
During fertilization, a sperm must first fuse with the plasma membrane and then penetrate the female egg cell to fertilize it. Fusing to the egg cell usually causes little problem, whereas penetrating through the egg's hard shell or extracellular matrix can be more difficult. Therefore, sperm cells go through a process known as the acrosome reaction, which is the reaction that occurs in the acrosome of the sperm as it approaches the egg.

The zona pellucida is a specialized extracellular matrix that surrounds the plasma membrane of mammalian oocytes. It is a vital constitutive part of the oocyte. The zona pellucida first appears in unilaminar primary oocytes. It is secreted by both the oocyte and the ovarian follicles. The zona pellucida is surrounded by the corona radiata. The corona is composed of cells that care for the egg when it is emitted from the ovary.
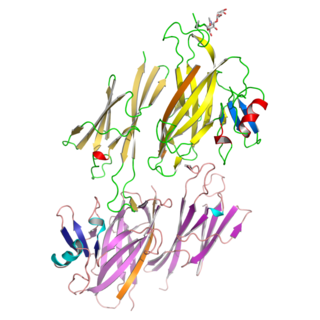
Zona pellucida sperm-binding protein 3, also known as zona pellucida glycoprotein 3 (Zp-3) or the sperm receptor, is a ZP module-containing protein that in humans is encoded by the ZP3 gene. ZP3 is the glycoprotein in the zona pellucida most important for inducting the acrosome reaction of sperm cells at the beginning of fertilization.

Trpc4-associated protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRPC4AP gene.
Olfactory receptor 1D2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OR1D2 gene.

Centromere protein J is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CENPJ gene. It is also known as centrosomal P4.1-associated protein (CPAP). During cell division, this protein plays a structural role in the maintenance of centrosome integrity and normal spindle morphology, and it is involved in microtubule disassembly at the centrosome. This protein can function as a transcriptional coactivator in the Stat5 signaling pathway and also as a coactivator of NF-kappaB-mediated transcription, likely via its interaction with the coactivator p300/CREB-binding protein.

Protein argonaute-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF2C1 gene.

Zona pellucida sperm-binding protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZP2 gene.

Leucine-rich repeats and immunoglobulin-like domains protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LRIG1 gene. It encodes a transmembrane protein that has been shown to interact with receptor tyrosine kinases of the EGFR family and with MET and RET.

Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 2 or Beta-fertilin is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADAM2 gene.

WW domain-binding protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WBP2 gene.

Cysteine-rich secretory protein 1 is a cysteine-rich secretory protein that in humans is encoded by the CRISP1 gene.

Putative Polycomb group protein ASXL1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ASXL1 gene.

SET and MYND domain-containing protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMYD4 gene.

Bromodomain testis-specific protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BRDT gene. It is a member of the Bromodomain and Extra-terminal motif (BET) protein family.
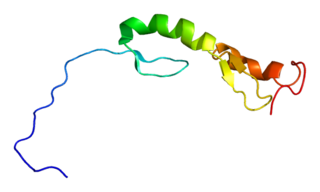
TRAF-type zinc finger domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRAFD1 gene.
Oocyteactivation is a series of processes that occur in the oocyte during fertilization.

Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ADAM7 gene. ADAM7 is an 85-kDa enzyme that is a member of the transmembrane ADAM protein family. Members of this family are membrane-anchored proteins structurally related to snake venom disintegrins, and have been implicated in a variety of biological processes involving cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions, including fertilization, muscle development, and neurogenesis. ADAM7 is important for the maturation of sperm cells in mammals. ADAM7 is also denoted as: ADAM_7, ADAM-7, EAPI, GP-83, and GP83.

Putative sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter 10, also known as solute carrier family 38 member 10, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC38A10 gene.

Izumo sperm-egg fusion protein 1 is encoded in humans by the IZUMO1 gene. In mammalian fertilisation, IZUMO1 binds to its egg receptor counterpart, Juno, to facilitate recognition and fusion of the gametes.


















