits premeditated murder–suicide mass killings driven by revenge fantasies, typically involving the stockpiling of weapons followed by a heavily armed commando-style attack.
Larry H. Strasburger is an American psychiatrist. He served at the Bridgewater State Hospital and had a contract with McLean Hospital. He also was a vice president of the American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law and later became its president.


