
M.U.L.E. is a 1983 multiplayer video game written for the Atari 8-bit family of home computers by Ozark Softscape. Designer Danielle Bunten Berry took advantage of the four joystick ports of the Atari 400 and 800 to allow four-player simultaneous play. M.U.L.E. was one of the first five games published in 1983 by new company Electronic Arts, alongside Axis Assassin, Archon: The Light and the Dark, Worms?, and Hard Hat Mack. Primarily a turn-based strategy game, it incorporates real-time elements where players compete directly as well as aspects that simulate economics.
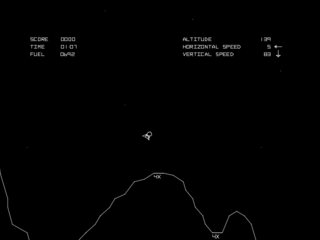
Lunar Lander is a genre of video games loosely based on the 1969 landing of the Apollo Lunar Module on the Moon. In Lunar Lander games, players generally control a spacecraft as it falls toward the surface of the Moon or other astronomical body, using thrusters to slow the ship's descent and control its horizontal motion to reach a safe landing area. Crashing into obstacles, hitting the surface at too high a velocity, or running out of fuel all result in failure. In some games in the genre, the ship's orientation must be adjusted as well as its horizontal and vertical velocities.

HAL Laboratory, Inc., formerly shortened as HALKEN, is a Japanese video game developer founded on 21 February 1980. While independent, it has been closely tied with Nintendo throughout its history, and is often referred to as a second-party developer for the company. HAL Laboratory is headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo, and it also has a building at Kai, Yamanashi. The company got its name because "each letter put them one step ahead of IBM". The company is most famous for their work on the Kirby and Mother series, as well as the first two Super Smash Bros. games.

Buck Rogers: Planet of Zoom, known as Zoom 909 in Japan, is a pseudo-3D rail shooter released as an arcade video game by Sega in 1982. The player controls a spaceship in a third-person perspective, adapting the three-dimensional perspective of Sega's earlier racing game Turbo (1981) for the space shoot 'em up genre. It used the Buck Rogers license, referencing the space battles, though Buck himself is never seen.

The PC-8800 series, commonly shortened to PC-88, are a brand of Zilog Z80-based 8-bit home computers released by Nippon Electric Company (NEC) in 1981 and primarily sold in Japan.

Colossal Adventure is a text based adventure game published by Level 9 Computing in 1982. It was originally released for the Nascom.

The PC-9800 series, commonly shortened to PC-98 or 98, is a lineup of Japanese 16-bit and 32-bit personal computers manufactured by NEC from 1982 to 2000. The platform established NEC's dominance in the Japanese personal computer market, and, by 1999, more than 18 million units had been sold. While NEC did not market these specific machines in the West, it sold the NEC APC series, which had similar hardware to early PC-98 models.

TI Invaders is a fixed shooter video game published by Texas Instruments in 1981 for the TI-99/4A home computer. The game is a Space Invaders clone where the goal is to shoot all of the aliens before they reach the bottom of the screen. TI Invaders is part of the TI Arcade Game Series which includes Tombstone City: 21st Century and Car Wars.

Pirates! Gold is a 1993 computer game, a remake to Sid Meier's 1987 release, Sid Meier's Pirates!.

The PC-8000 series is a line of personal computers developed for the Japanese market by NEC. The PC-8001 model was also sold in the United States and Canada as the PC-8001A.

Wizard and the Princess is a graphic adventure game written for the Apple II and published in 1980 by On-Line Systems. It was the second title released in the Hi-Res Adventures series after Mystery House. While Mystery House used monochrome drawings, Wizard and the Princess added color. Ports for the Atari 8-bit family and Commodore 64 were released in 1982 and 1984 respectively. The 1982 self-booting version for IBM PC compatibles was renamed Adventure in Serenia.

Microsoft Flight Simulator, commonly known as Microsoft Flight Simulator 1.0, is a flight simulator video game, released in November 1982 for the IBM PC. It is the first release in the Microsoft Flight Simulator series.

Lady Bug is a maze chase video game produced by Universal and released for arcades in 1981. Its gameplay is similar to Pac-Man, with the primary addition to the formula being gates that change the layout of the maze when used, adding an element of strategy to the genre. The arcade original was relatively obscure, but the game found wider recognition and success as a launch title for the ColecoVision console.

The Incredible Machine is a puzzle video game released in 1993, and the first release in The Incredible Machine video game series. The objective of the game is to create Rube Goldberg machines by arranging collections of objects in a complex fashion, so as to perform some simple task. The Even More Incredible Machine was an extended version of the original, also released in 1993; it had 160 levels, about twice the number of levels in the original game, and had more parts to use in the contraptions.

Mole Attack is a video game clone of the mechanical arcade game Whac-A-Mole. It was published by Commodore in 1981 for the VIC-20. HAL Laboratory later published a version for the PC-8001.

Laf Pak is an Apple II video game developed by Chuck Bueche and published by Sierra On-Line in 1982. Laf Pak is a compilation of four action games: Creepy Corridors, Mine Sweep, Apple Zap, and Space Race.

Kid Grid is a grid capture game which borrows heavily from the 1981 arcade video game Amidar. Written by Arti Haroutunian for the Atari 8-bit family, it was published by Tronix in 1982. A Commodore 64 port from the same programmer was released in 1983.

Mr. Cool is an action game designed by Peter Oliphant and published in 1983 by Sierra On-Line for the Atari 8-bit and Commodore 64 home computers. The ports for the IBM PC and Apple II were written by John Redekopp and released the same year. The game is heavily inspired by the 1982 arcade video game Q*bert.

Stanford Wong Video Poker is a 1990 video game published by Villa Crespo Software.



















