Related Research Articles
Extremal optimization (EO) is an optimization heuristic inspired by the Bak–Sneppen model of self-organized criticality from the field of statistical physics. This heuristic was designed initially to address combinatorial optimization problems such as the travelling salesman problem and spin glasses, although the technique has been demonstrated to function in optimization domains.
Oleg Sushkov is a professor at the University of New South Wales and a leader in the field of high temperature super-conductors. Educated in Russia in quantum mechanics and nuclear physics, he now teaches in Australia.

Marvin Lou Cohen is an American–Canadian theoretical physicist. He is a physics professor at the University of California, Berkeley. Cohen is a leading expert in the field of condensed matter physics. He is widely known for his seminal work on the electronic structure of solids.
Atomtronics is an emerging type of computing consisting of matter-wave circuits which coherently guide propagating ultra-cold atoms. The systems typically include components analogous to those found in electronic or optical systems, such as beam splitters and transistors. Applications range from studies of fundamental physics to the development of practical devices.
The topological entanglement entropy or topological entropy, usually denoted by , is a number characterizing many-body states that possess topological order.
Quantum dimer models were introduced to model the physics of resonating valence bond (RVB) states in lattice spin systems. The only degrees of freedom retained from the motivating spin systems are the valence bonds, represented as dimers which live on the lattice bonds. In typical dimer models, the dimers do not overlap.
Patrick A. Lee is a professor of physics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).

Xiao-Gang Wen is a Chinese-American physicist. He is a Cecil and Ida Green Professor of Physics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Distinguished Visiting Research Chair at the Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics. His expertise is in condensed matter theory in strongly correlated electronic systems. In Oct. 2016, he was awarded the Oliver E. Buckley Condensed Matter Prize.
Daniel L. Stein is an American physicist and Professor of Physics and Mathematics at New York University. From 2006 to 2012 he served as the NYU Dean of Science.
Eric R. Weeks is an American physicist. He completed his B.Sc. at the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign in 1992. He obtained a Ph.D. in physics from the University of Texas at Austin in 1997, working under Harry Swinney, and later completed post-doctoral research with David Weitz and Arjun Yodh at Harvard University and the University of Pennsylvania. He is currently a full professor at Emory University in Atlanta, Georgia.
In physical cosmology, warm inflation is one of two dynamical realizations of cosmological inflation. The other is the standard scenario, sometimes called cold inflation.

Michael Elmhirst Cates is a British physicist. He is the 19th Lucasian Professor of Mathematics at the University of Cambridge and has held this position since 1 July 2015. He was previously Professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Edinburgh, and has held a Royal Society Research Professorship since 2007.
Searches for Lorentz violation involving photons provide one possible test of relativity. Examples range from modern versions of the classic Michelson–Morley experiment that utilize highly stable electromagnetic resonant cavities to searches for tiny deviations from c in the speed of light emitted by distant astrophysical sources. Due to the extreme distances involved, astrophysical studies have achieved sensitivities on the order of parts in 1038.
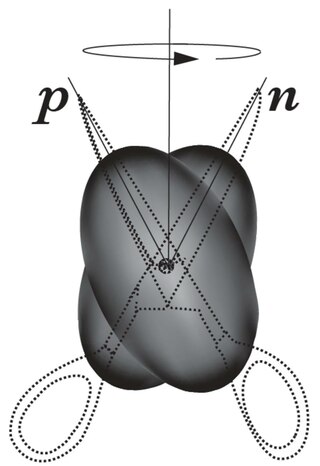
Scissors Modes are collective excitations in which two particle systems move with respect to each other conserving their shape. For the first time they were predicted to occur in deformed atomic nuclei by N. LoIudice and F. Palumbo, who used a semiclassical Two Rotor Model, whose solution required a realization of the O(4) algebra that was not known in mathematics. In this model protons and neutrons were assumed to form two interacting rotors to be identified with the blades of scissors. Their relative motion (Fig.1) generates a magnetic dipole moment whose coupling with the electromagnetic field provides the signature of the mode.
James (Jim) P. Eisenstein is the Frank J. Roshek Professor of Physics and Applied Physics at the physics department of California Institute of Technology.

Carlos O. Lousto is a Distinguished Professor in the School of Mathematical Sciences in Rochester Institute of Technology, known for his work on black hole collisions.
Frans Pretorius is a South African and Canadian physicist, specializing in computer simulations in astrophysics and numerical solutions of Einstein's field equations. He is professor of physics at Princeton University and director of the Princeton Gravity Initiative.
Terry Schalk is an American physicist currently professor emeritus at University of California, Santa Cruz and an Elected Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Bogdan Andrei Bernevig is a Romanian Quantum Condensed Matter Professor of Physics at Princeton University and the recipient of the John Simon Guggenheim Fellowship in 2017.
Hartmut Löwen is a German physicist working in the field of statistical mechanics and soft matter physics.
References
- ↑ Devreese, J T (30 May 2007). "Fröhlich polarons from 0D to 3D: concepts and recent developments". Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter. IOP Publishing. 19 (25): 255201. arXiv: 0709.4140 . Bibcode:2007JPCM...19y5201D. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/19/25/255201. ISSN 0953-8984. S2CID 8209037.
- ↑ J. T. Devreese, Optical Properties of Few and Many Fröhlich Polarons from 3D to 0D, in Polarons in Advanced Materials, Springer Series in Materials Science, Vol. 103, edited by A. S. Alexandrov (Canopus and Springer, Bath, UK, 2007), pp. 3–62
- ↑ Devreese, Jozef T; Alexandrov, Alexandre S (27 May 2009). "Fröhlich polaron and bipolaron: recent developments". Reports on Progress in Physics. 72 (6): 066501. arXiv: 0904.3682 . Bibcode:2009RPPh...72f6501D. doi:10.1088/0034-4885/72/6/066501. ISSN 0034-4885. S2CID 119240319.
- ↑ Alexandrov, Alexandre S.; Devreese, Jozef T. (2010). Advances in Polaron Physics. Springer Series in Solid-State Sciences. Vol. 159. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg. Bibcode:2010app..book.....A. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-01896-1. ISBN 978-3-642-01895-4. ISSN 0171-1873.
- ↑ Kartheuser, E.; Evrard, R.; Devreese, J. (20 January 1969). "Mechanism of Absorption of Light by Free Continuum Polarons". Physical Review Letters. American Physical Society (APS). 22 (3): 94–97. Bibcode:1969PhRvL..22...94K. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.22.94. ISSN 0031-9007.
- ↑ Tempere, J.; Devreese, J. T. (6 August 2001). "Optical absorption of an interacting many-polaron gas". Physical Review B. 64 (10): 104504. arXiv: cond-mat/0004436 . Bibcode:2001PhRvB..64j4504T. doi:10.1103/physrevb.64.104504. ISSN 0163-1829. S2CID 8697323.
- ↑ De Filippis, G.; Cataudella, V.; Mishchenko, A. S.; Perroni, C. A.; Devreese, J. T. (6 April 2006). "Validity of the Franck-Condon Principle in the Optical Spectroscopy: Optical Conductivity of the Fröhlich Polaron". Physical Review Letters. 96 (13): 136405. arXiv: cond-mat/0603219 . Bibcode:2006PhRvL..96m6405D. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.96.136405. hdl: 10067/577340151162165141 . ISSN 0031-9007. PMID 16712012. S2CID 28505622.
- ↑ Hodby, J. W.; Russell, G. P.; Peeters, F. M.; Devreese, J. T.; Larsen, D. M. (6 April 1987). "Cyclotron resonance of polarons in the silver halides: AgBr and AgCl". Physical Review Letters. American Physical Society (APS). 58 (14): 1471–1474. Bibcode:1987PhRvL..58.1471H. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.58.1471. ISSN 0031-9007. PMID 10034445.
- ↑ Van Camp, P. E.; Van Doren, V. E.; Devreese, J. T. (30 April 1979). "Microscopic Screening and Phonon Dispersion of Silicon: Moment Expansion for the Polarizability". Physical Review Letters. American Physical Society (APS). 42 (18): 1224–1227. Bibcode:1979PhRvL..42.1224V. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.42.1224. ISSN 0031-9007.
- ↑ Misko, V. R.; Fomin, V. M.; Devreese, J. T.; Moshchalkov, V. V. (11 April 2003). "Stable Vortex-Antivortex Molecules in Mesoscopic Superconducting Triangles". Physical Review Letters. American Physical Society (APS). 90 (14): 147003. arXiv: cond-mat/0203140 . Bibcode:2003PhRvL..90n7003M. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.90.147003. ISSN 0031-9007. PMID 12731940. S2CID 3648632.
- ↑ Van de Vondel, J.; Gladilin, V. N.; Silhanek, A. V.; Gillijns, W.; Tempere, J.; Devreese, J. T.; Moshchalkov, V. V. (29 March 2011). "Vortex Core Deformation and Stepper-Motor Ratchet Behavior in a Superconducting Aluminum Film Containing an Array of Holes". Physical Review Letters. 106 (13): 137003. arXiv: 1104.1129 . Bibcode:2011PhRvL.106m7003V. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.106.137003. ISSN 0031-9007. PMID 21517415. S2CID 119299573.
- ↑ J. T. Devreese and J. Tempere, Bose-Einstein Condensation, in McGraw-Hill 2006 Yearbook of Science and Technology (McGraw-Hill, New York, 2006), pp. 38–40
- ↑ Lemmens, L. F.; Brosens, F.; Devreese, J. T. (1 August 1977). "On the Ground State Energy of a Gas of Interacting Polarons". Physica Status Solidi B. Wiley. 82 (2): 439–447. Bibcode:1977PSSBR..82..439L. doi:10.1002/pssb.2220820204. ISSN 0370-1972.
- ↑ Devreese, J. T.; Brosens, F.; Lemmens, L. F. (15 February 1980). "Dielectric function of the electron gas with dynamical-exchange decoupling. I. Analytical treatment". Physical Review B. American Physical Society (APS). 21 (4): 1349–1362. Bibcode:1980PhRvB..21.1349D. doi:10.1103/physrevb.21.1349. ISSN 0163-1829.
- ↑ Brosens, F.; Devreese, J. T.; Lemmens, L. F. (15 February 1980). "Dielectric function of the electron gas with dynamical-exchange decoupling. II. Discussion and results". Physical Review B. American Physical Society (APS). 21 (4): 1363–1379. Bibcode:1980PhRvB..21.1363B. doi:10.1103/physrevb.21.1363. ISSN 0163-1829.
- ↑ Brosens, F.; Devreese, J. T.; Lemmens, L. F. (1 January 1997). "Thermodynamics of coupled identical oscillators within the path-integral formalism". Physical Review E. American Physical Society (APS). 55 (1): 227–236. arXiv: cond-mat/9609108 . Bibcode:1997PhRvE..55..227B. doi:10.1103/physreve.55.227. hdl: 10067/203170151162165141 . ISSN 1063-651X. S2CID 119019374.
- ↑ Tempere, J.; Silvera, Isaac F.; Devreese, J. T. (7 December 2001). "Effect of Pressure on Statics, Dynamics, and Stability of Multielectron Bubbles". Physical Review Letters. American Physical Society (APS). 87 (27): 275301. arXiv: cond-mat/0110569 . Bibcode:2001PhRvL..87A5301T. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.87.275301. hdl: 10067/408940151162165141 . ISSN 0031-9007. PMID 11800888. S2CID 18421096.
- ↑ Kleemans, N. A. J. M.; Bominaar-Silkens, I. M. A.; Fomin, V. M.; Gladilin, V. N.; Granados, D.; Taboada, A. G.; García, J. M.; Offermans, P.; Zeitler, U.; Christianen, P. C. M.; Maan, J. C.; Devreese, J. T.; Koenraad, P. M. (5 October 2007). "Oscillatory Persistent Currents in Self-Assembled Quantum Rings". Physical Review Letters. American Physical Society (APS). 99 (14): 146808. Bibcode:2007PhRvL..99n6808K. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.99.146808. hdl: 10261/11955 . ISSN 0031-9007. PMID 17930703.
- ↑ Fonoberov, Vladimir A.; Pokatilov, Evghenii P.; Fomin, Vladimir M.; Devreese, Jozef T. (24 March 2004). "Photoluminescence of Tetrahedral Quantum-Dot Quantum Wells". Physical Review Letters. American Physical Society (APS). 92 (12): 127402. arXiv: cond-mat/0401651 . Bibcode:2004PhRvL..92l7402F. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.92.127402. ISSN 0031-9007. PMID 15089704. S2CID 8607777.
- ↑ Devreese, Jozef T. (2007). "Importance of Nanosensors: Feynman's Vision and the Birth of Nanotechnology". MRS Bulletin. Cambridge University Press (CUP). 32 (9): 718–725. doi:10.1557/mrs2007.147. ISSN 0883-7694.
- ↑ "Antwerpse Kathedraalconcerten vzw".
- ↑ J. T. Devreese, G. Vanden Berghe, Wonder en is gheen wonder. De geniale wereld van Simon Stevin 1548-1620 (342 pp.), Davidsfonds, Leuven (2003)
- ↑ J. T. Devreese, G. Vanden Berghe, Magic is No Magic. The Wonderful World of Simon Stevin (310 pp.), WIT Press, Ashurst, Southampton (2007)